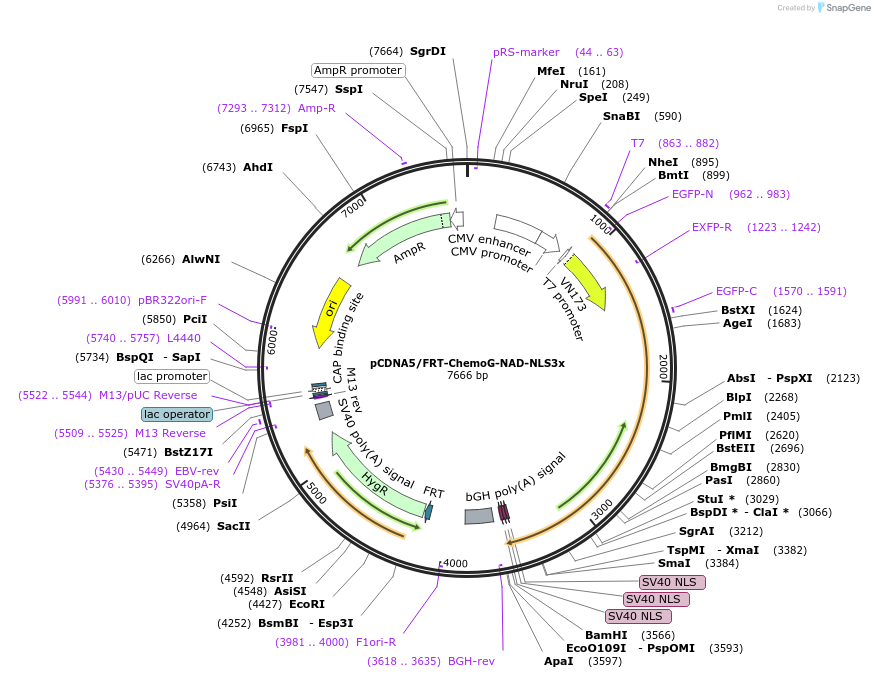
pCDNA5/FRT-ChemoG-NAD-NLS3x
(Plasmid
#193822)
-
PurposeCMV overexpression of ChemoG-NAD in the nucleus of mammalian cell lines
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 193822 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepcDNA5/FRT
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5000
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression
-
Selectable markersHygromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameChemoG-NAD-NLS3x
-
SpeciesSynthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)2700
-
MutationEGFP:A206K, T225R; HT7: L271E
- Promoter CMV
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gibson Cloning
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pCDNA5/FRT-ChemoG-NAD-NLS3x was a gift from Julien Hiblot (Addgene plasmid # 193822 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:193822 ; RRID:Addgene_193822) -
For your References section:
A general method for the development of multicolor biosensors with large dynamic ranges. Hellweg L, Edenhofer A, Barck L, Huppertz MC, Frei MS, Tarnawski M, Bergner A, Koch B, Johnsson K, Hiblot J. Nat Chem Biol. 2023 Jun 8. doi: 10.1038/s41589-023-01350-1. 10.1038/s41589-023-01350-1 PubMed 37291200