Xenorhabdus griffiniae Part Library
(Kit #
1000000274
)
Depositing Lab: Richard Murray
This collection contains plasmids that can be used to build constructs for genome integration at the Tn7 site of Xenorhabdus bacteria. Most plasmids contain a constitutive promoter (different strengths), RBS (different strengths), and TurboRFP.
This kit will be sent as bacterial glycerol stocks in 96-well plate format.
Original Publication
A DNA Part Library for Reliable Engineering of the Emerging Model Nematode Symbiotic Bacterium Xenorhabdus griffiniae HGB2511. Larsson EM, Wang OY, Murray RM. ACS Synth Biol. 2025 Oct 17;14(10):4122-4126. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.5c00414. PubMed (Link opens in a new window) Article (Link opens in a new window)
Please visit https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.06.09.658710 (Link opens in a new window) for bioRxiv preprint.
Description
This collection of plasmids includes part plasmids and plasmids that contain Golden Gate assemblies. The part plasmids can be used to create Golden Gate assemblies using the Golden Gate-Gibson (3G) assembly method. These part plasmids have unique nucleotide sequences (UNS) that help form linear fragments using the Golden Gate reaction. The linear fragment is amplified using PCR, then inserted into a backbone using Gibson assembly. These Golden Gate assembly plasmids can then be used to conjugate into the X. griffiniae genome, allowing for the Golden Gate fragment to be expressed in X. griffiniae.
The part plasmids consist of a terminator and various coding sequences. All of the part plasmids are ampicillin resistant. The eEMLP01 part plasmid contains a t0 terminator, used in all Golden Gate assemblies. The eEMLP02 part plasmid contains the TurboRFP coding sequence, which was used to create the following Golden Gate Assemblies: eOYW001–eOYW010, eOYW012–eOYW020, eEML017, and eOYW021–eOYW022. The eOYWP01 part plasmid contains the the lux gene, which produces bioluminescence that can be expressed in X. griffiniae and E. coli. The eOYWP01 part plasmid was used to construct eOYW023. The eOYWP01 part plasmid contains the phenazine gene.
The Golden Gate assemblies were constructed using the 3G assembly method and then inserted into the X. griffiniae genome at the Tn7 site by conjugation. Conjugation occurs between the donor E. coli strain with the Golden Gate plasmid, helper E. coli strain, and the wildtype X. griffiniae. The Golden Gate assembly plasmids are transformed into the donor E. coli strain for conjugation. The plasmids contain both constitutive and inducible promoters. Plasmids eOYW001–eOYW010, eOYW012–eOYW020, eOYW023, eEML021, eEML046, eEML006, and eEML009 have constitutive promoters, while eEML017, eOYW021, and eOYW022 contain IPTG inducible promoters. eOYW012–eOYW020 plasmids contain the TurboRFP gene with various promoter and ribosome binding sites (RBS), leading to different fluorescent strengths. The eEML017, eOYW021, and eOYW022 plasmids contain IPTG inducible constructs, consisting of a constitutive promoter for the lacI gene and an inducible promoter, Ptac, for the TurboRFP gene. In X. griffiniae, eEML017 has a weak signal, eOYW021 has a medium signal, and eOYW022 has a strong signal. The eOYW023 plasmid contains the constitutive construct for the lux gene. The eEML021 contains the green fluorescent sfGFP gene, while eEML046 contains the yellow fluorescent sfYFP. The eEML006 and eEML009 plasmids contain the GFPmut3 genes. eEML006 is ampicillin and streptomycin resistant, while eEML009 is ampicillin and gentamicin resistant. The other Golden Gate assembly plasmids (eOYW001–eOYW010, eOYW012–eOYW020, eOYW023, eEML021, and eEML046) are ampicillin and kanamycin resistant.
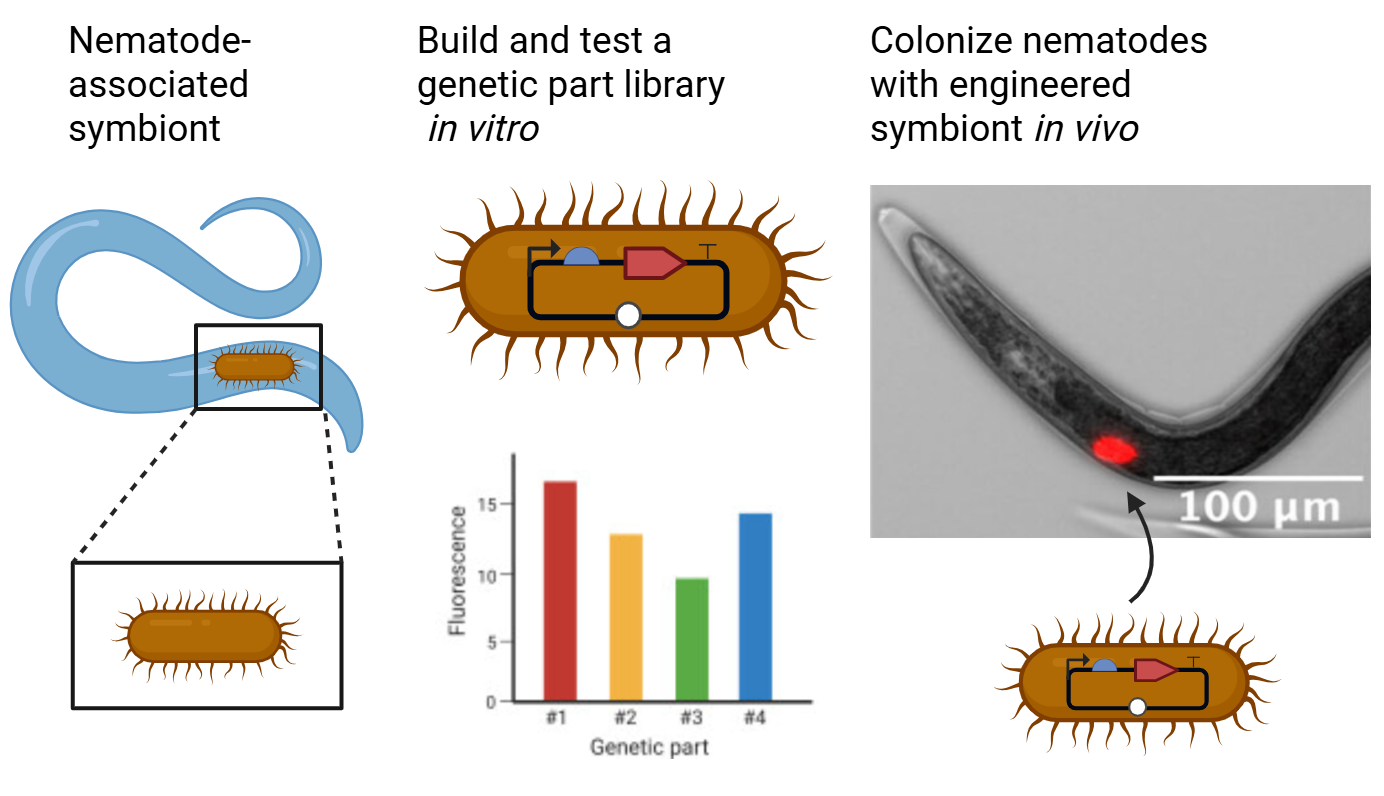
Figure 1: Summary of Xenorhabdus griffiniae Part Library kit development. Left: Engineering the nematode symbiont X. griffiniae. Center: Building a DNA part library for X. griffiniae. Right: Observing colonized nematodes with engineered symbiont.
Kit Documentation
Protocols are available in the published technical note (Larsson et al., 2025 (Link opens in a new window)).
How to Cite this Kit
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which they were created, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
For your Materials and Methods section:
"The Xenorhabdus griffiniae Part Library was a gift from Richard Murray (Addgene kit #1000000274)."
For your Reference section:
A DNA Part Library for Reliable Engineering of the Emerging Model Nematode Symbiotic Bacterium Xenorhabdus griffiniae HGB2511. Larsson EM, Wang OY, Murray RM. ACS Synth Biol. 2025 Oct 17;14(10):4122-4126. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.5c00414. PubMed (Link opens in a new window) Article (Link opens in a new window)
The Xenorhabdus griffiniae part library - #1000000274
- Resistance Color Key
Each circle corresponds to a specific antibiotic resistance in the kit plate map wells.
- Inventory
Searchable and sortable table of all plasmids in kit. The Well column lists the plasmid well location in its plate. The Plasmid column links to a plasmid's individual web page.
- Kit Plate Map
96-well plate map for plasmid layout. Hovering over a well reveals the plasmid name, while clicking on a well opens the plasmid page.
Resistance Color Key
| Ampicillin | |
| Ampicillin and Kanamycin | |
| Ampicillin and Streptomycin | |
| Ampicillin and Gentamicin |
Inventory
| Well | Plasmid | Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| A / 1 | eEMLP01 |
|
| A / 2 | eEMLP02 |
|
| A / 3 | eOYWP01 |
|
| A / 4 | eOYWP02 |
|
| A / 5 | eOYW001 |
|
| A / 6 | eOYW002 |
|
| A / 7 | eOYW003 |
|
| A / 8 | eOYW004 |
|
| A / 9 | eOYW005 |
|
| A / 10 | eOYW006 |
|
| A / 11 | eOYW007 |
|
| A / 12 | eOYW008 |
|
| B / 1 | eOYW009 |
|
| B / 2 | eOYW012 |
|
| B / 3 | eOYW013 |
|
| B / 4 | eOYW014 |
|
| B / 5 | eOYW015 |
|
| B / 6 | eOYW016 |
|
| B / 7 | eOYW017 |
|
| B / 8 | eOYW018 |
|
| B / 9 | eOYW019 |
|
| B / 10 | eOYW020 |
|
| B / 11 | eEML017 |
|
| B / 12 | eOYW021 |
|
| C / 1 | eOYW022 |
|
| C / 2 | eOYW023 |
|
| C / 3 | eEML021 |
|
| C / 4 | eEML046 |
|
| C / 5 | eEML006 |
|
| C / 6 | eEML009 |
|


