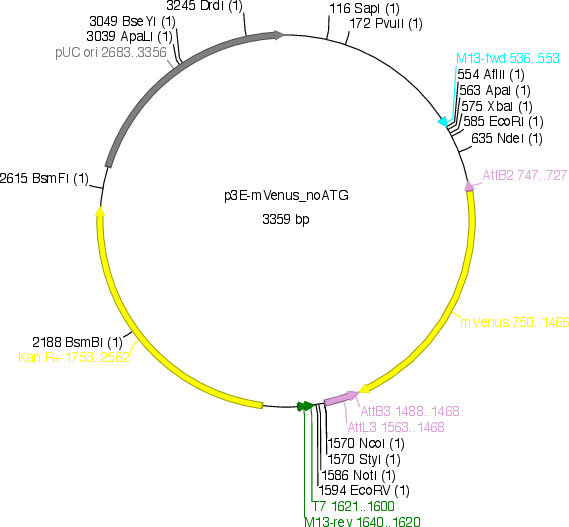
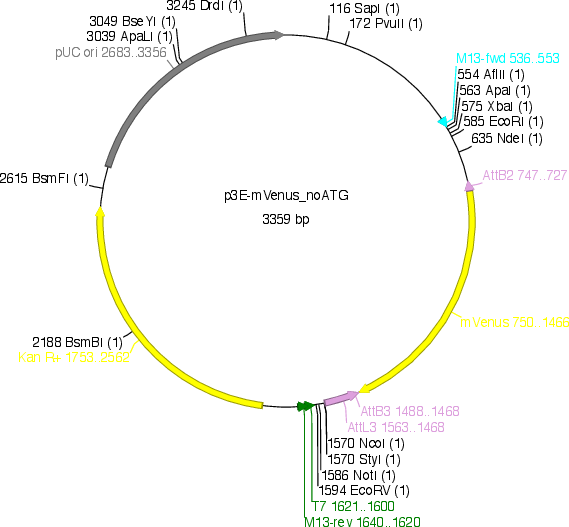
p3E-mVenus
(Plasmid
#67719)
-
PurposeMultisite gateway entry clone for adding C-terminal fusions of mVenus (no ATG)
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 67719 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepDONR P2R-p3
-
Backbone manufacturerInvitrogen
-
Vector typeGateway multisite 3' entry clone
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Kanamycin, 50 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)DH5alpha
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
Gene/Insert namemVenus
-
SpeciesSynthetic
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Gateway Cloning
- 5′ sequencing primer M13F
- 3′ sequencing primer M13R (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
Article Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
p3E-mVenus was a gift from Rob Parton (Addgene plasmid # 67719 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:67719 ; RRID:Addgene_67719) -
For your References section:
In vivo characterization of microglial engulfment of dying neurons in the zebrafish spinal cord. Morsch M, Radford R, Lee A, Don EK, Badrock AP, Hall TE, Cole NJ, Chung R. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Aug 31;9:321. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00321. eCollection 2015. 10.3389/fncel.2015.00321 PubMed 26379496