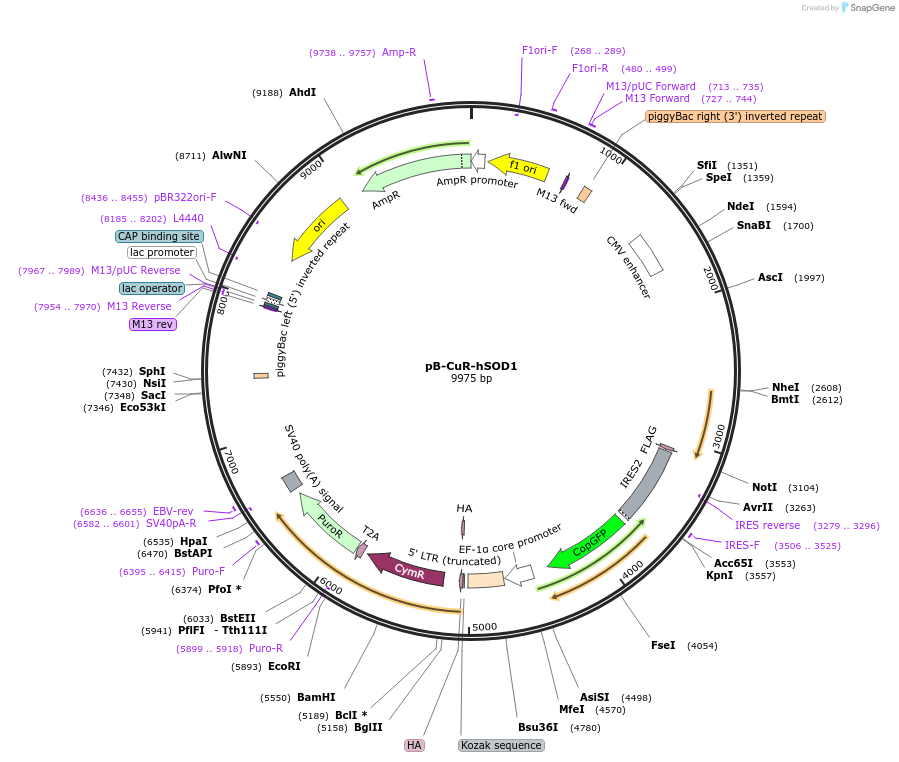
pB-CuR-hSOD1
(Plasmid
#232477)
-
PurposeThe inducible PiggyBac Cumate Switch vector (PBQM812A-1 System Biosciences) expressing human SOD1gene including flag -tag (DYKDDDDK) on the 3' end
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 232477 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonePB-CuO-CMV-MCS-EF1a-CymR-T2A-Puro piggyBac Inducible cDNA Cloning and Expression Vector
-
Backbone manufacturerSBI -System Biosciences
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 9509
- Total vector size (bp) 9975
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression ; transposon system
-
Selectable markersPuromycin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameHomo sapiens superoxide dismutase 1
-
Alt nameSOD1
-
SpeciesH. sapiens (human)
-
Insert Size (bp)461
-
GenBank IDEF151142.1
-
Entrez GeneSOD1 (a.k.a. ALS, ALS1, HEL-S-44, IPOA, SOD, STAHP, hSod1, homodimer)
- Promoter CMV-CuO
-
Tag
/ Fusion Protein
- DYKDDDDK (FLAG-tag) (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site NheI (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site NotI (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer agacgccatccacgctgttttgacctc
- 3′ sequencing primer agggtgcgtacggccctggggacgt
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pB-CuR-hSOD1 was a gift from Lukas Trantirek (Addgene plasmid # 232477 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:232477 ; RRID:Addgene_232477) -
For your References section:
Protein structure and interactions elucidated with in-cell NMR for different cell cycle phases and in 3D human tissue models. Rynes J, Istvankova E, Dzurov Krafcikova M, Luchinat E, Barbieri L, Banci L, Kamarytova K, Loja T, Fafilek B, Rico-Llanos G, Krejci P, Macurek L, Foldynova-Trantirkova S, Trantirek L. Commun Biol. 2025 Feb 7;8(1):194. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07607-w. 10.1038/s42003-025-07607-w PubMed 39920376