OpenPlant Kit
(Kit #
1000000272
)
Depositing Lab: Jim Haseloff
The OpenPlant toolkit is a collection of standardized DNA parts and vectors, for genetic engineering of the nuclear and plastid genomes of the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha, an emerging plant synthetic biology model. Although primarily developed for Marchantia, the toolkit can also be used in other plants such as the angiosperm Arabidopsis thaliana and the hornwort Anthoceros agrestis.
This kit will be sent as bacterial glycerol stocks in 96-well plate format.
Original Publication
Systematic Tools for Reprogramming Plant Gene Expression in a Simple Model, Marchantia polymorpha. Sauret-Güeto S, Frangedakis E, Silvestri L, Rebmann M, Tomaselli M, Markel K, Delmans M, West A, Patron NJ, Haseloff J. ACS Synth Biol. 2020 Apr 17;9(4):864-882. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00337. PubMed (Link opens in a new window) Article (Link opens in a new window)
Construction of DNA Tools for Hyperexpression in Marchantia Chloroplasts. Frangedakis E, Guzman-Chavez F, Rebmann M, Markel K, Yu Y, Perraki A, Tse SW, Liu Y, Rever J, Sauret-Gueto S, Goffinet B, Schneider H, Haseloff J. ACS Synth Biol. 2021 Jul 16;10(7):1651-1666. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.0c00637. PubMed (Link opens in a new window) Article (Link opens in a new window)
Description
The OpenPlant toolkit is based on Loop assembly (Pollack et al., 2018 (Link opens in a new window)), a Golden Gate cloning method for DNA construct generation that employs Type IIS restriction enzymes and a recursive strategy to greatly simplify the process of plasmid assembly. It allows rapid and efficient production of large DNA constructs from DNA parts that follow a common assembly syntax. Unlike other systems that require elaborate sets of vectors, Loop assembly requires only two sets of four complementary vectors. In a series of reactions, standardized DNA parts can be assembled into multi-transcriptional units.
