CRISPR Plasmids: Epigenetics
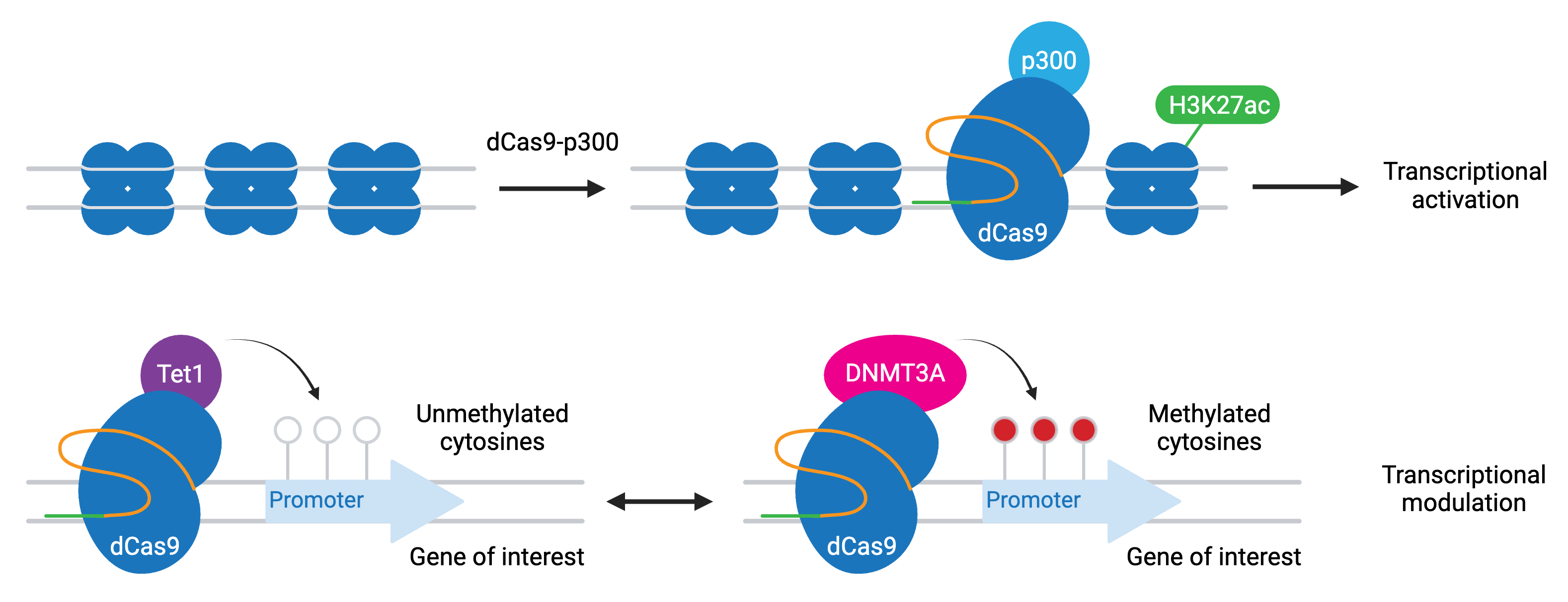
To make targeted epigenetic modifications, researchers have fused catalytically dead Cas9 (dCas9) to epigenetic modifiers. Common modifiers include:
- P300 — activation through increased H3K27 acetylation
- TET1 — activation through cytosine demethylation
- DNMT3A — repression through cytosine methylation
- MQ1 — repression through cytosine methylation with improved kinetics
- LSD1 — repression through targeted removal of H3K4 and H3K9 methylation
Epigenetic modification is typically targeted to a specific promoter or enhancer for your gene of interest. These modifications persist over time and are potentially heritable in dividing cells. CRISPR activation and interference technologies also indirectly modify local chromatin state.
Browse, sort, or search the tables below for CRISPR plasmids designed for epigenetic modification. To learn more about epigenetic modification with CRISPR and other CRISPR topics, read our CRISPR Guide.
Mammalian
| ID | Plasmid | Gene/Insert | Promoter | Selectable Marker | PI | Publication |
|---|
Plant
| ID | Plasmid | Gene/Insert | Promoter | Selectable Marker | PI | Publication |
|---|
CRISPR Resources
Addgene has a large selection of CRISPR plasmids and resources. Find more CRISPR functions along with plasmids categorized by organism by visiting our CRISPR plasmids page. Find a comprehensive list of CRISPR resources by visiting our CRISPR reference page.
Content last reviewed: 17 October 2025
Do you have suggestions for other plasmids that should be added to this list?
Fill out our Suggest a Plasmid form or e-mail [email protected] to help us improve this resource!



