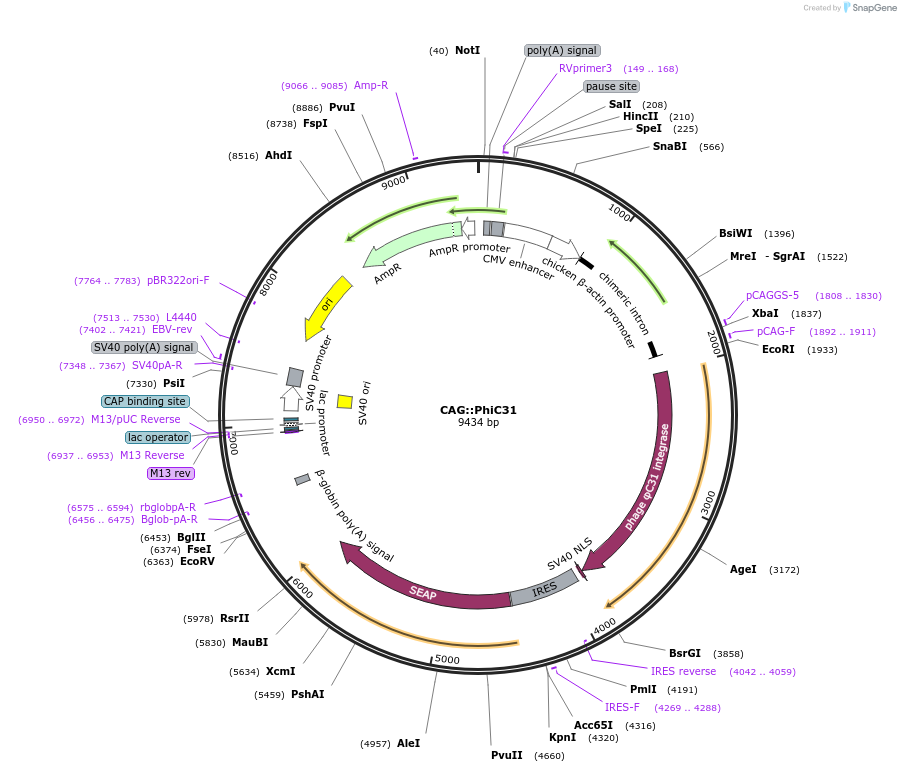
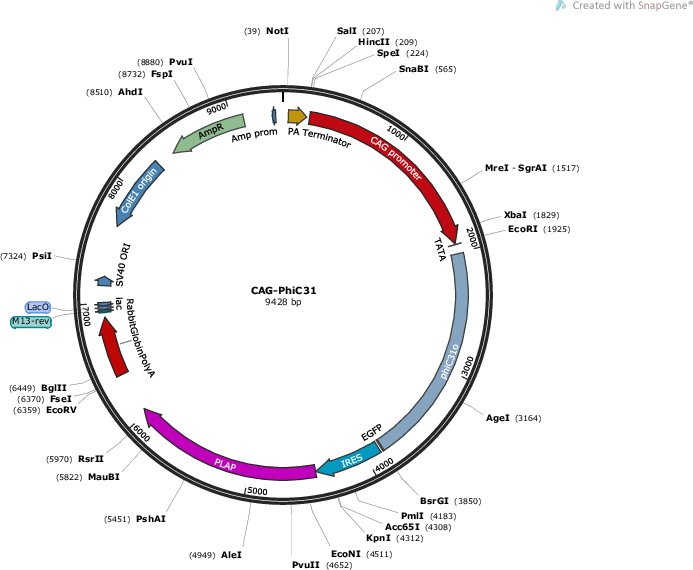
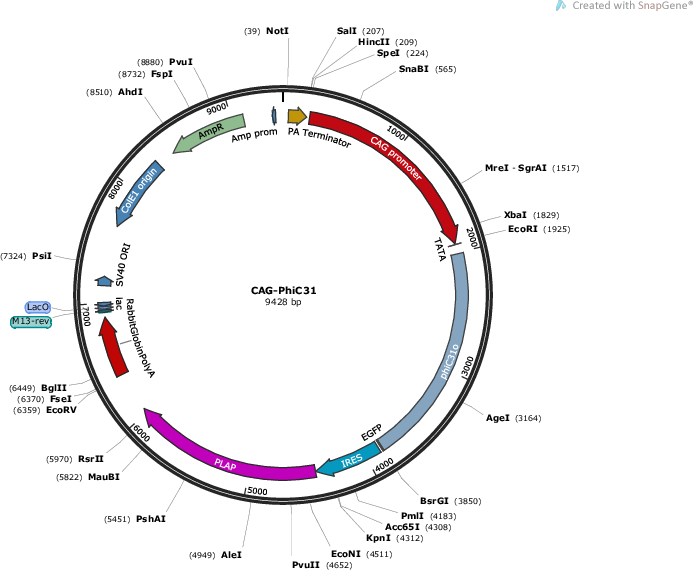
CAG::PhiC31
(Plasmid
#140506)
-
PurposeEncodes PhiC31 recombinase driven by the CAG promoter
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 140506 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonebp::PhiC31
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 7728
- Total vector size (bp) 9428
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression ; Chicken Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameCAG promoter
-
Insert Size (bp)1701
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site SalI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site EcorI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer GTTCCGCGCACATTTCCCCG
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byCAG from Addgene plasmid #14757
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
The depositor notes that this plasmid contains a ~20bp deletion near the start of the IRES sequence, which may impact IRES function, but was not of concern for this particular study.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
CAG::PhiC31 was a gift from Mark Emerson (Addgene plasmid # 140506 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:140506 ; RRID:Addgene_140506) -
For your References section:
Lineage tracing analysis of cone photoreceptor associated cis-regulatory elements in the developing chicken retina. Schick E, McCaffery SD, Keblish EE, Thakurdin C, Emerson MM. Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 27;9(1):9358. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45750-7. 10.1038/s41598-019-45750-7 PubMed 31249345