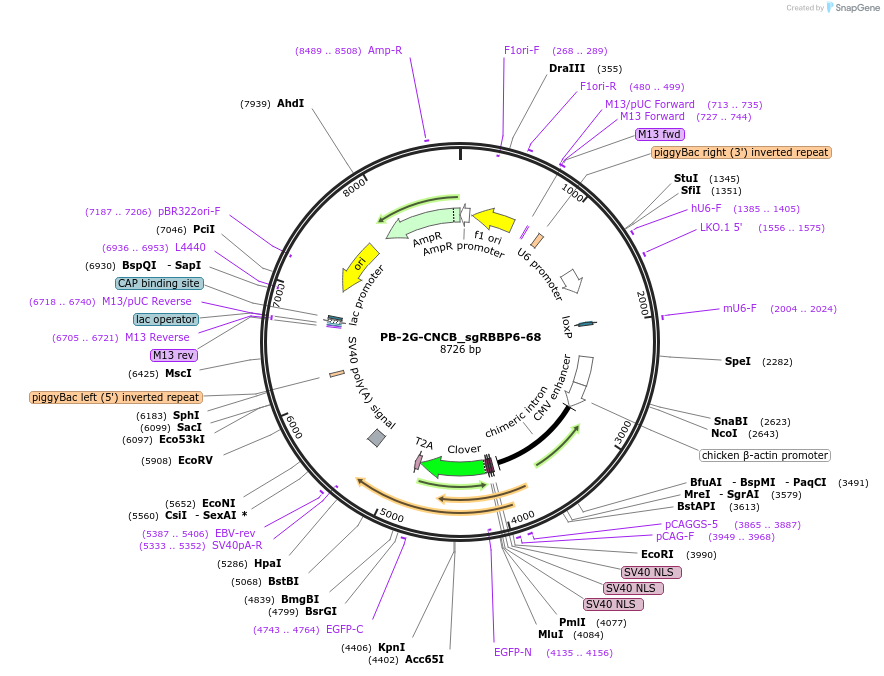
PB-2G-CNCB_sgRBBP6-68
(Plasmid
#237555)
-
PurposeA piggybac-based vector containing mouse U6 promoter-driven RBBP6 sgRNA #6, human U6 promoter-driven RBBP6 sgRNA #8 and CAG promoter-driven nuclear-localized Clover-T2A-BSR.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 237555 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonePB-2G-CNCB
-
Backbone manufacturerSynthetic
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 8714
- Total vector size (bp) 8730
-
Modifications to backboneThe RBBP6 sgRNAs #6 and #8 were inserted into the Esp3I and BbsI sites of PB-2G-CNCB, respectively.
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression ; PiggyBac
-
Selectable markersBlasticidin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameRBBP6
-
gRNA/shRNA sequenceTCGGACGAGCGCCCCACTG
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
GenBank IDNM_006910.5
-
Entrez GeneRBBP6 (a.k.a. MY038, P2P-R, PACT, RBQ-1, SNAMA)
- Promoter mouse U6 promoter
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site Esp3I (destroyed during cloning)
- 3′ cloning site Esp3I (destroyed during cloning)
- 5′ sequencing primer GAGGCTTAATGTGCGATAAAAGA
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
PB-2G-CNCB_sgRBBP6-68 was a gift from Kazutoshi Takahashi (Addgene plasmid # 237555 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:237555 ; RRID:Addgene_237555) -
For your References section:
EIF3D safeguards the homeostasis of key signaling pathways in human primed pluripotency. Okubo C, Nakamura M, Sato M, Shichino Y, Mito M, Takashima Y, Iwasaki S, Takahashi K. Sci Adv. 2025 Apr 11;11(15):eadq5484. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adq5484. Epub 2025 Apr 9. 10.1126/sciadv.adq5484 PubMed 40203091