MoClo Yeast Secretion Biosensor (YSB) Toolkit
(Kit #
1000000268
)
Depositing Lab: Joseph Brock
The MoClo YSB Toolkit contains a library of plasmids for use in protein secretion optimization in yeast. This kit contains 46 signal peptides (Type 3a*), two yeast episomal expression vectors with GFP or RFP dropout sites (Type ‘234’), eight C-terminal tags (Type 4a), including C-myc negative control and various alpha-mating factor tag designs, and a human serum albumin (HSA) coding sequence (Type 3b*). The components can be assembled via Golden Gate assembly (standard or combinatorial), along with parts from the MoClo Yeast Toolkit (YTK), to create protein expression cassettes.
This kit will be sent as bacterial glycerol stocks in 96-well plate format.
Original Publication
High-throughput optimisation of protein secretion in yeast via an engineered biosensor. Cleaver A, Luo R, Smith OB, Murphy L, Schwessinger B, Brock J. Trends Biotechnol. 2025 Apr;43(4):838-867. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2024.11.010. PubMed (Link opens in a new window) Article (Link opens in a new window)
Please visit https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.05.15.594099 (Link opens in a new window) for bioRxiv preprint.
Description
The MoClo Yeast Secretion Biosensor (YSB) toolkit is designed for optimizing secretion of recombinant proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The kit's components are best used with the protein secretion biosensor strain detailed in the original publication (Cleaver et al., 2025), but can be applied in other yeast strains. The protein secretion biosensor assay is intended as an initial optimization tool, after which the ideal protein of interest (POI) expression cassette can be inserted into an industrial or high protein production yeast strain.
Successful secretion of a given POI relies on the use of an optimal secretion signal or signal peptide (SP). The kit contains 46 SPs (Type 3a*), 24 from S. cerevisiae and 22 from Homo sapiens. They originate from experimentally characterized secreted proteins found on UniProt and were selected for maximal sequence diversity. The SP components are compatible with other species like Komagataella phaffii (formerly Pichia pastoris).
The kit also contains two yeast episomal expression vectors with either GFP or RFP dropout sites (Type ‘234’). These include a CEN6/ARS4 yeast origin of replication, as well as an ampicillin resistance gene, and a pBR322 origin of replication for Escherichia coli. Expression cassettes can be assembled into these vectors via Golden Gate assembly, using BsaI.
As the Type 3a-3b cloning junction between the SP and POI introduces two amino acids, we redesigned the junction to encode an alanine-proline (Ala-Pro) rather than the glycine-serine (Gly-Ser) defined by the MoClo assembly standard. These altered junctions are denoted by the symbol ‘*’. This reuses the MoClo YTK Type 8-1 overhang (CCCT), which should be taken into account when assembling expression cassettes in alternative vectors.
The seven C-terminal alpha-mating factor tags (Type 4a) contain the S. cerevisiae 13-amino-acid alpha-mating factor (aMF). This peptide is detected by the G protein-coupled receptor Ste13, which in the protein secretion biosensor strain is coupled to a sfGFP reporter gene. When the POI is successfully secreted, the aMF tag is secreted alongside and triggers activation of the biosensor pathway, resulting in a green fluorescent read-out. The Type 4a C-terminal c-Myc tag is intended as a negative control for the secretion biosensor assay.
Recombinant HSA was used as the test protein for the secretion biosensor assay. The HSA coding sequence (Type 3b*) can be used as a positive control, as well as a template for designing custom POI coding sequences (Type 3b*).
