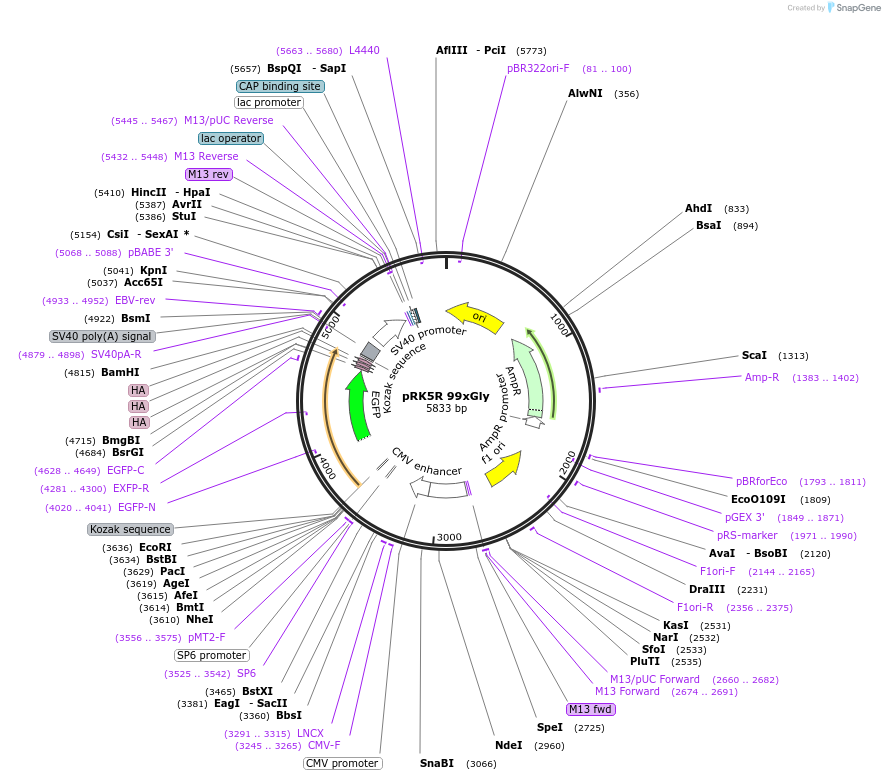
pRK5R 99xGly
(Plasmid
#211356)
-
PurposeTransient expression of 99xGly-EGFP-3xHA
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 211356 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepRK5R
-
Modifications to backboneReversed origin of replication versus pRK5.
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert name99xGly-EGFP-3xHA
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- EGFP-3xHA (C terminal on insert)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
This material includes a long poly-glycine repeat that is challenging to maintain and sequence accurately. Addgene’s long-read sequencing results confirm approximately 94 repeats in the current samples. The depositor recommends that the length of repeats should be verified for each prep via restriction digest, Nanopore sequencing, or both. The depositing lab is happy to provide guidance if needed.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pRK5R 99xGly was a gift from Raghu Chivukula (Addgene plasmid # 211356 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:211356 ; RRID:Addgene_211356) -
For your References section:
Polyglycine-mediated aggregation of FAM98B disrupts tRNA processing in GGC repeat disorders. Yang J, Xu Y, Ziehr DR, Taylor MS, Valenstein ML, Frenkel EM, Bush JR, Rutter K, Stevanovski I, Shi CY, Kesavan M, Pinto RM, Deveson I, Bartel DP, Sabatini DM, Chivukula RR. Science. 2025 Jul 17;389(6757):eado2403. doi: 10.1126/science.ado2403. Epub 2025 Jul 17. 10.1126/science.ado2403 PubMed 40674500