The OpenPlant toolkit was deposited by Jim Haseloff’s lab and is a collection of 79 plasmids including Loop nuclear transformation vectors, Loop vectors for chloroplast transformation, Loop vectors for CRISPR genome editing, and a series of standardized DNA L0 parts (promoters, 5' untranslated regions, signal peptides, coding sequences, and terminators) for expression in Marchantia. pCk and Loop vectors for CRISPR genome editing are supplied as individual stabs (please see Accessory Plasmids tab).
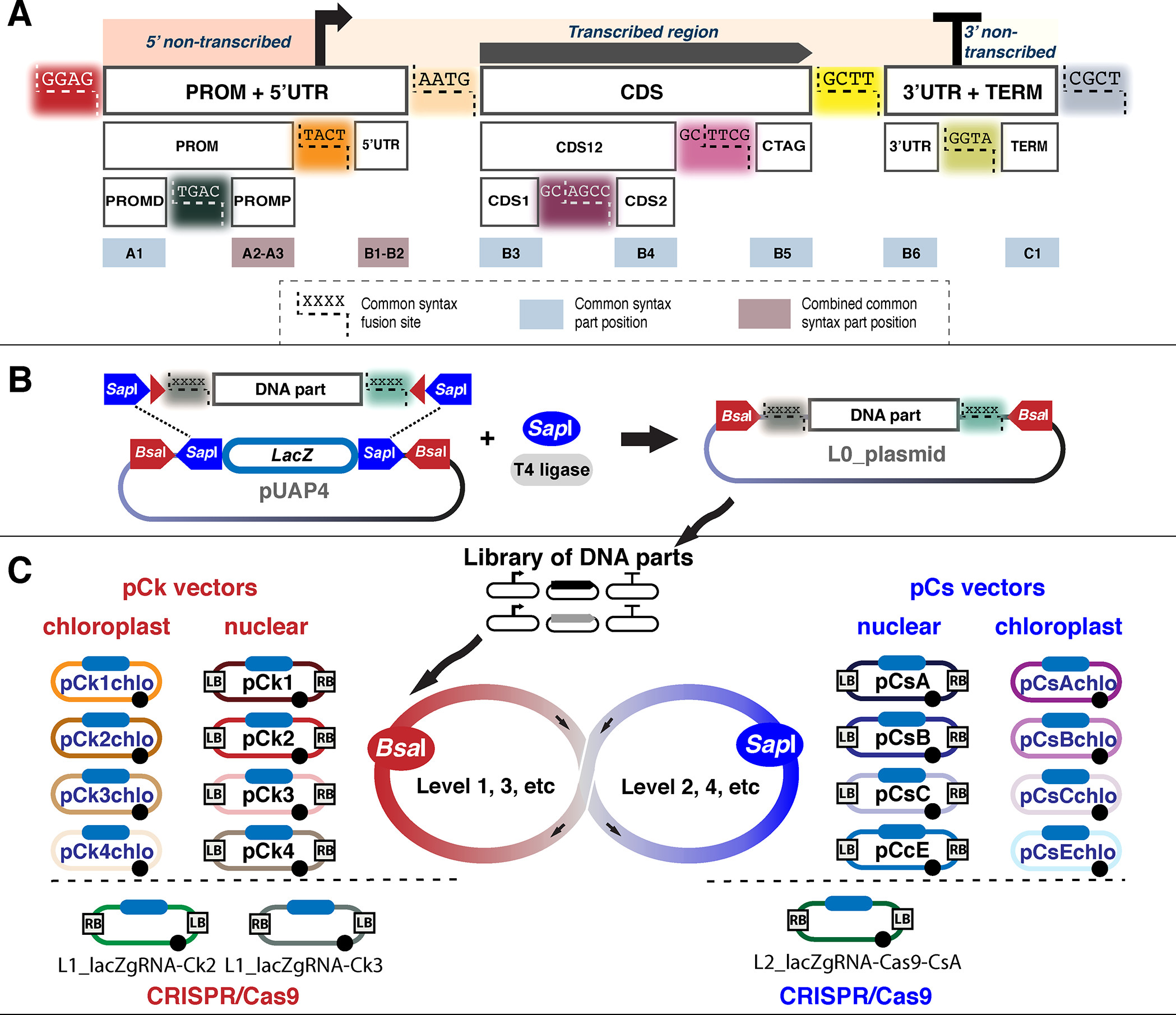
Figure 1: Key elements in the OpenPlant Loop assembly toolkit. (A) Schematic of the parts and common syntax used in OpenPlant Loop assembly. A transcriptional unit is divided into a 5' non-transcribed region, a transcribed region, and a 3' non-transcribed region. These parts can be further broken down into the 5' UTR, the distal (PROMD) and proximal (PROMP) promoters, CDS12 (which can be split into CDS1 and CDS2), CTAG, 3' UTR, and the terminator (TERM). (B) Schematic of the pUAP4 vector containing SapI sites to accept L0 parts and BsaI sites to assemble L0 parts into transcription units (L1). (C) Summary of the Loop acceptor vectors of the OpenPlant toolkit. For nuclear genome transformation: pCk (1, 2, 3, and 4) assembles L0 parts into a Level 1 plasmid using BsaI, and pCs (A,B,C,E) assembles up to four Level 1 plasmids into a Level 2 construct using SapI. For chloroplast applications, pCkchlo (1, 2, 3, and 4) and pCschlo (A, B, C, and E) can be used for assembly. L1_lacZgRNA-Ck2, L1_lacZgRNA-Ck3, and L2_lacZgRNA-Cas9 are designed for CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. LB and RB: left and right border repeats from nopaline C58 T-DNA. Filled blue rounded rectangle: lacZα cassette for blue-white screening. Filled black circles: pSa origin of replication. Image and caption derived from Figure 2 in Sauret-Güeto et al., 2020 (Link opens in a new window).
