-
PurposeExpresses the DREADD receptor hM3Dq-mCherry under the control of tet-inducible promoter for use in TetTaging
-
Depositing Lab
-
Sequence Information
Ordering
| Item | Catalog # | Description | Quantity | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmid | 66795 | Standard format: Plasmid sent in bacteria as agar stab | 1 | $85 | |
Backbone
-
Vector backbonepUC
- Backbone size w/o insert (bp) 3000
- Total vector size (bp) 7159
-
Vector typeMammalian Expression, AAV
Growth in Bacteria
-
Bacterial Resistance(s)Ampicillin, 100 μg/mL
-
Growth Temperature37°C
-
Growth Strain(s)NEB Stable
-
Copy numberHigh Copy
Gene/Insert
-
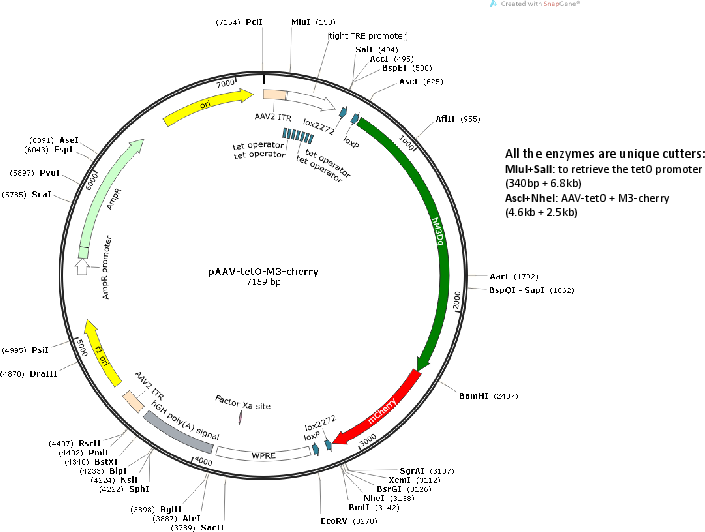
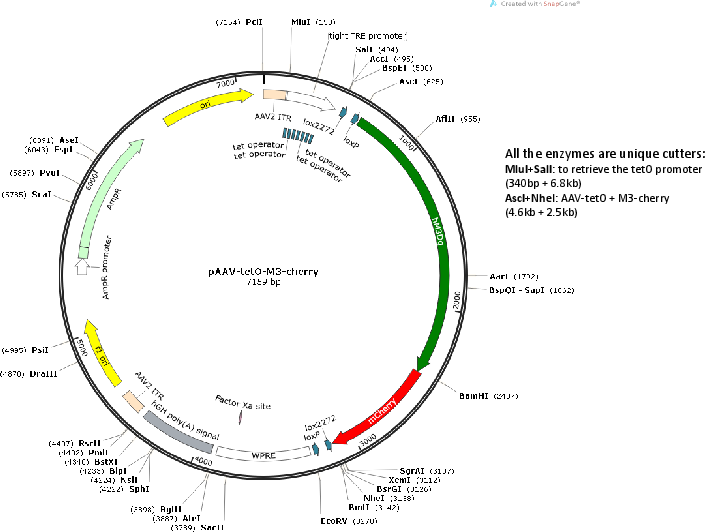
Gene/Insert namepTIGHT promoter-hM3Dq-mCherry
-
SpeciesSynthetic
-
Insert Size (bp)4400
- Promoter pTIGHT TRE
Cloning Information
- Cloning method Restriction Enzyme
- 5′ cloning site MluI (unknown if destroyed)
- 3′ cloning site NheI (unknown if destroyed)
- 5′ sequencing primer Tggaaagagaactgtgcctc
- 3′ sequencing primer Cagttcatgtacggctccaag (Common Sequencing Primers)
Resource Information
-
A portion of this plasmid was derived from a plasmid made byBrian Roth provided the hM3Dq-mCherry gene
-
Articles Citing this Plasmid
Terms and Licenses
-
Academic/Nonprofit Terms
-
Industry Terms
- Not Available to Industry
Trademarks:
- Zeocin® is an InvivoGen trademark.
Depositor Comments
hM3Dq-mCherry reading frame was obtained from pAAV-hSyn-DIO-hM3D(Gq)-mCherry (Addgene plasmid #44361) and cloned in the sense orientation between the lox sites. Please see the associated publication for additional cloning details.
These plasmids were created by your colleagues. Please acknowledge the Principal Investigator, cite the article in which the plasmids were described, and include Addgene in the Materials and Methods of your future publications.
-
For your Materials & Methods section:
pAAV-PTRE-tight-hM3Dq-mCherry was a gift from William Wisden (Addgene plasmid # 66795 ; http://n2t.net/addgene:66795 ; RRID:Addgene_66795) -
For your References section:
Neuronal ensembles sufficient for recovery sleep and the sedative actions of alpha2 adrenergic agonists. Zhang Z, Ferretti V, Guntan I, Moro A, Steinberg EA, Ye Z, Zecharia AY, Yu X, Vyssotski AL, Brickley SG, Yustos R, Pillidge ZE, Harding EC, Wisden W, Franks NP. Nat Neurosci. 2015 Apr;18(4):553-61. doi: 10.1038/nn.3957. Epub 2015 Feb 23. 10.1038/nn.3957 PubMed 25706476