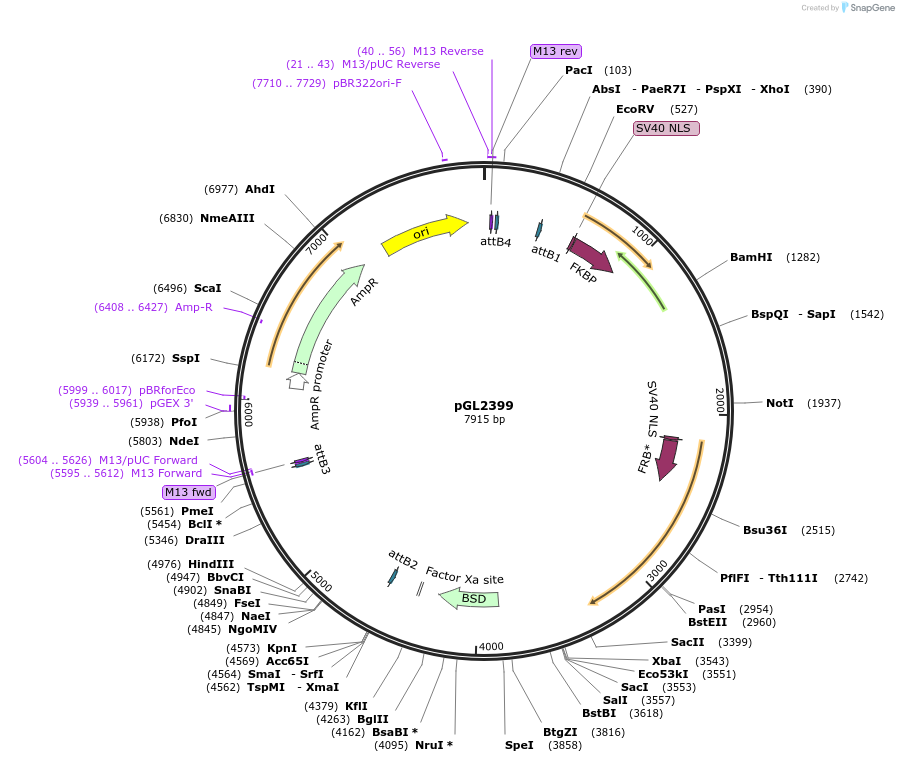
pGL2399
(Plasmid
#137051)
-
PurposeExpression of rapamycin-inducible dimerisation of split Cre from ribosomal locus in Leishmania parasite; pRIB-DiCre
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 137051 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $89 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepDEST
-
Vector typeCre/Lox ; Leishmania Ribosomal Locus Expression
-
Selectable markersBlasticidin
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert 1
-
Gene/Insert nameSplit Cre Recombinase Rapamycin Inducible Dimerisation
-
Alt nameDiCre
- Promoter For integration into the 18S ribosomal locus
Cloning Information for Gene/Insert 1
- Cloning method Unknown
- 5′ sequencing primer na
- (Common Sequencing Primers)
Gene/Insert 2
-
Gene/Insert nameBlasticidin-S Deaminase
Resource Information
-
Supplemental Documents
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pGL2399 was a gift from Jeremy Mottram (Addgene plasmid # 137051 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:137051 ; RRID:Addgene_137051) -
For your References section:
DiCre-Based Inducible Disruption of Leishmania Genes. Duncan SM, Myburgh E, Alves-Ferreira EV, Mottram JC. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1971:211-224. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9210-2_10. 10.1007/978-1-4939-9210-2_10 PubMed 30980305