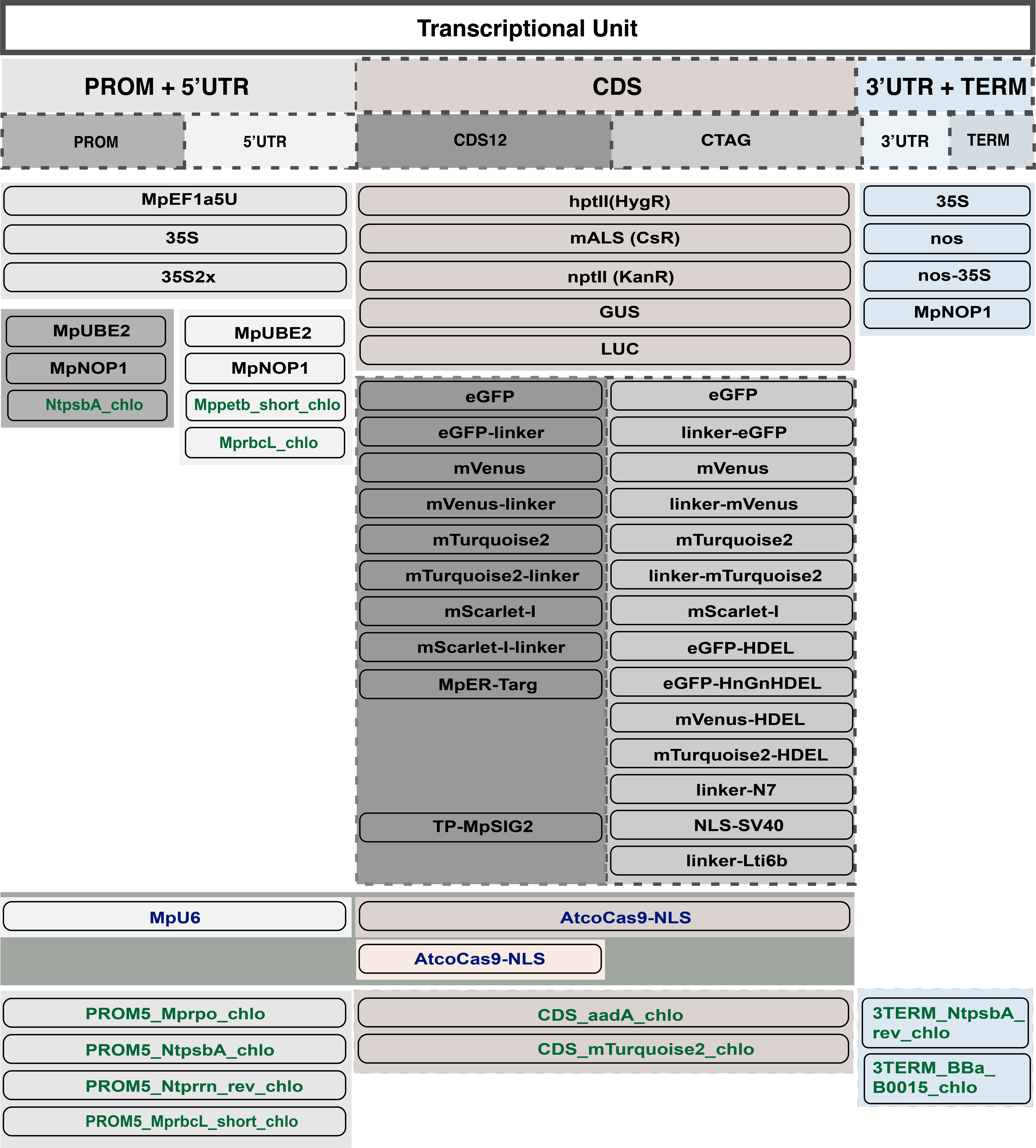
Figure 2: OpenPlant Kit DNA parts. Image modified from Sauret-Güeto et al., 2020 (Link opens in a new window).
