We narrowed to 8,684 results for: PAN
-
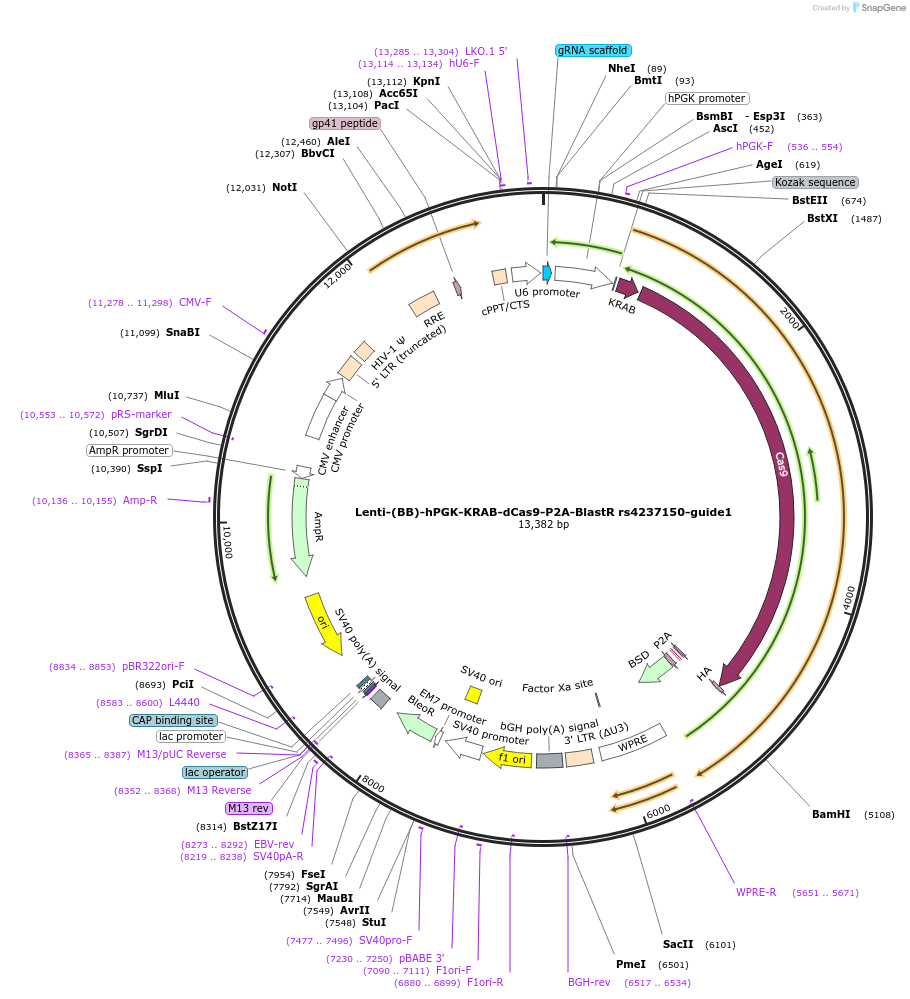
Plasmid#125397PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of human islet enhancer containing T1D/T2D-associated variant rs4237150 (GLIS3 GWAS locus)DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceJuly 23, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
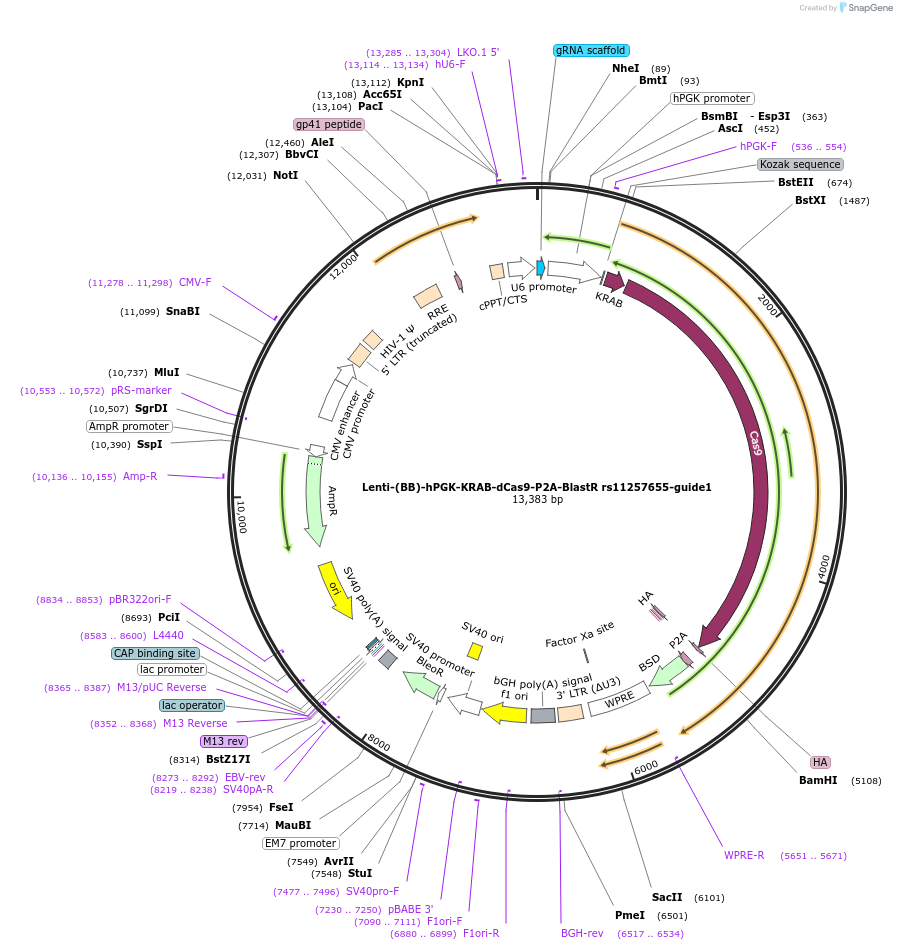
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR rs11257655-guide1
Plasmid#125393PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of human islet enhancer containing T2D-associated variant rs11257655 (CDC123/CAMK1D GWAS locus)DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceJuly 23, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
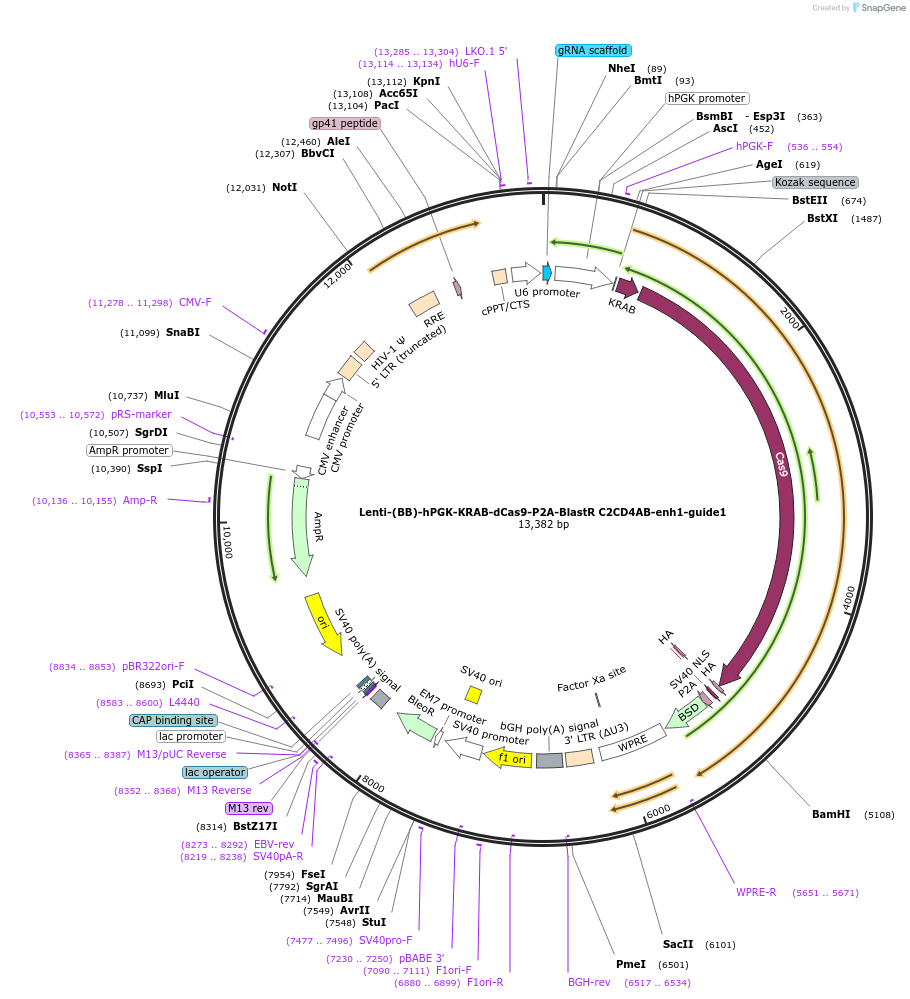
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR C2CD4AB-enh1-guide1
Plasmid#125400PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of human islet enhancer containing T2D-associated variant rs182222907 (C2CD4A/B GWAS locus)DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceJuly 9, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
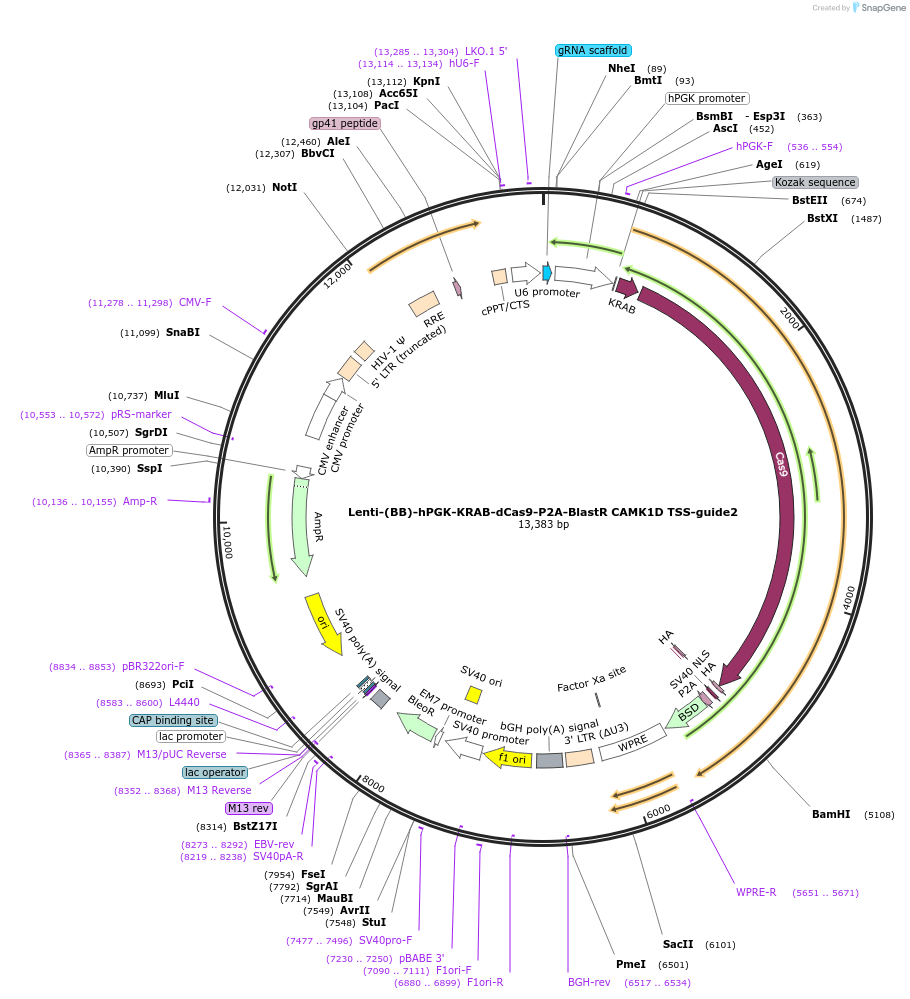
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR CAMK1D TSS-guide2
