CRISPR Plasmids: RNA Targeting
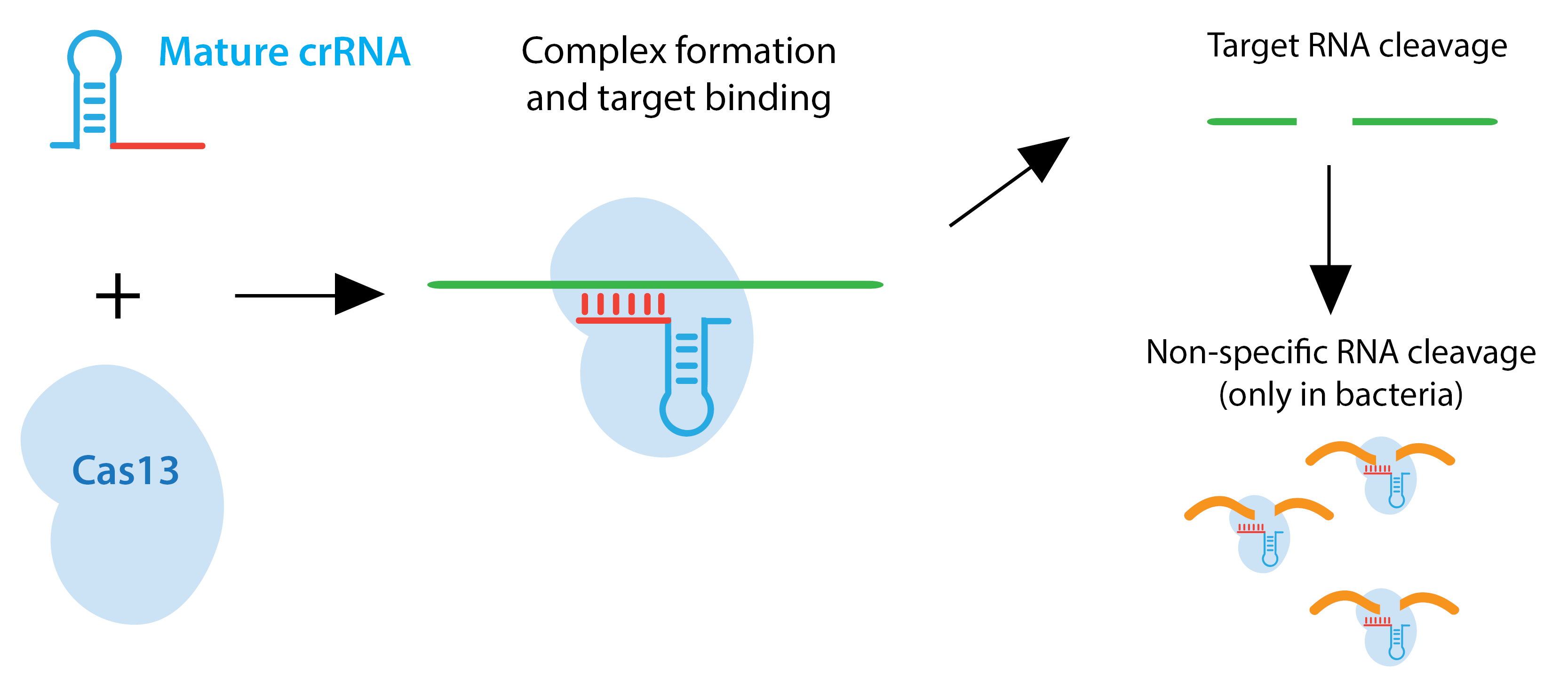
Type VI CRISPR systems, including the enzymes Cas13a/C2c2 and Cas13b, target RNA rather than DNA. In bacteria, once they have recognized and cleaved the target RNA sequence, they adopt an enzymatically active state and can bind and cleave additional RNAs regardless of homology to the crRNA. This activity provides a stark contrast to Cas9 and Cas12, which require that each DNA target have high sequence identity to the spacer sequence and contain a PAM sequence just downstream of the sequence to be cleaved. This non-specific cleavage is thought to activate programmed cell death or dormancy for phage-infected bacterial cells so as to limit the spread of infection throughout the entire population.
Type VI enzymes that function in mammalian cells can be used to attentuate RNA levels. In mammalian systems, Cas13a does not exhibit the collateral RNA degradation seen in bacteria.
Browse, sort, or search the tables below for CRISPR plasmids designed for RNA targeting. To learn more about RNA targeting and other CRISPR topics, read our CRISPR Guide.
Mammalian
| ID | Plasmid | Gene/Insert | Promoter | Selectable Marker | PI | Publication |
|---|
Bacteria
| ID | Plasmid | Gene/Insert | PI | Publication |
|---|
Plant
| ID | Plasmid | Gene/Insert | PI | Publication |
|---|
CRISPR Resources
Addgene has a large selection of CRISPR plasmids and resources. Find more CRISPR functions along with plasmids categorized by organism by visiting our CRISPR plasmids page. Find a comprehensive list of CRISPR resources by visiting our CRISPR reference page.
Content last reviewed: 17 October 2025
Do you have suggestions for other plasmids that should be added to this list?
Fill out our Suggest a Plasmid form or e-mail [email protected] to help us improve this resource!