Kit Documentation
OpenPlant protocols are available at:
- Benchling, OpenPlant Kit (Link opens in a new window)
- Protocols.io, OpenPlant Project (Link opens in a new window)
- SynBryo Group (Link opens in a new window)
How to Cite this Kit
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which they were created, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
For your Materials and Methods section:
"The OpenPlant Kit was a gift from Jim Haseloff (Addgene kit #1000000272)."
For your Reference section:
Systematic Tools for Reprogramming Plant Gene Expression in a Simple Model, Marchantia polymorpha. Sauret-Güeto S, Frangedakis E, Silvestri L, Rebmann M, Tomaselli M, Markel K, Delmans M, West A, Patron NJ, Haseloff J. ACS Synth Biol. 2020 Apr 17;9(4):864-882. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00337. PubMed (Link opens in a new window) Article (Link opens in a new window)
Construction of DNA Tools for Hyperexpression in Marchantia Chloroplasts. Frangedakis E, Guzman-Chavez F, Rebmann M, Markel K, Yu Y, Perraki A, Tse SW, Liu Y, Rever J, Sauret-Gueto S, Goffinet B, Schneider H, Haseloff J. ACS Synth Biol. 2021 Jul 16;10(7):1651-1666. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.0c00637. PubMed (Link opens in a new window) Article (Link opens in a new window)
OpenPlant kit - #1000000272
- Resistance Color Key
Each circle corresponds to a specific antibiotic resistance in the kit plate map wells.
- Inventory
Searchable and sortable table of all plasmids in kit. The Well column lists the plasmid well location in its plate. The Plasmid column links to a plasmid's individual web page.
- Kit Plate Map
96-well plate map for plasmid layout. Hovering over a well reveals the plasmid name, while clicking on a well opens the plasmid page.
Resistance Color Key
| Spectinomycin | |
| Kanamycin | |
| Chloramphenicol |
Inventory
| Well | Plasmid | Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| A / 1 | pCsA |
|
| A / 2 | pCsB |
|
| A / 3 | pCsC |
|
| A / 4 | pCsE |
|
| A / 5 | pCk1_spacer |
|
| A / 6 | pCk2_spacer |
|
| A / 7 | pCk3_spacer |
|
| A / 8 | pCk4_spacer |
|
| A / 9 | pCsA_spacer |
|
| A / 10 | pCsB_spacer |
|
| A / 11 | pCsC_spacer |
|
| A / 12 | pCsE_spacer |
|
| B / 1 | pUAP4 |
|
| B / 2 | CDS_nptII |
|
| B / 3 | CDS_mALS |
|
| B / 4 | CDS_hptII |
|
| B / 5 | CDS_GUS |
|
| B / 6 | CDS12_mScarlet-I |
|
| B / 7 | CDS12_mScarletI-linker |
|
| B / 8 | CDS12_mTurquoise2 |
|
| B / 9 | CDS12_mTurquoise2-linker |
|
| B / 10 | CDS12_mVenus |
|