Plasmid#118178PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of CAMK1D. KRAB domain and catalytically inactive Cas9 from S. pyogenes with 2A-BlastR under the hPGK promoter.DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceJune 18, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
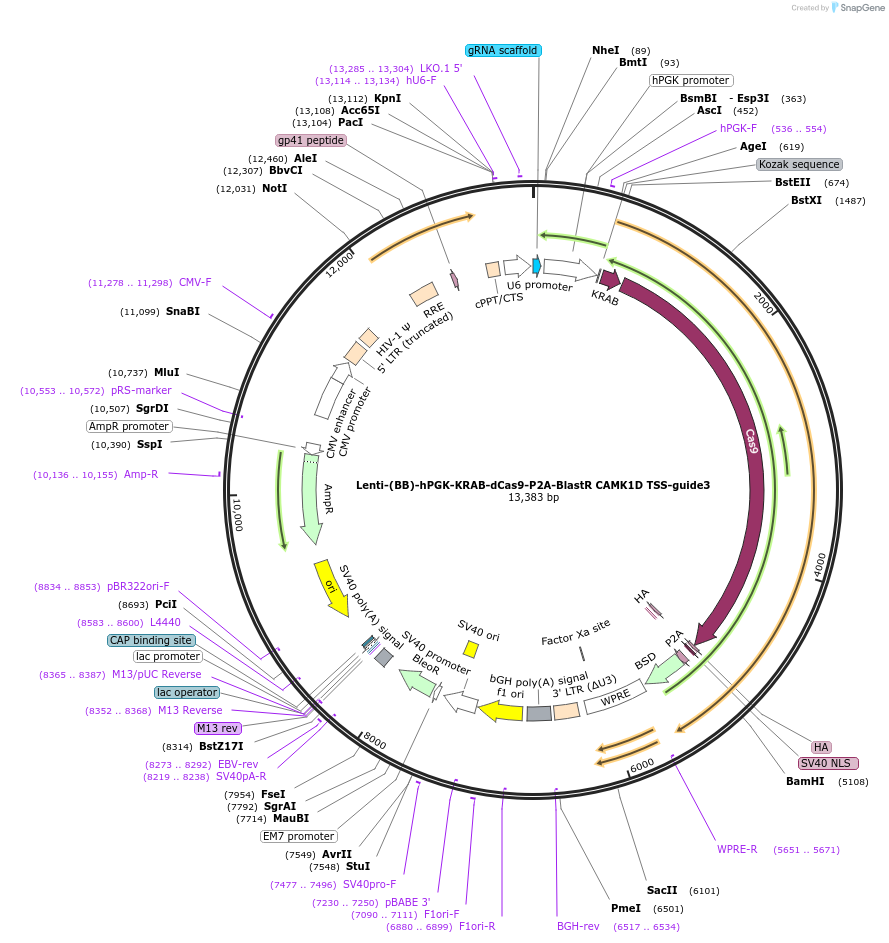
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR CAMK1D TSS-guide3
Plasmid#118179PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of CAMK1D. KRAB domain and catalytically inactive Cas9 from S. pyogenes with 2A-BlastR under the hPGK promoter.DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceApril 3, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
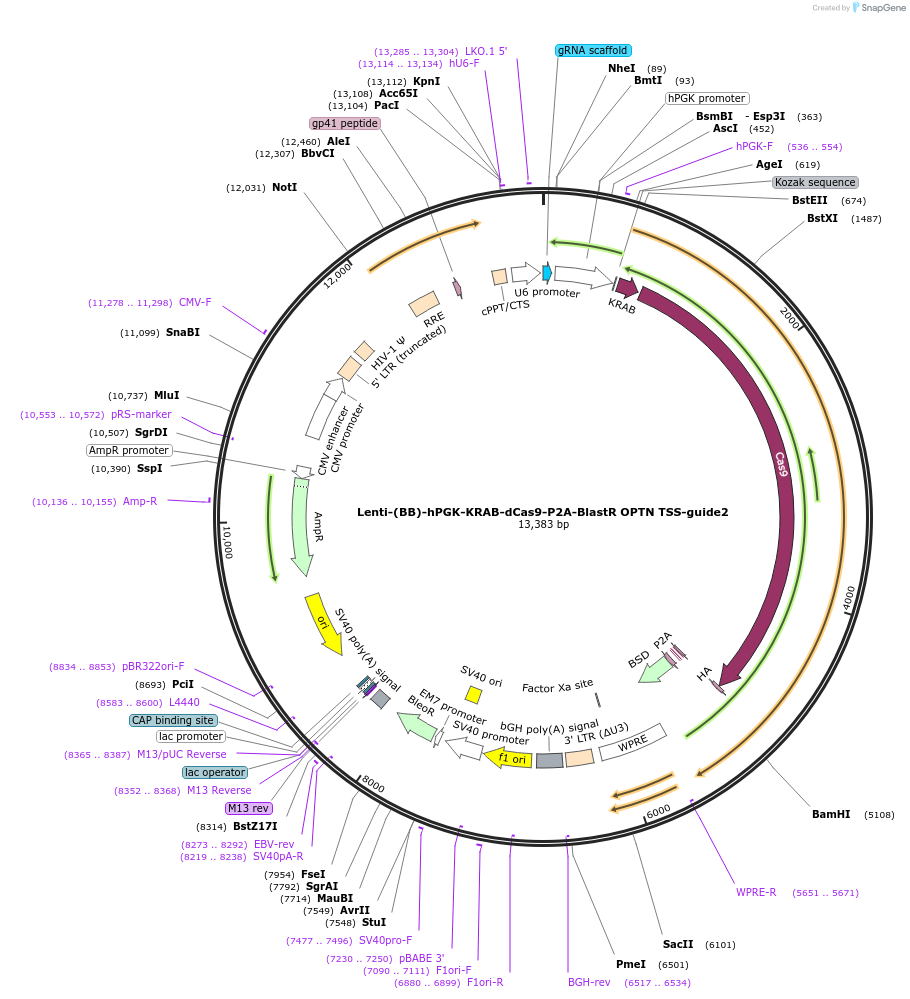
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR OPTN TSS-guide2
Plasmid#118182PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of OPTN. KRAB domain and catalytically inactive Cas9 from S. pyogenes with 2A-BlastR under the hPGK promoter.DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceApril 3, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
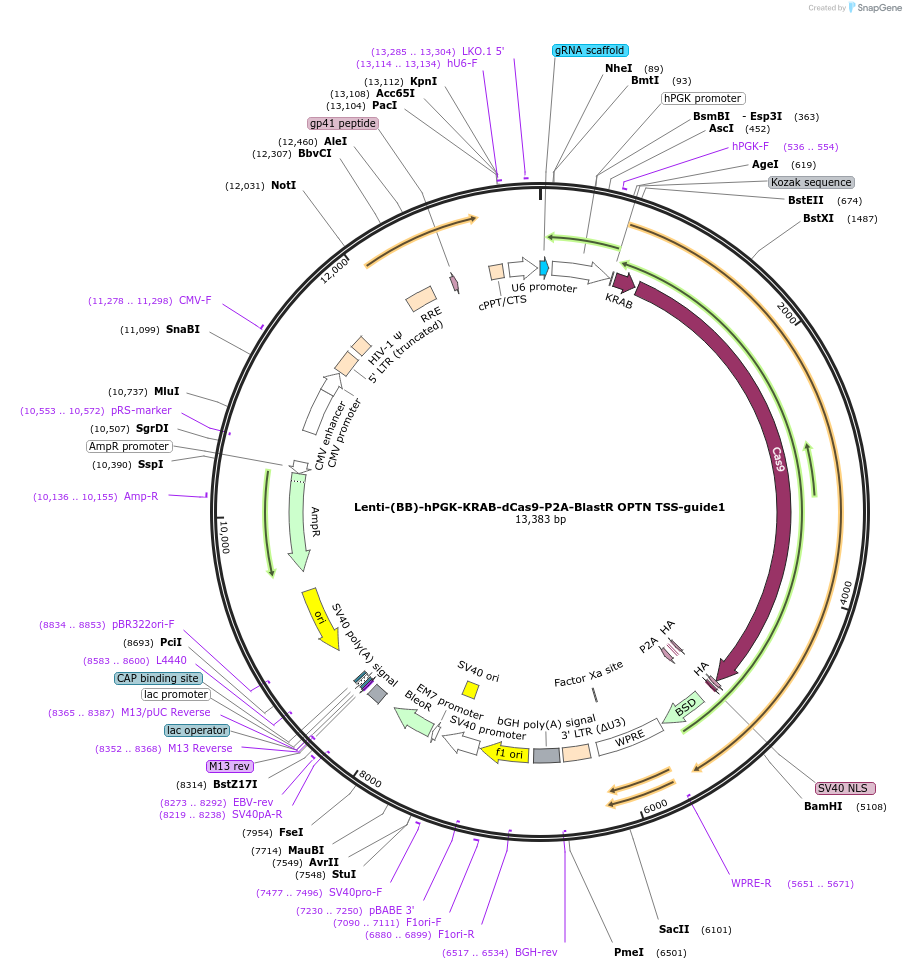
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR OPTN TSS-guide1
Plasmid#118181PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of OPTN. KRAB domain and catalytically inactive Cas9 from S. pyogenes with 2A-BlastR under the hPGK promoter.DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceApril 2, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
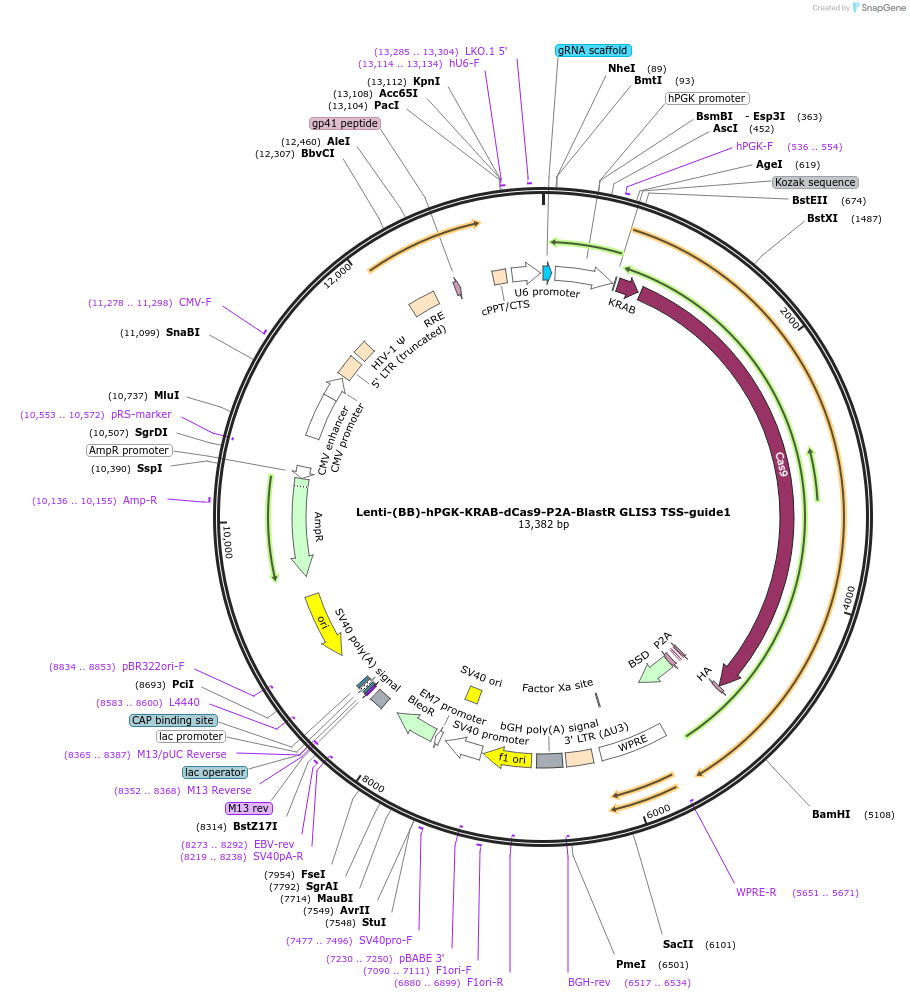
