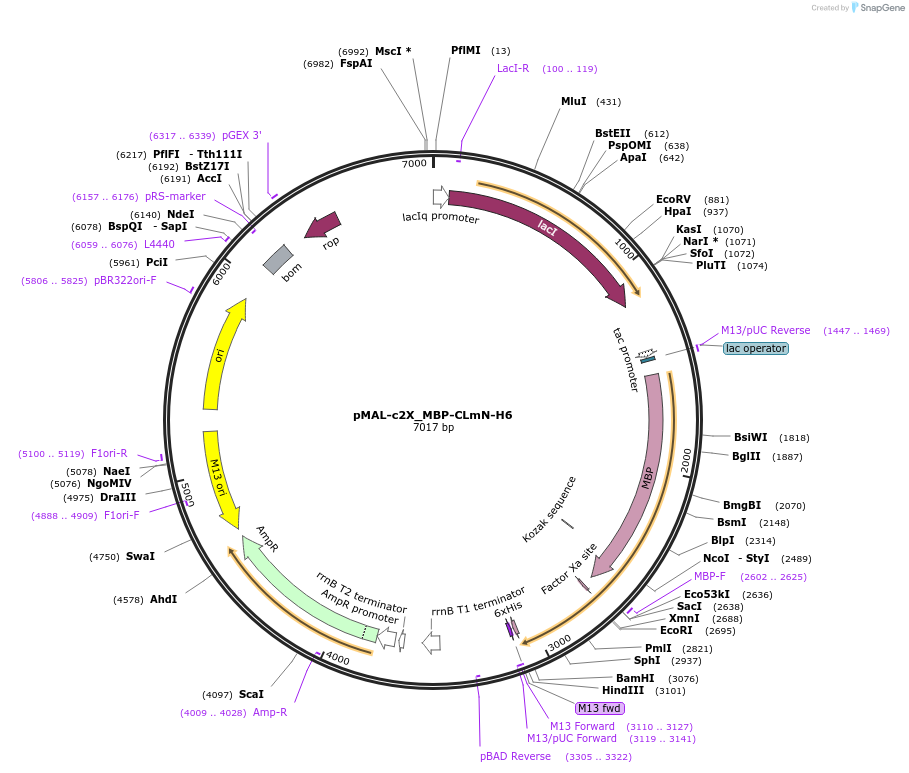
pMAL-c2X_MBP-CLmN-H6
(Plasmid
#234487)
-
PurposeMaltose binding protein N-terminally fused to His-tagged CLmN split intein
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 234487 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepMAL-c2X
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 5445
- Total vector size (bp) 7020
-
Vector typeBacterial Expression
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberUnknown
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameN-terminal Fragment of the CLm Split Intein
-
Alt nameCLmN
-
SpeciesAeromonas phage Aes123
-
Insert Size (bp)360
-
MutationT69K, F75H, M118N within the N-terminal fragment of the Aes123 PoB1 intein
-
GenBank IDAFN69891.1 JN377899
-
Tags
/ Fusion Proteins
- Maltose Binding Protein (MBP) (N terminal on insert)
- Hexahistidine Tag (C terminal on insert)
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site HindIII (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer malE
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
Please visit https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.01.22.634254 for bioRxiv preprint.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pMAL-c2X_MBP-CLmN-H6 was a gift from Henning Mootz (Addgene plasmid # 234487 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:234487 ; RRID:Addgene_234487) -
For your References section:
A cysteine-less and ultra-fast split intein rationally engineered from being aggregation-prone to highly efficient in protein trans-splicing. Humberg C, Yilmaz Z, Fitzian K, Dorner W, Kummel D, Mootz HD. Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 19;16(1):2723. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57596-x. 10.1038/s41467-025-57596-x PubMed 40108172