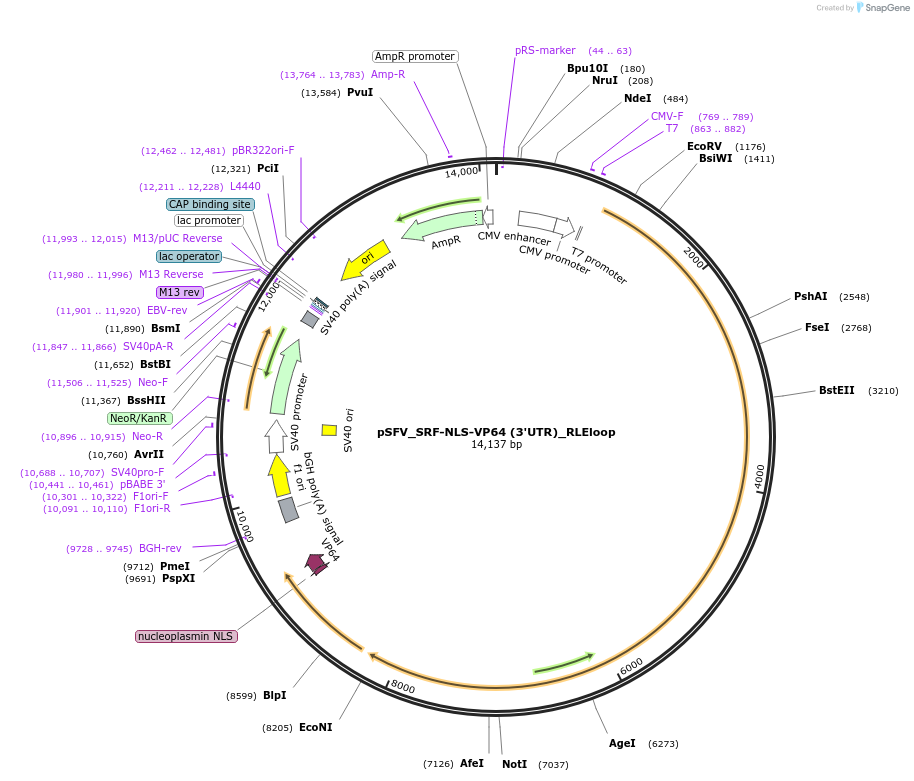
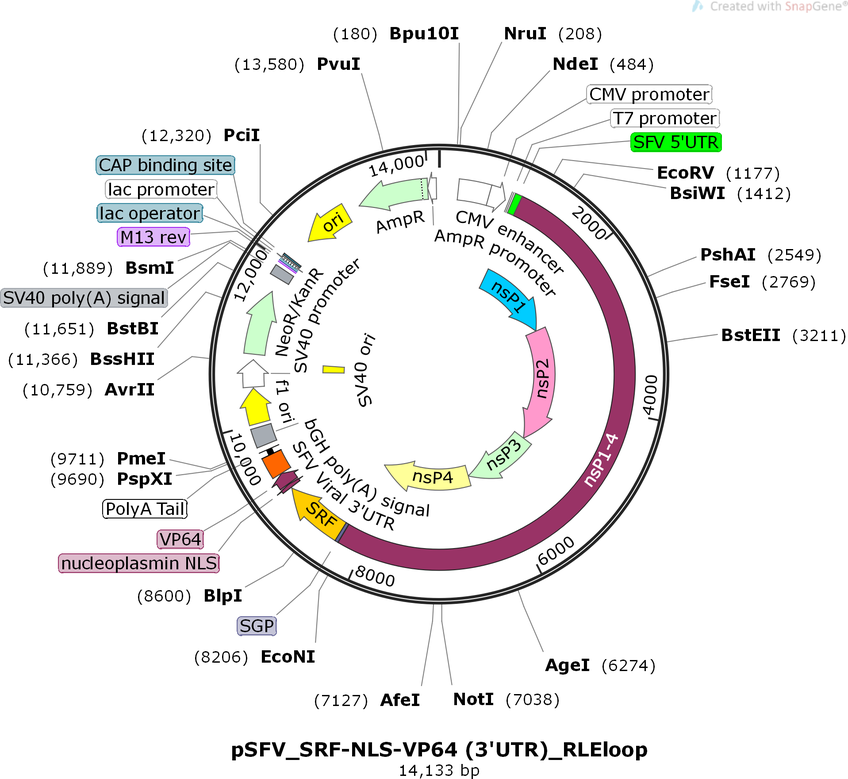
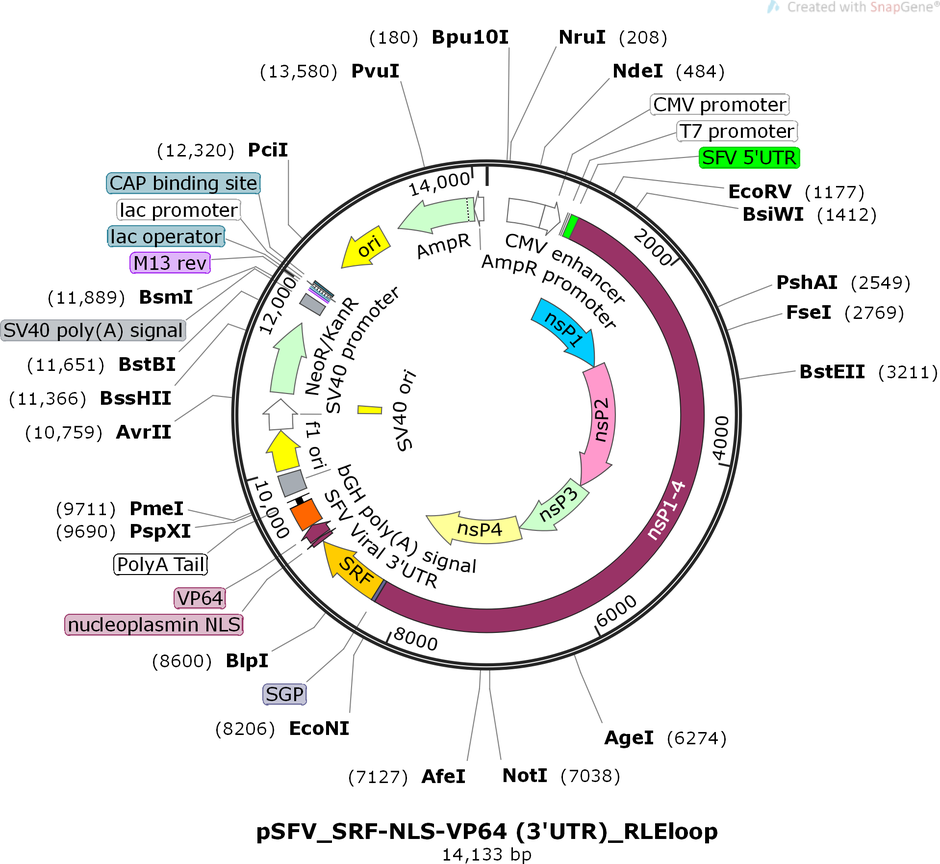
pSFV_SRF-NLS-VP64 (3'UTR)_RLEloop
(Plasmid
#240258)
-
PurposeAttenuated PROTEUS vector with SRF-VP64 transgene. Package VLVs with an envelope-expressing vector such as pCMV-VSV-G, or a transgene-responsive VSV-G expression vector.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 240258 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepcDNA3.1(+)
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersNeomycin (select with G418)
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameSRF
-
Alt nameSRF-VP64
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
MutationSRF[aa1-265]; VP64 = 4*VP16[aa437-447]
- Promoter SFV subgenomic promoter
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- NLS-VP64 (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Other
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byIDT
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
SRF and VP64 sequences were synthesized by IDT.
Addgene observed 2 base pair insertion and 2 base pair deletion in the ORF. This discrepancy likely does not affect plasmid function.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pSFV_SRF-NLS-VP64 (3'UTR)_RLEloop was a gift from Gregory Neely (Addgene plasmid # 240258 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:240258 ; RRID:Addgene_240258) -
For your References section:
A chimeric viral platform for directed evolution in mammalian cells. Cole AJ, Denes CE, Moreno CL, Hunault L, Dobson T, Hesselson D, Neely GG. Nat Commun. 2025 May 7;16(1):4250. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59438-2. 10.1038/s41467-025-59438-2 PubMed 40335481