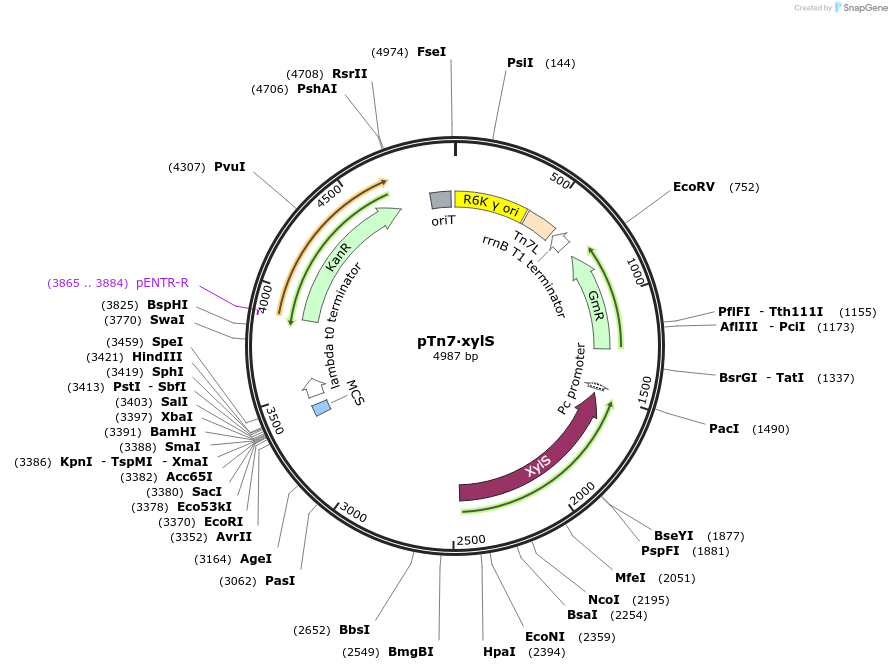
pTn7·xylS
(Plasmid
#122591)
-
PurposePlasmid for genomic integraction of the xylS regulator into the Tn7 insertion site
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 122591 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepTn7-M
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 3147
- Total vector size (bp) 4976
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression, Synthetic Biology ; Tn7 genomic integration
-
Selectable markersGentamicin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)Pir1
-
Copy numberLow Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namexylS
-
SpeciesPseudomonas putida
-
Insert Size (bp)1863
- Promoter Pm
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Ligation Independent Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer AGGGCGGCGGATTTGTCC
- 3′ sequencing primer GCGGCAACCGAGCGTTC
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pTn7·xylS was a gift from Pablo Ivan Nikel (Addgene plasmid # 122591 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:122591 ; RRID:Addgene_122591) -
For your References section:
Physical decoupling of XylS/Pm regulatory elements and conditional proteolysis enable precise control of gene expression in Pseudomonas putida. Volke DC, Turlin J, Mol V, Nikel PI. Microb Biotechnol. 2019 Mar 12. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13383. 10.1111/1751-7915.13383 PubMed 30864281