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR GLIS3 TSS-guide1
Plasmid#118173PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of GLIS3. KRAB domain and catalytically inactive Cas9 from S. pyogenes with 2A-BlastR under the hPGK promoter.DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceApril 2, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
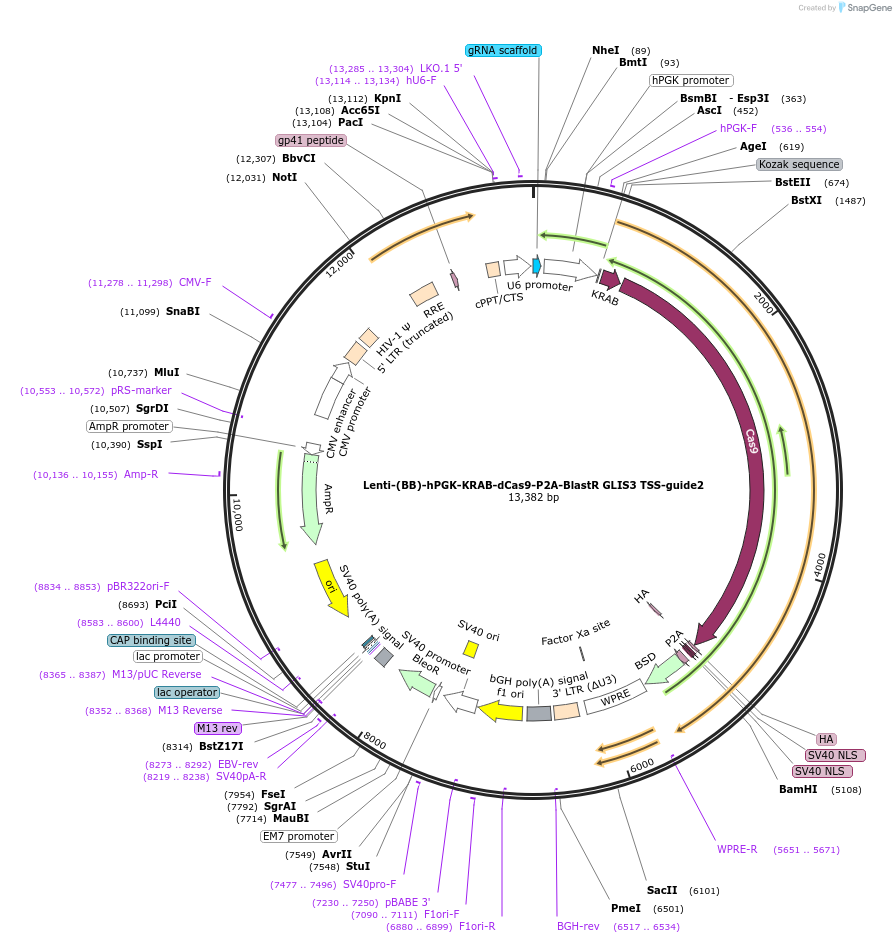
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR GLIS3 TSS-guide2
Plasmid#118174PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of GLIS3. KRAB domain and catalytically inactive Cas9 from S. pyogenes with 2A-BlastR under the hPGK promoter.DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceApril 2, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
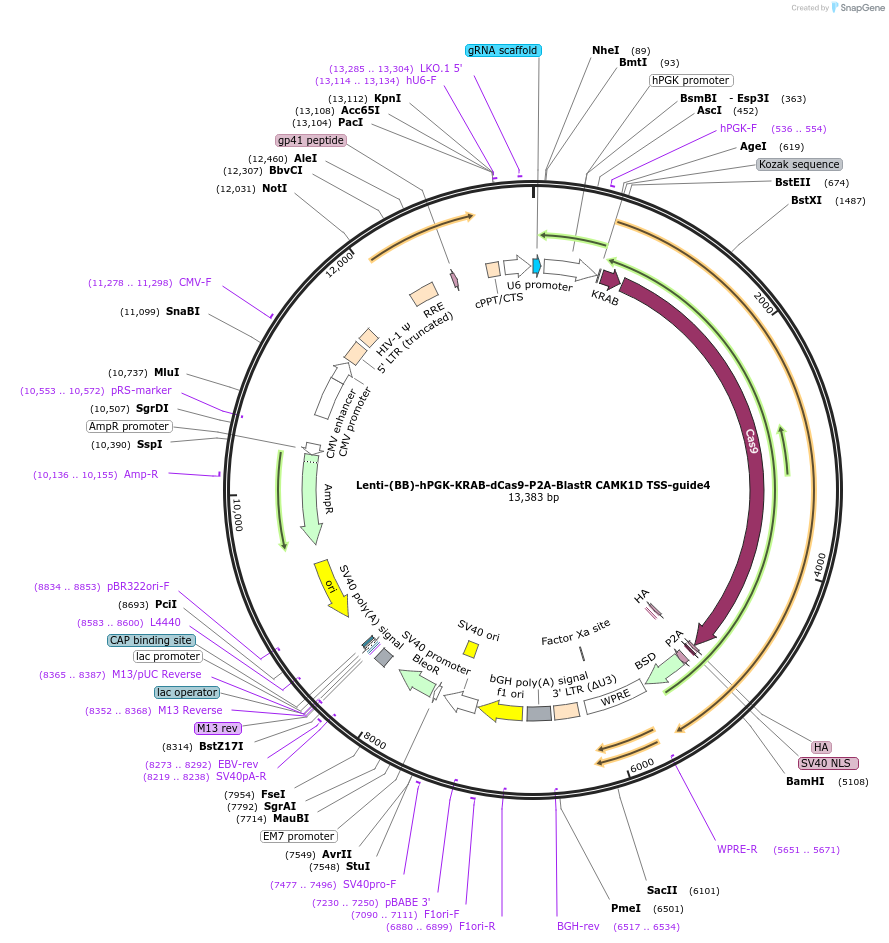
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR CAMK1D TSS-guide4
Plasmid#118180PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of CAMK1D. KRAB domain and catalytically inactive Cas9 from S. pyogenes with 2A-BlastR under the hPGK promoter.DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceApril 2, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
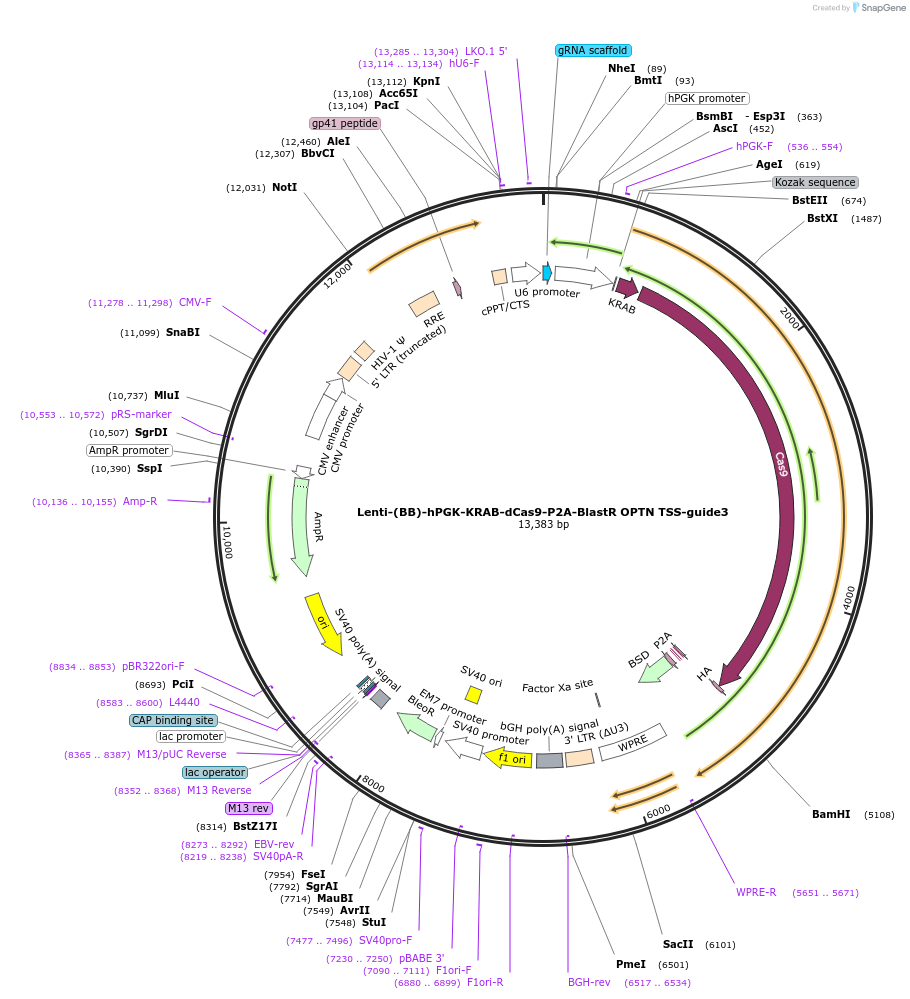
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR OPTN TSS-guide3
