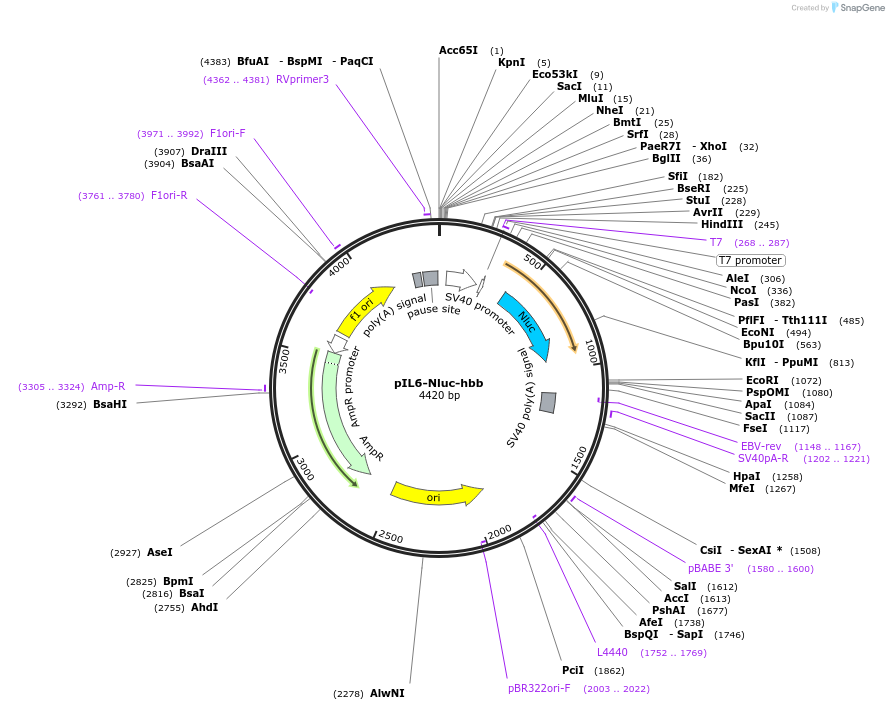
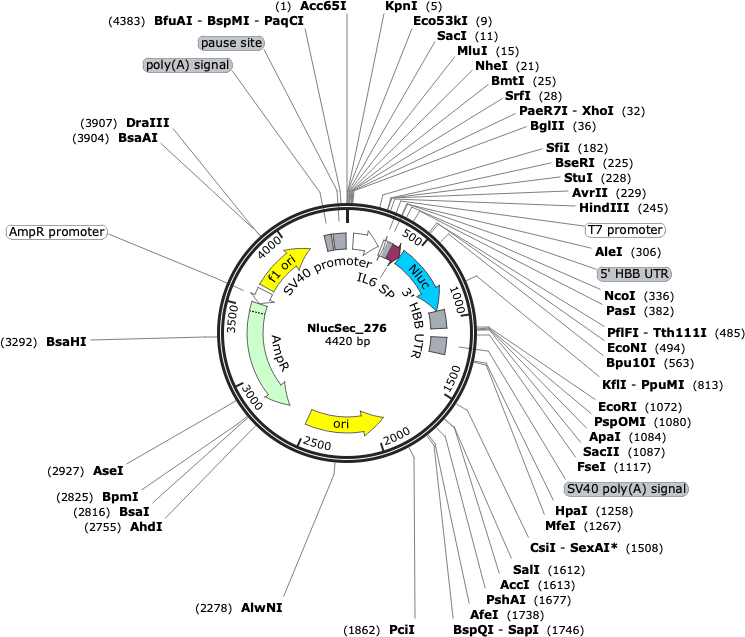
pIL6-Nluc-hbb
(Plasmid
#239843)
-
PurposeTemplate for in vitro transcription of secreted nanoluciferase, with interleukin 6 signal peptide, flanked by the human haemoglobin beta 5' and 3' UTRs.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 239843 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepGL3Control
-
Backbone manufacturerPromega
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 3636
- Total vector size (bp) 4420
-
Modifications to backboneIntroduction of multiple cloning site at 3' end of luciferase gene.
-
Vector typeLuciferase
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameSecreted nanoluciferase, with interleukin 6 signal peptide, flanked by human haemoglobin beta 5' and 3' UTRs
-
Alt nameSecNluc
-
SpeciesEngineered reporter (from Promega)
-
Insert Size (bp)784
-
GenBank IDJQ513380.1
- Promoter T7 (included as part of insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site HindIII (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer TCTGCGATCTGCATCTCAATTA
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byDesigned as a Gene Block based on Promega SecNluc sequence.
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pIL6-Nluc-hbb was a gift from Catherine Jopling (Addgene plasmid # 239843 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:239843 ; RRID:Addgene_239843) -
For your References section:
A proximity-labeling-based approach to directly detect mRNA delivery to specific subcellular locations. Smart AD, Hughes ME, Ruiz Velasco AD, Hori N, Stolnik S, Jopling CL. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025 Jun 24;36(3):102602. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102602. eCollection 2025 Sep 9. 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102602 PubMed 40661784