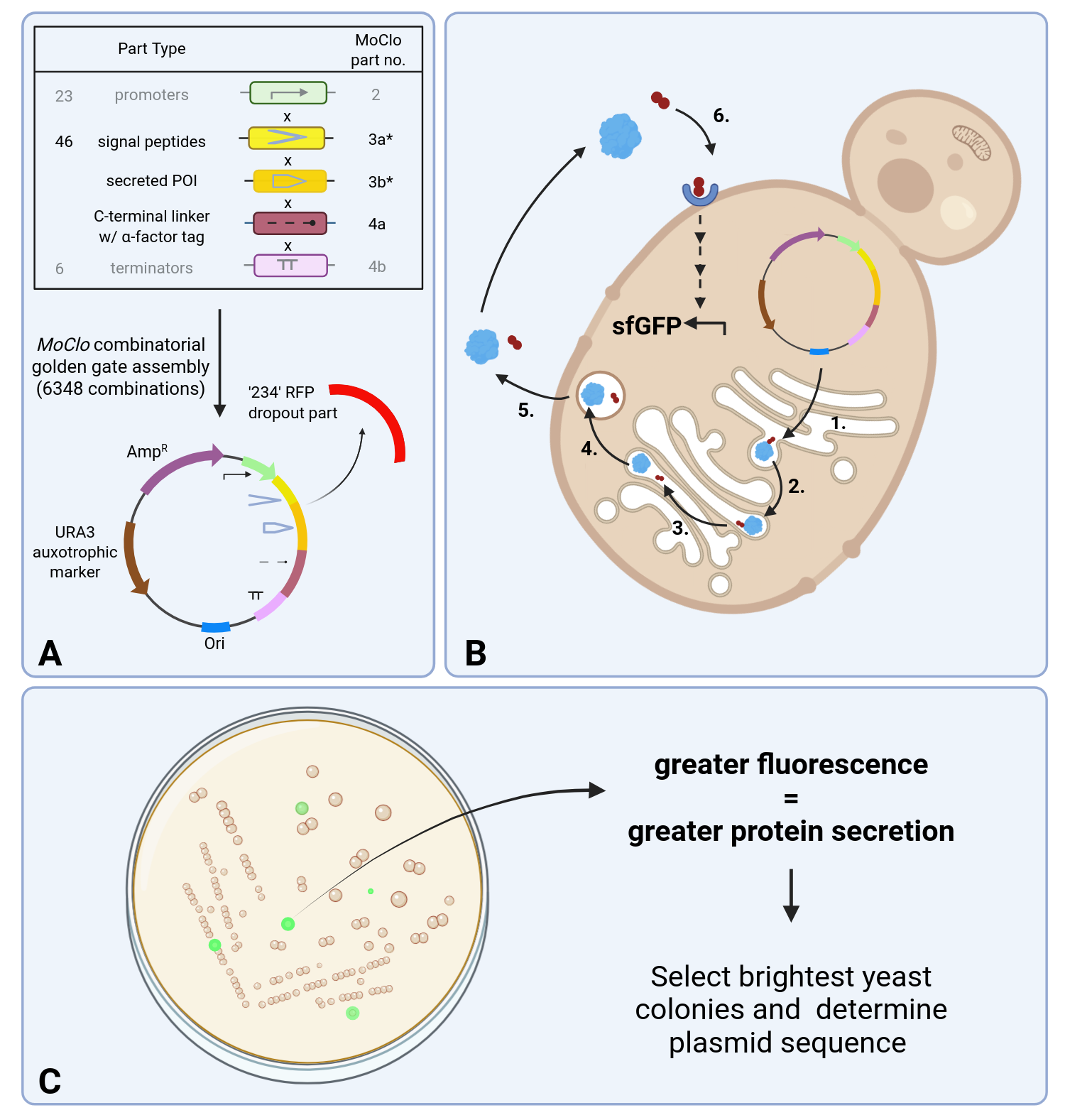
Figure 1: Yeast protein secretion biosensor assay schematic. (A) MoClo Combinatorial Golden gate assembly of 23 promoters (from MoClo YTK, not included in this kit), 46 signal peptides, a protein of interest (POI), a C-terminal linker with alpha-mating factor (aMF) tag, and six terminators (from MoClo YTK, not included in this kit), into the RFP (Type ‘234’) dropout site of a yeast episomal expression vector (6,348 total expression cassette combinations). Assembled plasmids are then transformed into the secretion assay yeast strain, containing a G protein-coupled receptor biosensor for aMF with GFP output. (B) 1. POI represented in blue, along with aMF tag represented in red, is expressed and translocated to the endoplasmic reticulum. 2. POI with aMF tag is translocated to the Golgi apparatus. 3. In the Golgi apparatus, proteases cleave the tag from the POI (dependent on tag design used). 4. POI and cleaved aMF tag are translocated to a secretory vesicle. 5. POI and cleaved aMF tag are secreted from the cell. 6. aMF tag interacts with biosensor cell surface receptor triggering GFP expression. (C) Cells are plated out on -URA auxotrophic selective media, cell fluorescence indicates successful POI secretion. The most fluorescent colonies can be plasmid sequenced to determine successful expression cassette combinations for POI secretion.