Plasmid#118183PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of OPTN. KRAB domain and catalytically inactive Cas9 from S. pyogenes with 2A-BlastR under the hPGK promoter.DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceApril 2, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
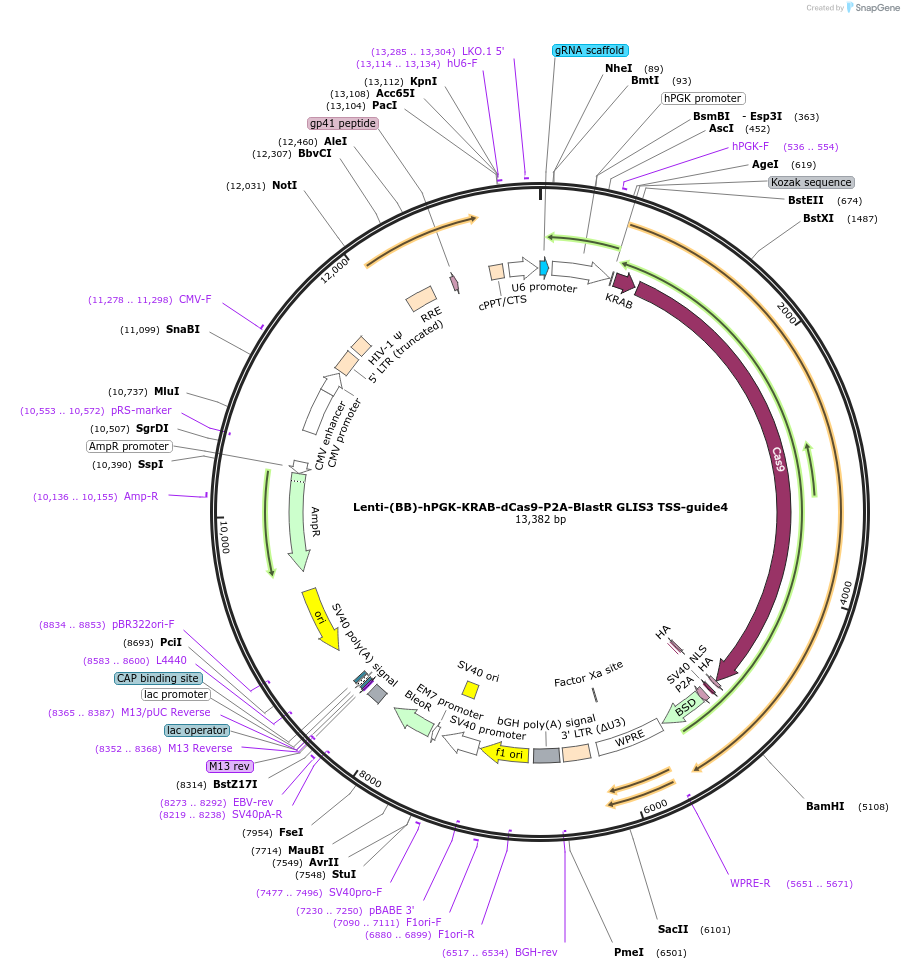
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR GLIS3 TSS-guide4
Plasmid#118176PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of GLIS3. KRAB domain and catalytically inactive Cas9 from S. pyogenes with 2A-BlastR under the hPGK promoter.DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceApril 2, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
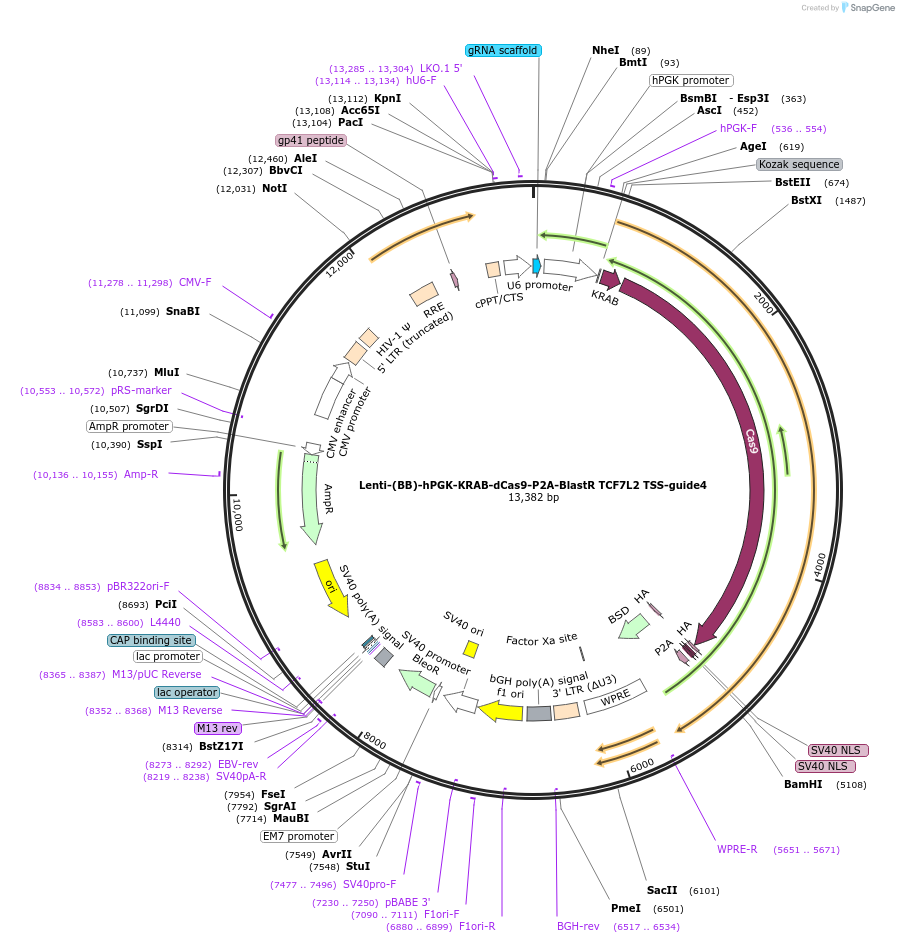
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR TCF7L2 TSS-guide4
Plasmid#118172PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of TCF7L2. KRAB domain and catalytically inactive Cas9 from S. pyogenes with 2A-BlastR under the hPGK promoter.DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceApril 2, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
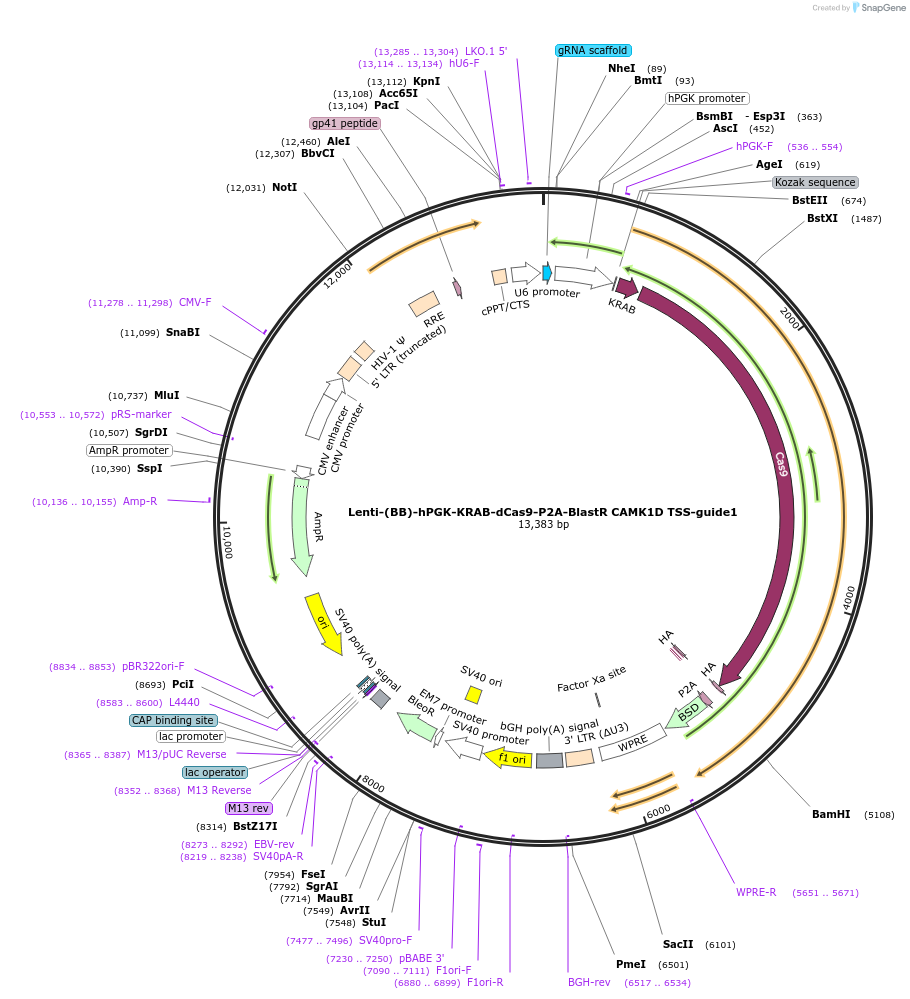
Lenti-(BB)-hPGK-KRAB-dCas9-P2A-BlastR CAMK1D TSS-guide1
Plasmid#118177PurposeCRISPR-mediated repression of CAMK1D. KRAB domain and catalytically inactive Cas9 from S. pyogenes with 2A-BlastR under the hPGK promoter.DepositorInsertKRAB-dCas9-2A-BlastR
UseCRISPR and LentiviralTagsHAExpressionMammalianPromoterhPGK and U6Available SinceApril 1, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