| B / 11 | CDS12_mVenus-linker |
|
| B / 12 | CDS12_TP-MpSIG2 |
|
| C / 1 | CDS12-MpER-Targ |
|
| C / 2 | CTAG_linker-Lti6b |
|
| C / 3 | CTAG_linker-mTurquoise2 |
|
| C / 4 | CTAG_linker-mVenus |
|
| C / 5 | CTAG_linker-N7 |
|
| C / 6 | CTAG_mScarlet-I |
|
| C / 7 | CTAG_mTurquoise2 |
|
| C / 8 | CTAG_mTurquoise2-HDEL |
|
| C / 9 | CTAG_mVenus |
|
| C / 10 | CTAG_mVenus-HDEL |
|
| C / 11 | CTAG_NLS-SV40 |
|
| C / 12 | PROM_MpUBE2 |
|
| D / 1 | 5UTR_MpUBE2 |
|
| D / 2 | PROM5_35S |
|
| D / 3 | PROM5_35Sx2 |
|
| D / 4 | PROM5_MpEF1a |
|
| D / 5 | 3TERM_35S |
|
| D / 6 | 3TERM_Nos |
|
| D / 7 | 3TERM_Nos-35S |
|
| D / 8 | PROM_MpNOP1 |
|
| D / 9 | 5UTR_MpNOP1 |
|
| D / 10 | 3TERM_MpNOP1 |
|
| D / 11 | L1_KanR-Ck1 |
|
| D / 12 | L1_CsR-Ck1 |
|
| E / 1 | L1_HyR-Ck1 |
|
| E / 2 | L1_NOP1:mS-N7-Ck2 |
|
| E / 3 | L1_UBE2:mT-N7-Ck2 |
|
| E / 4 | L1_UBE2:mT-N7-Ck3 |
|
| E / 5 | L1_UBE2:mS-Lt-Ck3 |
|
| E / 6 | L1_UBE2:mS-Lt-Ck4 |
|
| E / 7 | L2_UBE2:mT-N7-CsA |
|
| E / 8 | pCk1chlo |
|
| E / 9 | pCk2chlo |
|
| E / 10 | pCk3chlo |
|
| E / 11 | pCk4chlo |
|
| E / 12 | pCsAchlo |
|
| F / 1 | pCsBchlo |
|
| F / 2 | pCsCchlo |
|
| F / 3 | pCsEchlo |
|
| F / 4 | PROM_Ntpsba_chlo |
|
| F / 5 | PROM5_Mprnpo_chlo |
|
| F / 6 | PROM5_Ntprrn_rev_chlo |
|
| F / 7 | PROM5_Ntpsba_chlo |
|
| F / 8 | PROM5_MprbcL_short_chlo |
|
| F / 9 | 3TERM_bba_b0015_rev_chlo |
|
| F / 10 | 3TERM_Ntpsba_rev_chlo |
|
| F / 11 | 5UTR_Mppetb_short_chlo |
|
| F / 12 | 5UTR_Mprbcl_chlo |
|
| G / 1 | CDS_aadA_chlo |
|
| G / 2 | CDS_mTurqcp_chlo |
|
| G / 3 | L1-Ck1-hs1-l-chlo |
|
| G / 4 | L1-Ck1-hs2-l-chlo |
|
| G / 5 | L1-Ck2-smR-chlo |
|
| G / 6 | L1-Ck4-hs1-r-chlo |
|
| G / 7 | L1-Ck4-hs2-r-chlo |
|
Kit Plate Map - #1000000272
Accessory Plasmids
Additional DNA parts plasmids are available from the Jim Haseloff lab. These plasmids are not included in the kit, but can be ordered separately:
- #136083: CDS_LUC
- #136085: CDS12_eGFP
- #136086: CDS12_eGFP-linker
- #136095: CTAG_eGFP
- #136096: CTAG_eGFP-GHtag-HDEL
- #136097: CTAG_eGFP-HDEL
- #136098: CTAG_linker-eGFP
- #136120: PROM5_MpU6
- #136121: CDS_Cas9-NLS
- #136122: CDS12_Cas9-NLS
- #136129: L1_UBE2:eG-Lt-Ck3
- #136130: L1_UBE2:eG-Lt-Ck4
- #136134: L2_UBE2:eG-Lt-CsA
- #136135: L1_Cas9-Ck4
- #136136: L1_lacZgRNA-Ck3
- #136137: L1_lacZgRNA-Ck2
- #136138: L2_lacZgRNA-Cas9-CsA
- #136139: L2_NOP1gRNA-Cas9-CsA
- #136140: L2_2xNOP1gRNA-Cas9-CsA
Additional acceptor plasmids are available from the Nicola Patron lab. These plasmids are not included in the kit, but can be ordered separately:


