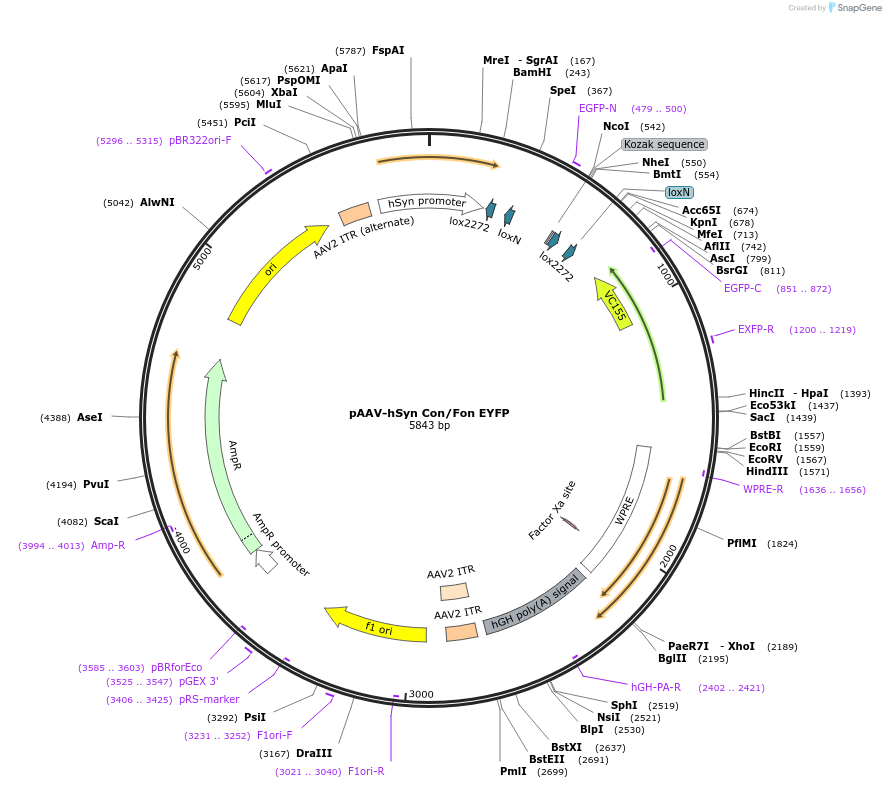
-
PurposeCre-on/Flp-on EYFP under the Synapsin promoter
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 55650 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
| AAV8 | 55650-AAV8 | Virus (100 µL at titer ≥ 1×10¹³ vg/mL) and Plasmid. | $405 | ||
| AAV Retrograde | 55650-AAVrg | Virus (100 µL at titer ≥ 7×10¹² vg/mL) and Plasmid. | $405 | ||

Don’t see the serotype you want?
Make a packaging request and we'll get back to you.
Please log in to submit a packaging request.
-
SerotypeSelect serotype for details See details about
-
PricingSelect serotype and quantity $ USD for preparation of µL virus + $30 USD for plasmid.
-
How this works
- Place a request for a quantity of 10 (1 mL), 25 (2.5 mL), or 50 (5 mL). Our all-inclusive pricing includes DNA production and QC.
- Addgene will quickly confirm that we can produce a high-quality prep for you.
- Track your request and place an order from within your account. Payment information must be added before we can begin processing your order.
- Receive your prep in 6–9 weeks after the MTA is approved by your organization.
- Learn more about our Packaged on Request Service.
Backbone
-
Vector backboneAAV
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 4536
- Total vector size (bp) 5854
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, AAV ; Cre on/Flp on eYFP
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert nameeYFP with introns
-
SpeciesSynthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)1310
- Promoter hSyn
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site BamHI (not destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site EcoRI (not destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer ccacgcgaggcgcgagatag
- 3′ sequencing primer GCAATAGCATGATACAAAGG (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Information for AAV8 (Catalog # 55650-AAV8) ( Back to top)
Purpose
Ready-to-use AAV8 particles produced from pAAV-hSyn Con/Fon EYFP (#55650). In addition to the viral particles, you will also receive purified pAAV-hSyn Con/Fon EYFP plasmid DNA.
Synapsin driven, Cre and Flp-dependent EYFP expression. These AAV preparations are suitable purity for injection into animals.Delivery
- Volume 100 µL
- Titer ≥ 1×10¹³ vg/mL
- Pricing $375 USD for preparation of 100 µL virus + $30 USD for plasmid.
- Storage Store at -80℃. Thaw just before use and keep on ice.
- Shipment Viral particles are shipped frozen on dry ice. Plasmid DNA (≥ 200ng) will also be included in the shipment.
Viral Production & Use
- Packaging Plasmids encode adenoviral helper sequences and AAV rep gene, AAV8 cap gene
- Buffer PBS + 0.001% Poloxamer 188
- Serotype AAV8
- Purification Iodixanol gradient ultracentrifugation
- Reporter Gene EYFP (Cre- and Flp-dependent)
Biosafety
Requestor is responsible for compliance with their institution's biosafety regulations. Lentivirus is generally considered BSL-2. AAV is generally considered BSL-1, but may require BSL-2 handling depending on the insert. Biosafety Guide
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Viral Quality Control
- Addgene ensures high quality viral vectors by optimizing and standardizing production protocols and performing rigorous quality control (QC) (see a list of our QC assays). The specific QC assays performed varies for each viral lot. To learn which specific QC assays were performed on your lot, please contact us.
- Titer: the exact titer of your sample will be reported on the tube. The titer you see listed on this page is the guaranteed minimum titer. See how titers are measured.
Visit our viral production page for more information.
Addgene Comments
Using FLEX vectors in vivo: LoxP sites in FLEX plasmids are known to recombine during DNA amplification and viral vector production, which may result in a minority of Cre-activated (i.e., "flipped") viral vectors. Addgene has measured this occurs in 0.1-0.8% of viral particles in our typical production protocol. This can lead to a small number of cells exhibiting Cre-independent transgene expression in vivo. To address this, it is necessary to optimize the injection volume and viral titer to find the optimal AAV dosage required for Cre-dependent transgene expression and function in vivo. This may include reducing the viral particle dosage in order to reduce the likelihood of Cre-independent expression.
Information for AAV Retrograde (Catalog # 55650-AAVrg) ( Back to top)
Purpose
Ready-to-use AAV Retrograde particles produced from pAAV-hSyn Con/Fon EYFP (#55650). In addition to the viral particles, you will also receive purified pAAV-hSyn Con/Fon EYFP plasmid DNA.
Synapsin driven, Cre and Flp-dependent EYFP expression. These AAV were produced with a retrograde serotype, which permits retrograde access to projection neurons. These AAV preparations are suitable purity for injection into animals.Delivery
- Volume 100 µL
- Titer ≥ 7×10¹² vg/mL
- Pricing $375 USD for preparation of 100 µL virus + $30 USD for plasmid.
- Storage Store at -80℃. Thaw just before use and keep on ice.
- Shipment Viral particles are shipped frozen on dry ice. Plasmid DNA (≥ 200ng) will also be included in the shipment.
Viral Production & Use
- Packaging Plasmids encode adenoviral helper sequences and AAV rep gene, AAV retrograde cap gene from rAAV2-retro helper (plasmid #81070)
- Buffer PBS + 0.001% Poloxamer 188 + 200 mM NaCl
- Serotype AAV retrograde (AAVrg)
- Purification Iodixanol gradient ultracentrifugation
- Reporter Gene EYFP (Cre- and Flp-dependent)
Biosafety
Requestor is responsible for compliance with their institution's biosafety regulations. Lentivirus is generally considered BSL-2. AAV is generally considered BSL-1, but may require BSL-2 handling depending on the insert. Biosafety Guide
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Viral Quality Control
- Addgene ensures high quality viral vectors by optimizing and standardizing production protocols and performing rigorous quality control (QC) (see a list of our QC assays). The specific QC assays performed varies for each viral lot. To learn which specific QC assays were performed on your lot, please contact us.
- Titer: the exact titer of your sample will be reported on the tube. The titer you see listed on this page is the guaranteed minimum titer. See how titers are measured.
Visit our viral production page for more information.
Addgene Comments
Retrograde functionality is dependent on high viral titers. Addgene recommends not diluting your AAV preps prior to use.Using FLEX vectors in vivo: LoxP sites in FLEX plasmids are known to recombine during DNA amplification and viral vector production, which may result in a minority of Cre-activated (i.e., "flipped") viral vectors. Addgene has measured this occurs in 0.1-0.8% of viral particles in our typical production protocol. This can lead to a small number of cells exhibiting Cre-independent transgene expression in vivo. To address this, it is necessary to optimize the injection volume and viral titer to find the optimal AAV dosage required for Cre-dependent transgene expression and function in vivo. This may include reducing the viral particle dosage in order to reduce the likelihood of Cre-independent expression.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pAAV-hSyn Con/Fon EYFP was a gift from Karl Deisseroth (Addgene plasmid # 55650 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:55650 ; RRID:Addgene_55650) For viral preps, please replace (Addgene plasmid # 55650) in the above sentence with: (Addgene viral prep # 55650-AAV8) or (Addgene viral prep # 55650-AAVrg) -
For your References section:
Targeting cells with single vectors using multiple-feature Boolean logic. Fenno LE, Mattis J, Ramakrishnan C, Hyun M, Lee SY, He M, Tucciarone J, Selimbeyoglu A, Berndt A, Grosenick L, Zalocusky KA, Bernstein H, Swanson H, Perry C, Diester I, Boyce FM, Bass CE, Neve R, Huang ZJ, Deisseroth K. Nat Methods. 2014 Jul;11(7):763-72. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2996. Epub 2014 Jun 8. 10.1038/nmeth.2996 PubMed 24908100