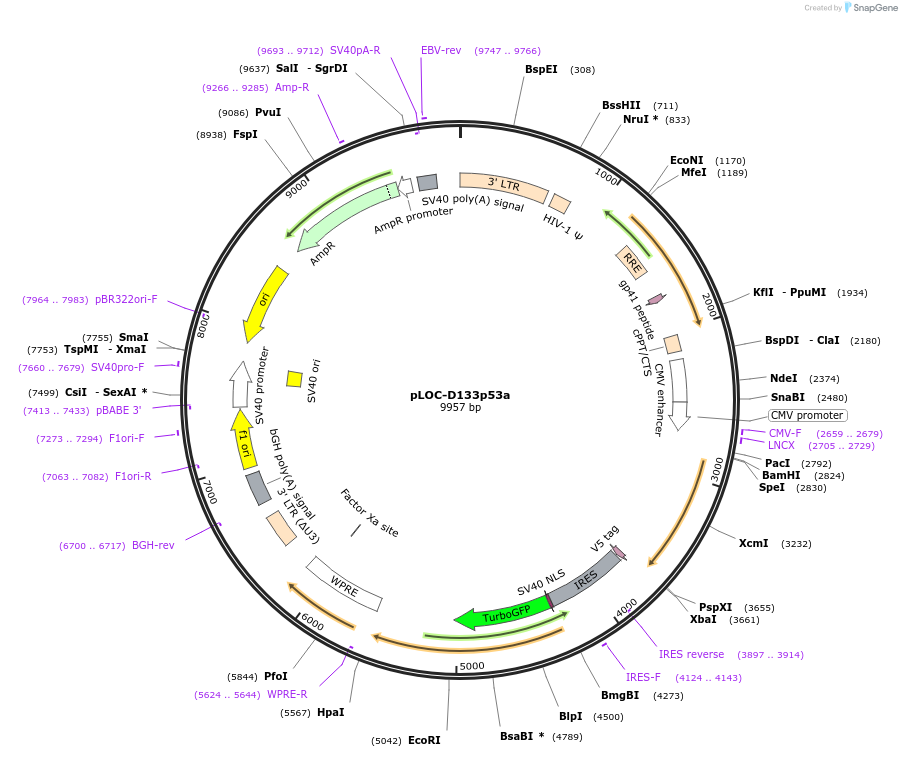
pLOC-D133p53a
(Plasmid
#241916)
-
PurposeLentiviral vector driving a p53 isoform delta133p53alpha. Stable expression in cultured human cells and possibly cells of other species.
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 241916 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepLOC-TurboRFP
-
Backbone manufacturerOpen Biosystems (currently available from Horizon Discovery)
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 9264
- Total vector size (bp) 10050
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, Lentiviral
-
Selectable markersBlasticidin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameDelta133p53alpha
-
Alt nameD133p53a
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)786
-
GenBank IDNM_001126115.1
-
Entrez GeneTP53 (a.k.a. BCC7, BMFS5, LFS1, P53, TRP53)
- Promoter CMV
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site SpeI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site AscI (destroyed during cloning)
- 5′ sequencing primer CMV-Forward
- 3′ sequencing primer Internal
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pLOC-D133p53a was a gift from Curtis Harris (Addgene plasmid # 241916 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:241916 ; RRID:Addgene_241916) -
For your References section:
Delta133p53alpha Protects Human Astrocytes from Amyloid-beta Induced Senescence and Neurotoxicity. Ungerleider K, Beck JA, Lissa D, Joruiz S, Horikawa I, Harris CC. Neuroscience. 2022 Aug 21;498:190-202. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.06.004. Epub 2022 Jun 15. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.06.004 PubMed 35716965