How to Cite this Kit
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which they were created, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
For your Materials and Methods section:
"The MoClo Yeast Secretion Biosensor (YSB) Toolkit was a gift from Joseph Brock (Addgene kit #1000000268)."
For your Reference section:
High-throughput optimisation of protein secretion in yeast via an engineered biosensor. Cleaver A, Luo R, Smith OB, Murphy L, Schwessinger B, Brock J. Trends Biotechnol. 2025 Apr;43(4):838-867. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2024.11.010. PubMed (Link opens in a new window) Article (Link opens in a new window)
MoClo Yeast Secretion Biosensor (YSB) Toolkit - #1000000268
- Resistance Color Key
Each circle corresponds to a specific antibiotic resistance in the kit plate map wells.
- Inventory
Searchable and sortable table of all plasmids in kit. The Well column lists the plasmid well location in its plate. The Plasmid column links to a plasmid's individual web page.
- Kit Plate Map
96-well plate map for plasmid layout. Hovering over a well reveals the plasmid name, while clicking on a well opens the plasmid page.
Resistance Color Key
| Ampicillin | |
| Chloramphenicol |
Inventory
| Well | Plasmid | Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| A / 1 | YEE_GFP |
|
| A / 2 | YEE_RFP |
|
| A / 3 | SP_A1 |
|
| A / 4 | SP_A2 |
|
| A / 5 | SP_A3 |
|
| A / 6 | SP_A4 |
|
| A / 7 | SP_A5 |
|
| A / 8 | SP_A6 |
|
| A / 9 | SP_B1 |
|
| A / 10 | SP_B2 |
|
| A / 11 | SP_B3 |
|
| A / 12 | SP_B4 |
|
| B / 1 | SP_B5 |
|
| B / 2 | SP_B6 |
|
| B / 3 | SP_C1 |
|
| B / 4 | SP_C2 |
|
| B / 5 | SP_C3 |
|
| B / 6 | SP_C4 |
|
| B / 7 | SP_C5 |
|
| B / 8 | SP_C6 |
|
| B / 9 | SP_D1 |
|
| B / 10 | SP_D2 |
|
| B / 11 | SP_D3 |
|
| B / 12 | SP_D4 |
|
| C / 1 | SP_D5 |
|
| C / 2 | SP_D6 |
|
| C / 3 | SP_E1 |
|
| C / 4 | SP_E2 |
|
| C / 5 | SP_E3 |
|
| C / 6 | SP_E4 |
|
| C / 7 | SP_E5 |
|
| C / 8 | SP_E6 |
|
| C / 9 | SP_F1 |
|
| C / 10 | SP_F2 |
|
| C / 11 | SP_F3 |
|
| C / 12 | SP_F4 |
|
| D / 1 | SP_F5 |
|
| D / 2 | SP_F6 |
|
| D / 3 | SP_G1 |
|
| D / 4 | SP_G2 |
|
| D / 5 | SP_G3 |
|
| D / 6 | SP_G6 |
|
| D / 7 | SP_H1 |
|
| D / 8 | SP_H2 |
|
| D / 9 | SP_H3 |
|
| D / 10 | SP_H4 |
|
| D / 11 | SP_H5 |
|
| D / 12 | SP_H6 |
|
| E / 1 | HSA_3b*_AP |
|
| E / 2 | C-term_aMFx1 (4a) |
|
| E / 3 | C-term_aMFx1_noKREAEA (4a) |
|
| E / 4 | C-term_aMFx4 (4a) |
|
| E / 5 | C-term_TEV_aMFx1 (4a) |
|
| E / 6 | twinStrep_FLAG_aMFx1 (4a) |
|
| E / 7 | twinStrep_HA_aMFx1 (4a) |
|
| E / 8 | twinStrep_aMFx1 (4a) |
|
| E / 9 | C-term_C-myc (4a) |
|