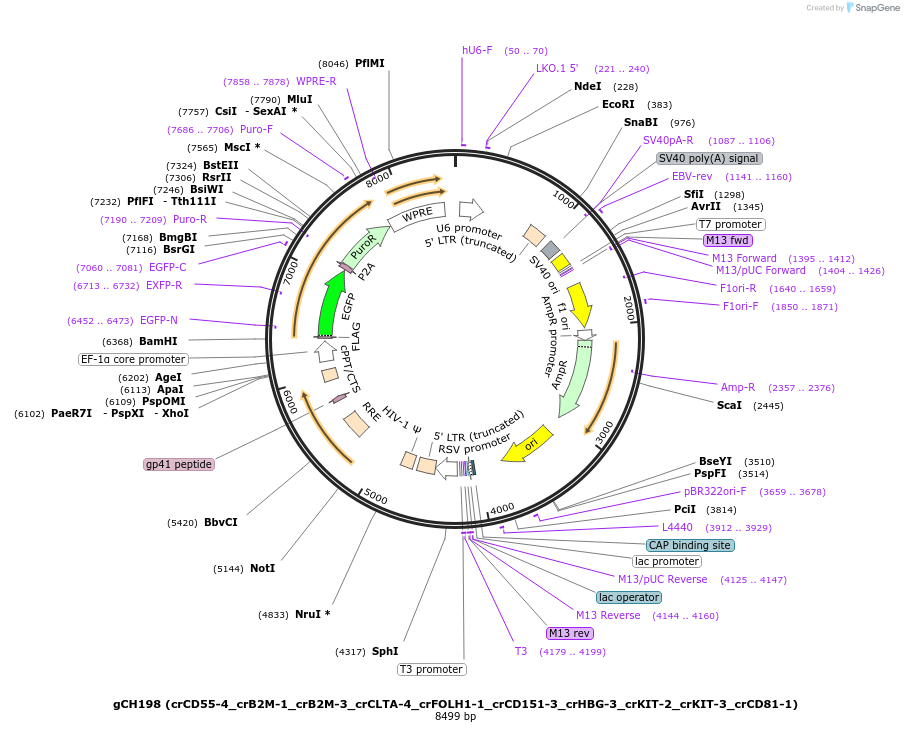
gCH198 (crCD55-4_crB2M-1_crB2M-3_crCLTA-4_crFOLH1-1_crCD151-3_crHBG-3_crKIT-2_crKIT-3_crCD81-1)
Plasmid#217345PurposecrRNA array targeting CD55, B2M, CLTA, FOLH1, CD151, HBG1/HBG2, KIT, CD81DepositorInsertscrCD55-4 gRNA: actggtattgcggagccacgagg (CD55 Human)
crB2M-1 gRNA: atataagtggaggcgtcgcgctg (B2M Human)
crB2M-3 gRNA: aggaatgcccgccagcgcgacgc (B2M Human)
crCLTA-4 gRNA: ggctctgcaacaccgcctagacc (CLTA Human)
crFOLH1-1 gRNA: gctccagacctggggtccagttt (FOLH1 Human)
crCD151-3 gRNA: cgggaggccgcacccaccgcctg (CD151 Human)
crHBG-3 gRNA: ttcttcatccctagccagccgcc (HBG1, HBG2 Human)
crKIT-2 gRNA: tctgcgttctgctcctactgctt (KIT Human)
crKIT-3 gRNA: agctctcgcccaagtgcagcgag (KIT Human)
crCD81-1 gRNA: ggcgcgacccccaggaaggtctc (CD81 Human)
UseCRISPR and LentiviralPromoterhU6Available SinceMarch 27, 2024AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
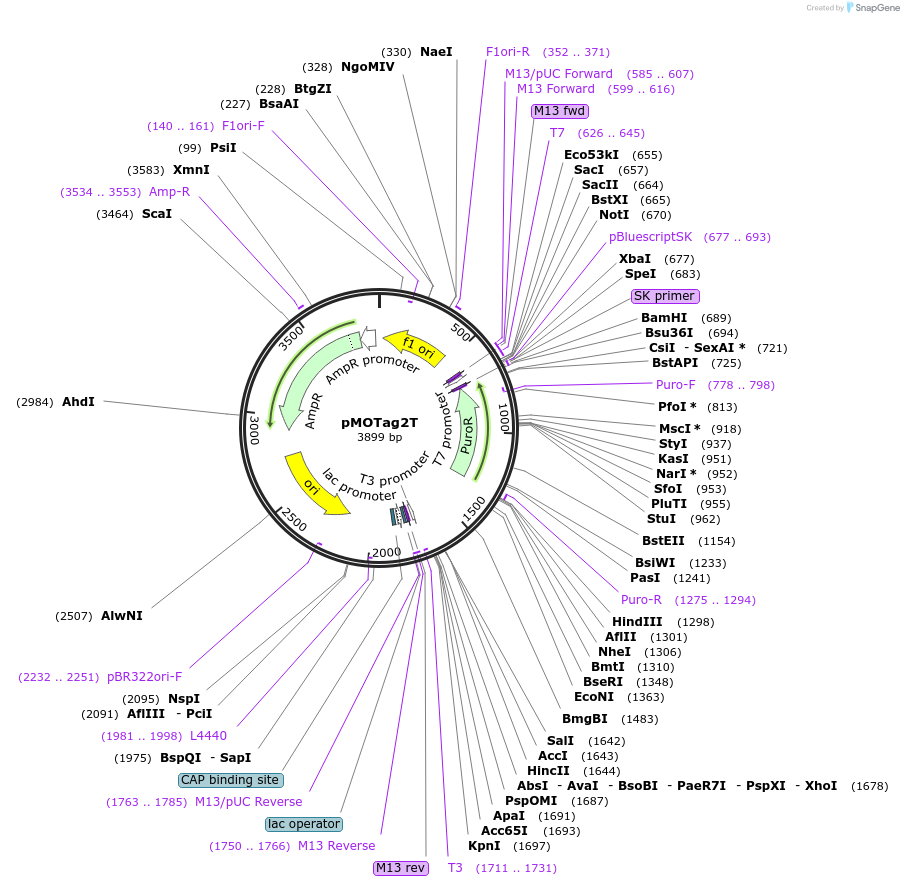
pMOTag2T
Plasmid#26295DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosome in-situ tagging vectorTagsTy-1Available SinceSept. 16, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
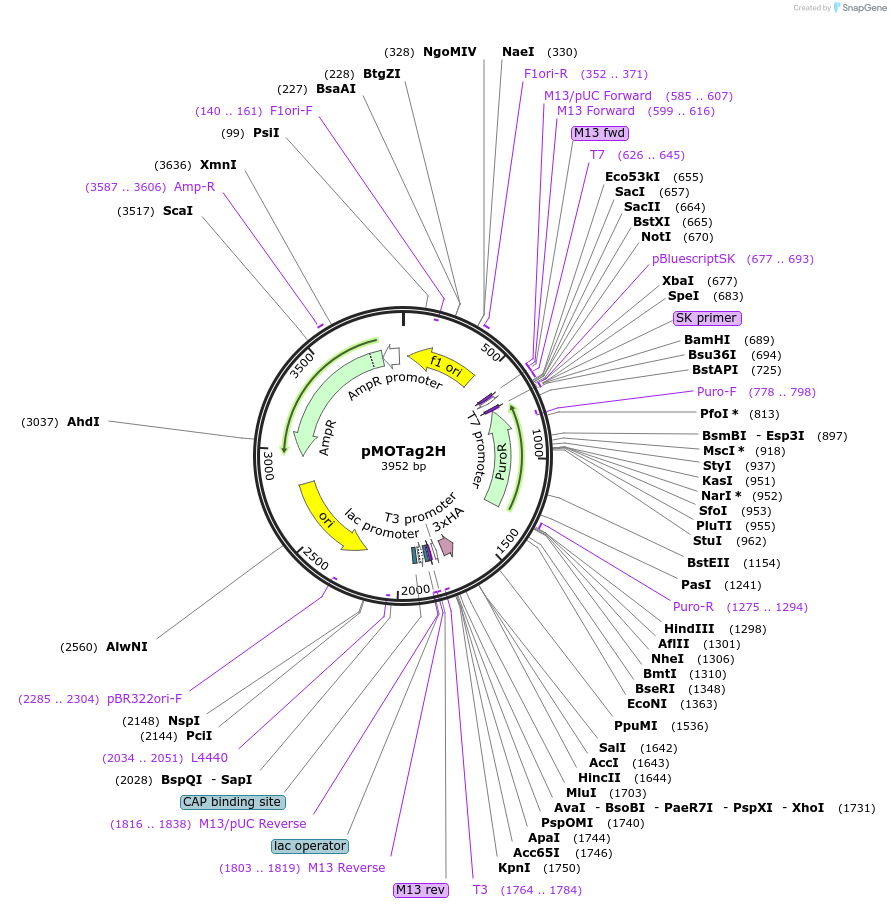
pMOTag2H
Plasmid#26296DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosome in-situ tagging vectorTagsTriple HAAvailable SinceSept. 16, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
pMOTag5H
Plasmid#26299DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosome in-situ tagging vectorTagstriple HAAvailable SinceSept. 16, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
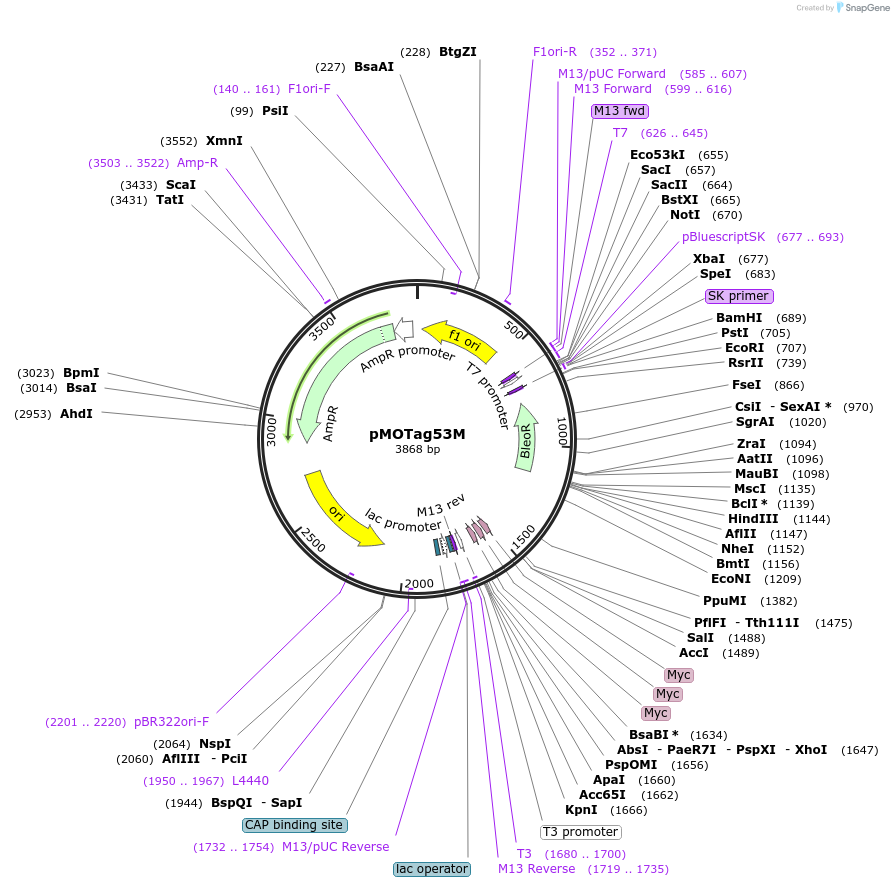
pMOTag53M
Plasmid#26297DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosome in-situ tagging vectorTagstriple cMycAvailable SinceSept. 16, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
ZM2
Plasmid#32784DepositorInsertT7rnap
UseCre/Lox; Floxed targeting vector for trypanosomeAvailable SinceDec. 13, 2011AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
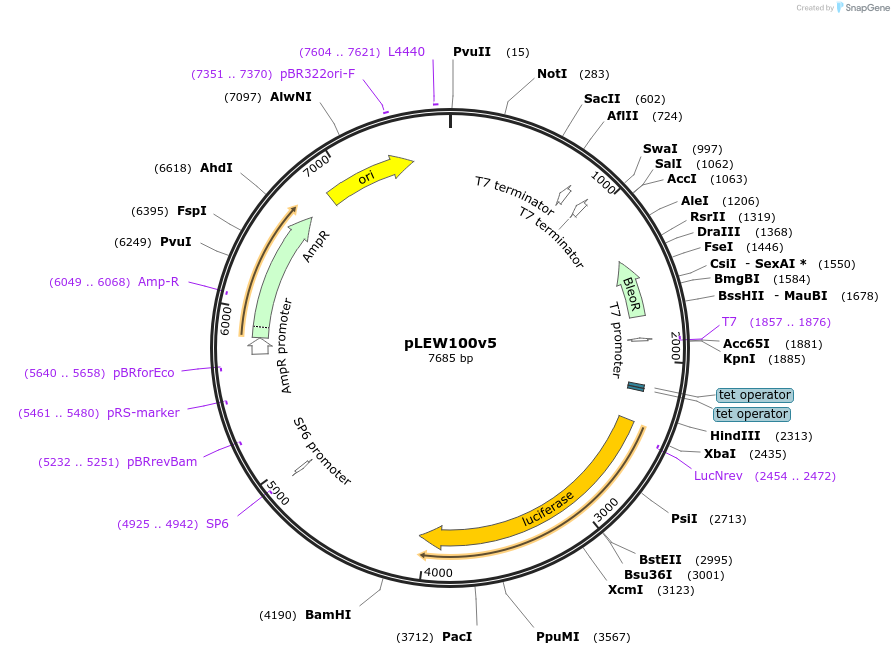
pLEW100v5
Plasmid#24011DepositorInsertLuciferase
UseTrypanosome expressionAvailable SinceFeb. 25, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
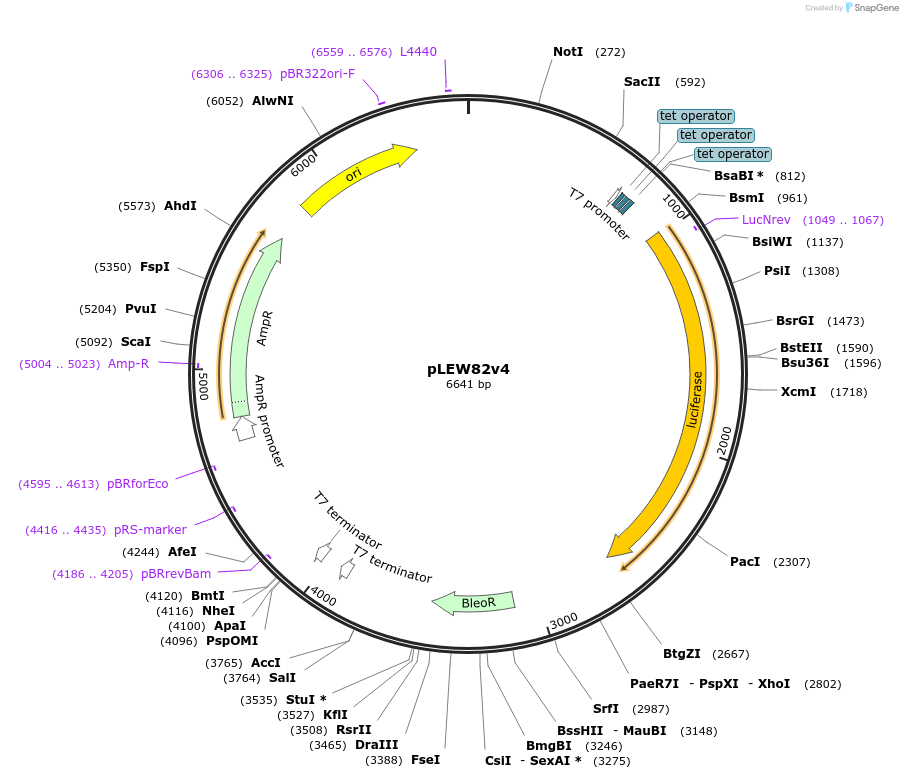
pLEW82v4
Plasmid#24009DepositorInsertLuciferase
UseTrypanosome expressionAvailable SinceApril 7, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
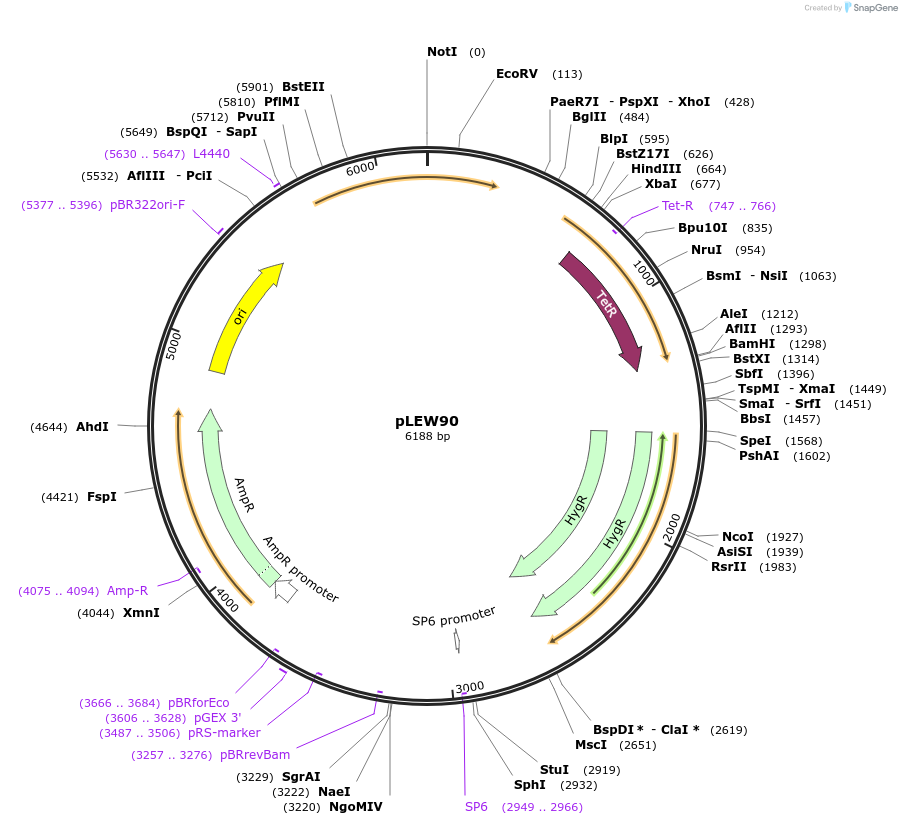
pLEW90
Plasmid#24008DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosome expressionAvailable SinceMay 11, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
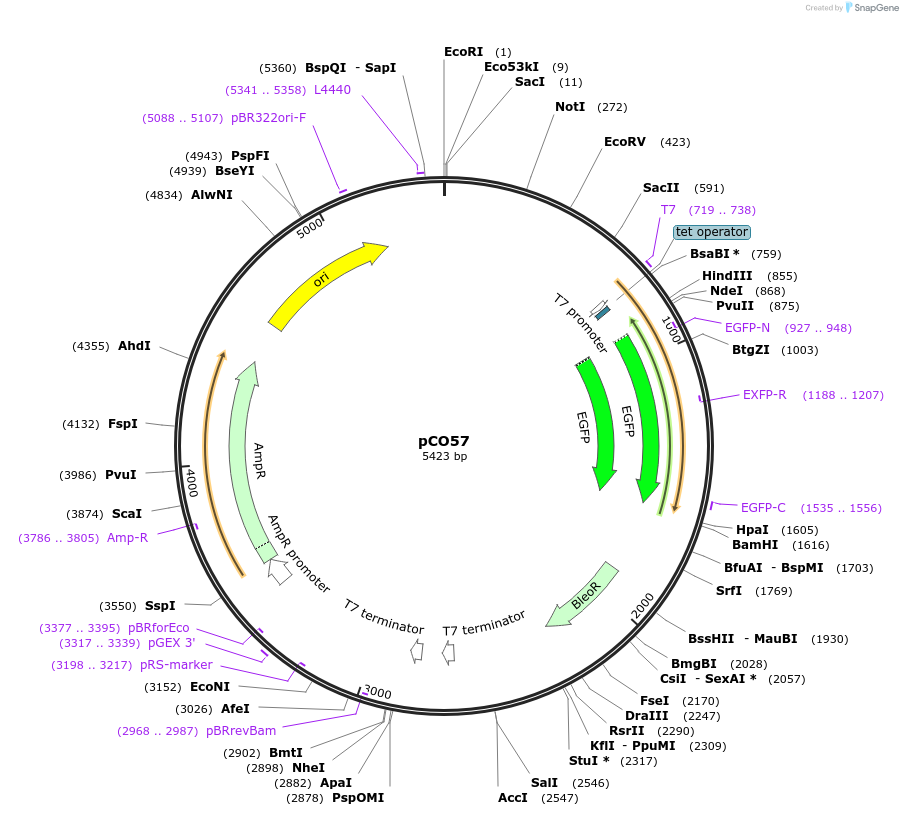
pCO57
Plasmid#24015DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosome expressionTagsEGFPAvailable SinceFeb. 25, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
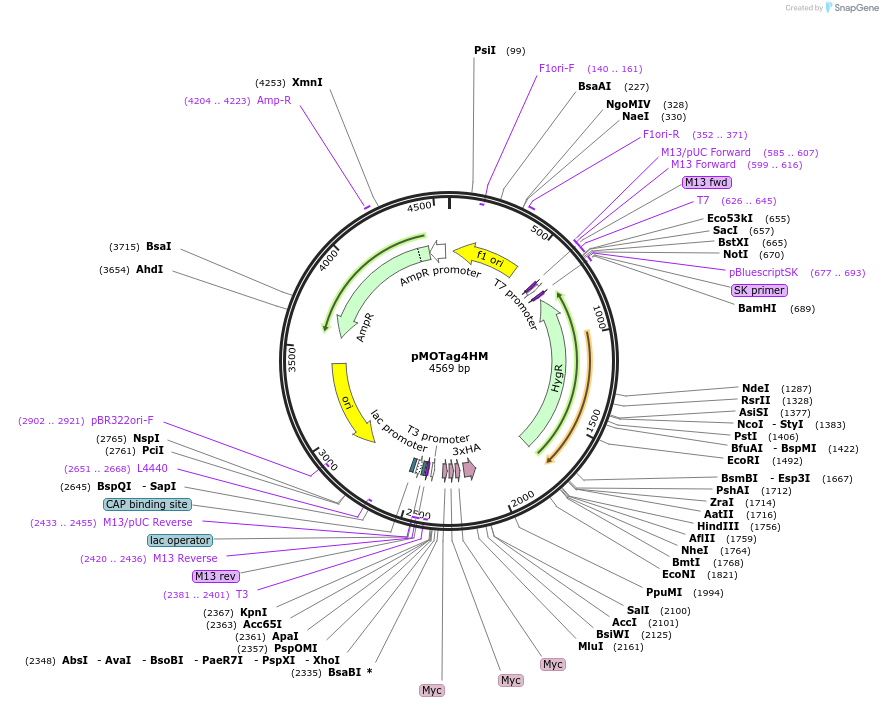
pMOTag4HM
Plasmid#26298DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosome in-situ tagging vectorTagstriple cMyc and triple HA in tandemAvailable SinceOct. 22, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
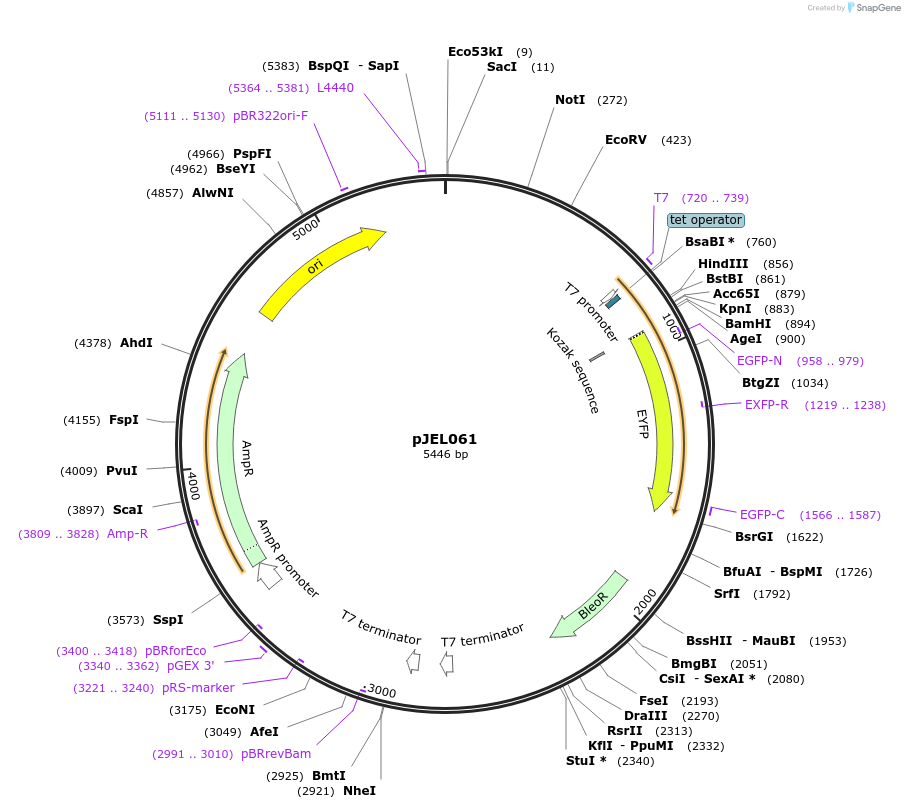
pJEL061
Plasmid#24016DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosome expressionTagsEYFPAvailable SinceFeb. 25, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
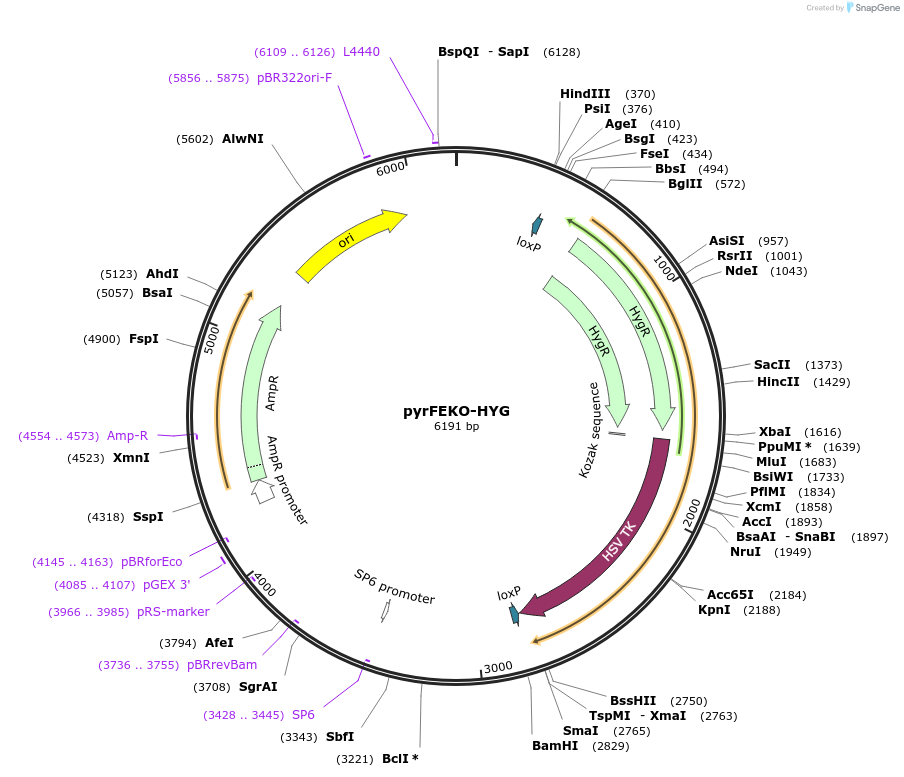
pyrFEKO-HYG
Plasmid#24020DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseFloxed targeting vector for trypanosomeAvailable SinceFeb. 25, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
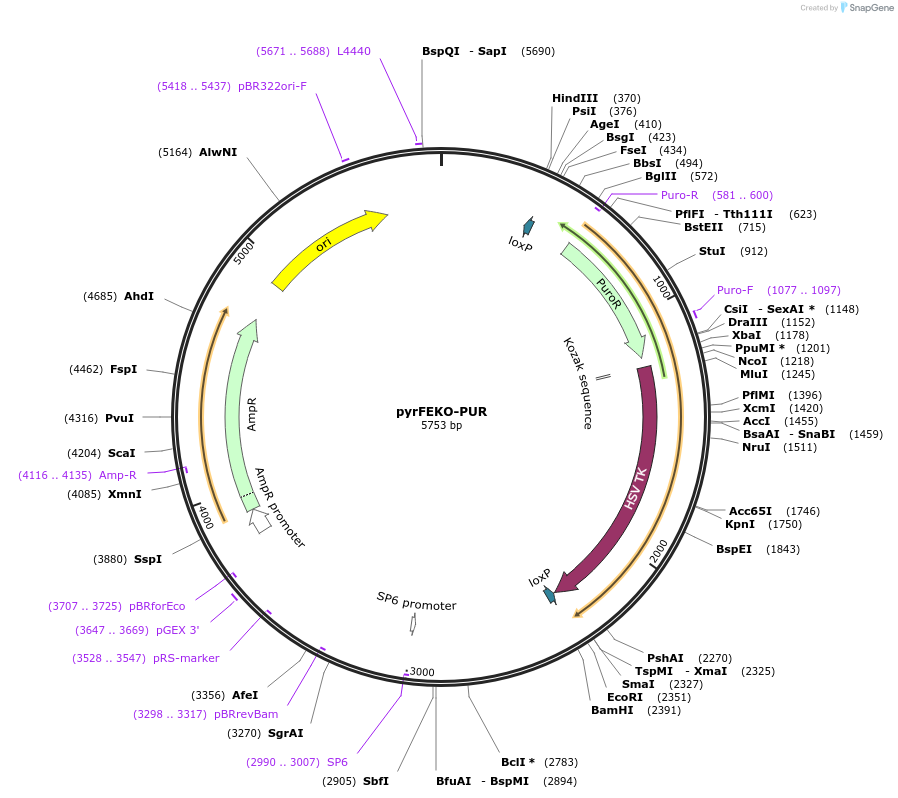
pyrFEKO-PUR
Plasmid#24021DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseFloxed targeting vector for trypanosomeAvailable SinceMay 11, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
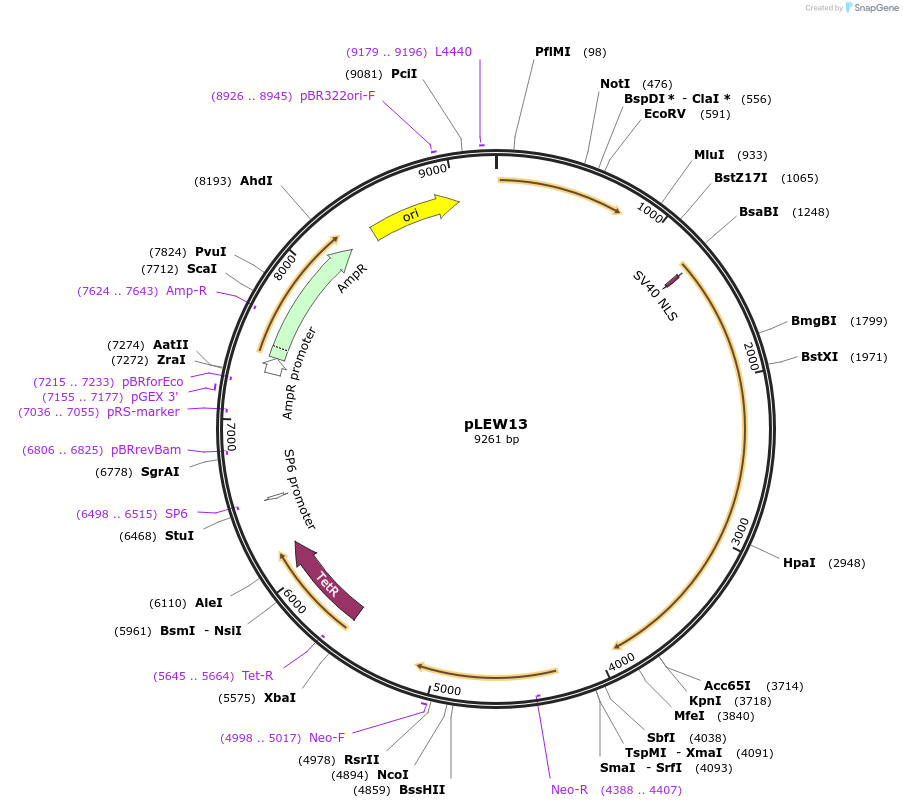
pLEW13
Plasmid#24007DepositorInsertT7 RNA Polymerase
UseTrypanosome expressionAvailable SinceMay 11, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
pLEW100V5-BSD
Plasmid#27658DepositorInsertBSD
UseTrypanosme expressionAvailable SinceAug. 19, 2011AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
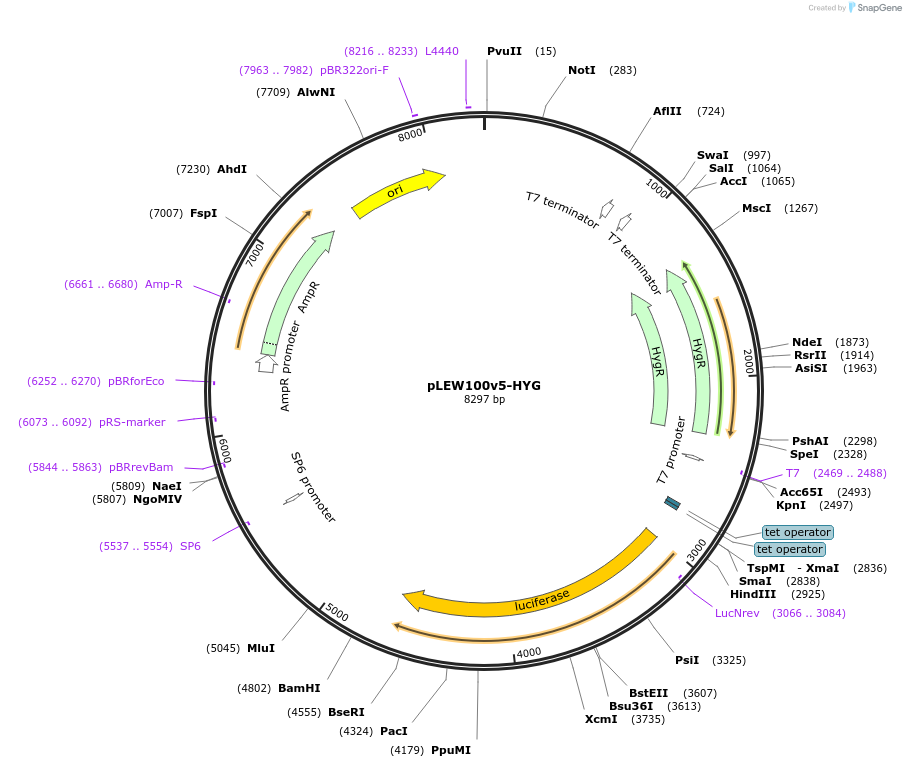
pLEW100v5-HYG
Plasmid#24012DepositorInsertLuciferase
UseTrypanosome expressionAvailable SinceMay 11, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
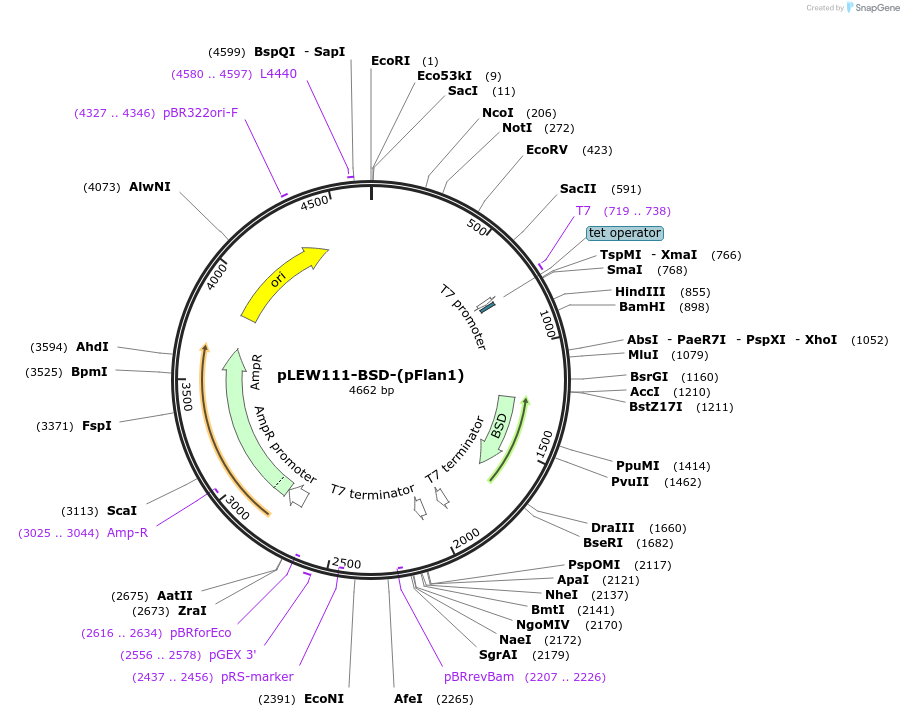
pLEW111-BSD-(pFlan1)
Plasmid#24010DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosome expressionAvailable SinceFeb. 25, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
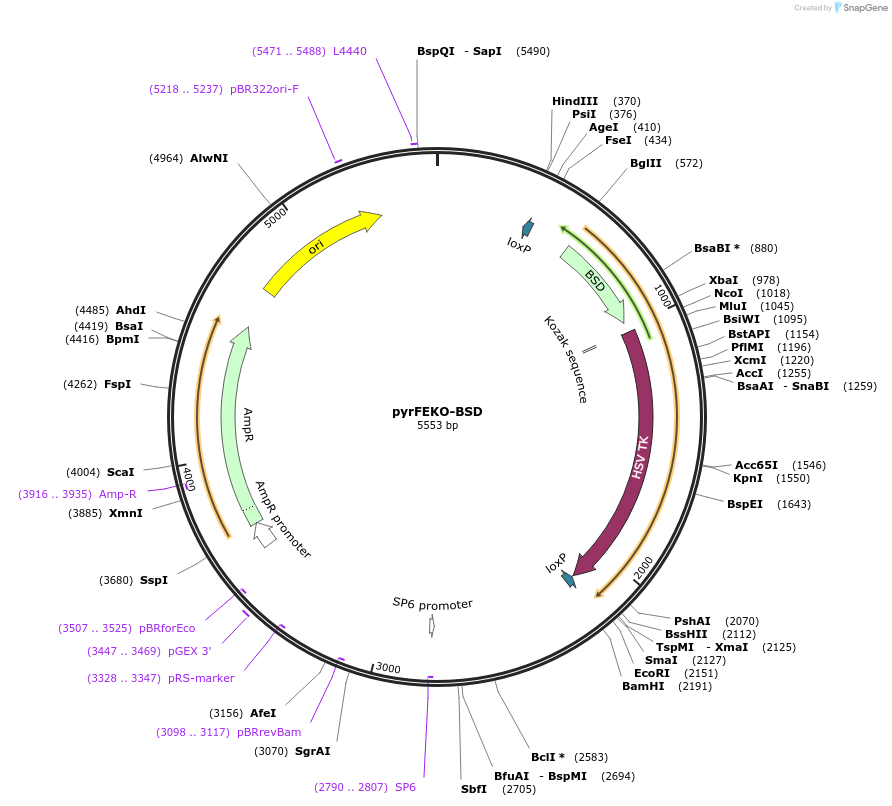
pyrFEKO-BSD
Plasmid#24024DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseFloxed targeting vector for trypanosomeAvailable SinceFeb. 25, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
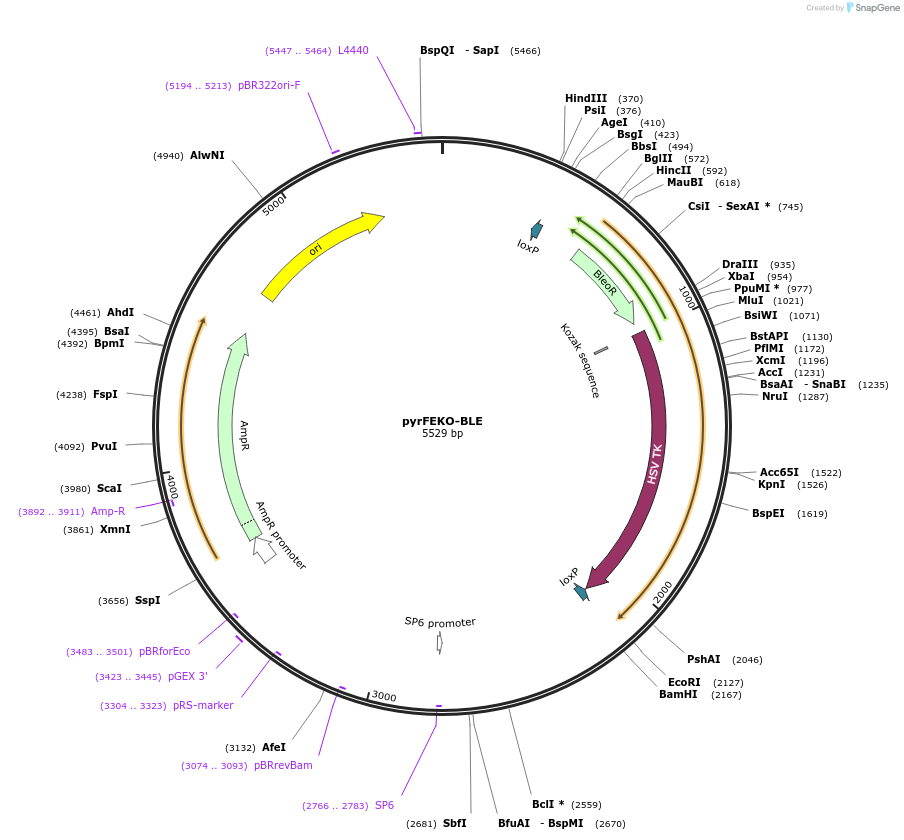
pyrFEKO-BLE
Plasmid#24023DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseFloxed targeting vector for trypanosomeAvailable SinceFeb. 25, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
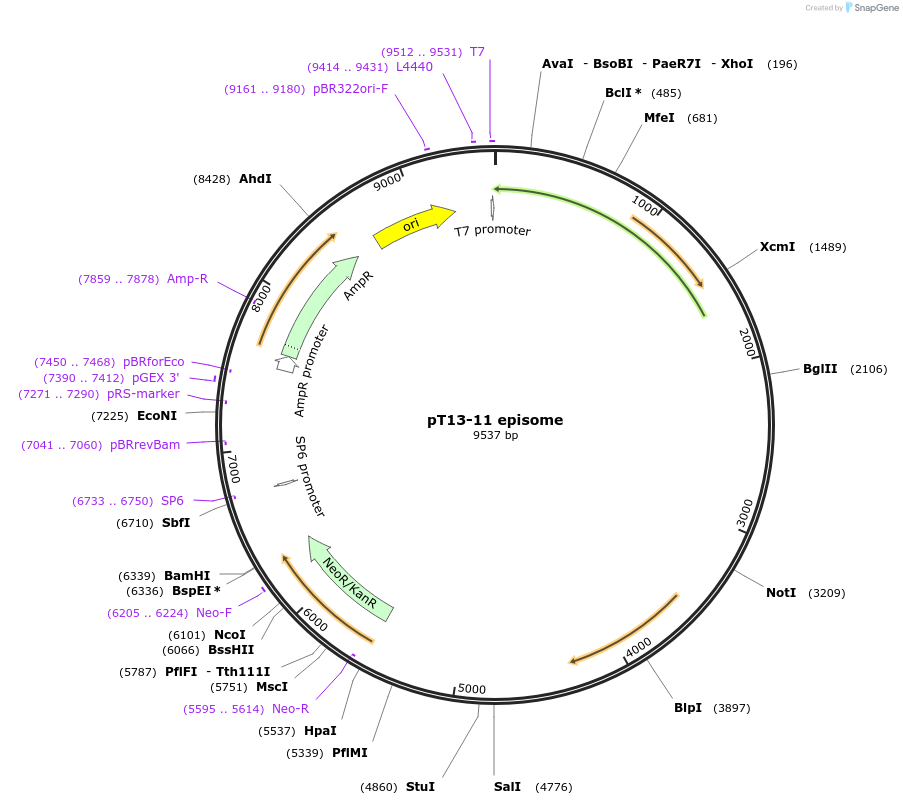
pT13-11 episome
Plasmid#24017DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosome expressionAvailable SinceMarch 15, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
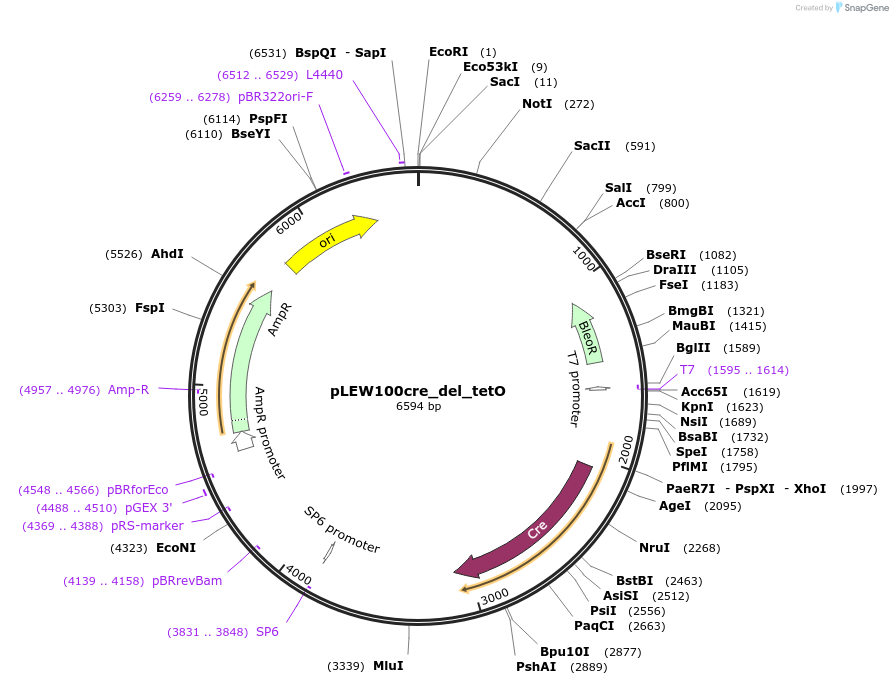
pLEW100cre_del_tetO
Plasmid#24019DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosome transient expressionTagsCre RecombinaseAvailable SinceMay 11, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
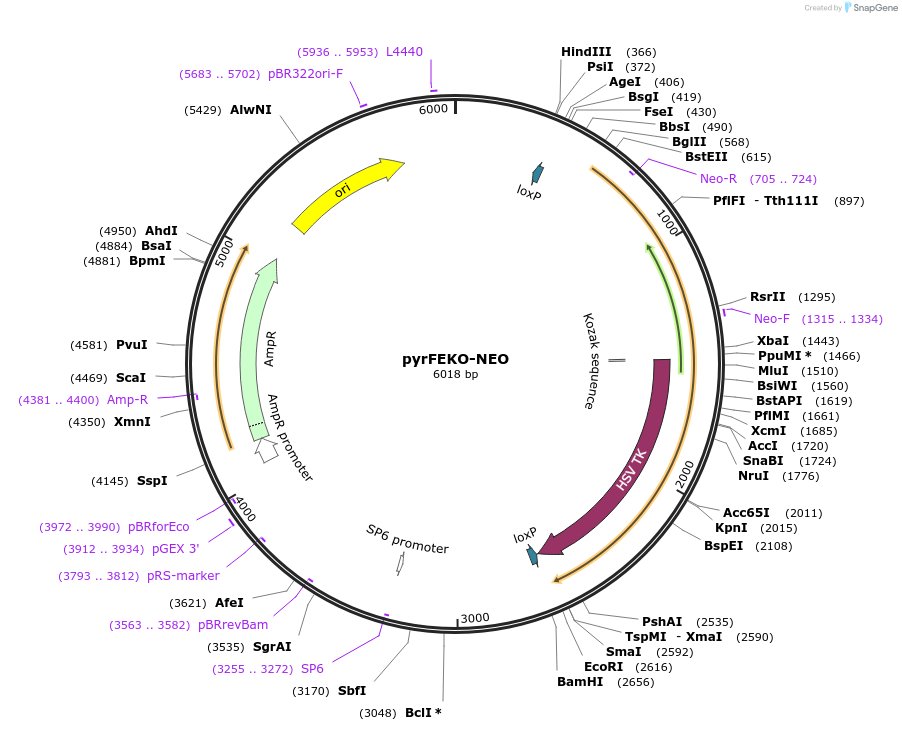
pyrFEKO-NEO
Plasmid#24022DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseFloxed targeting vector for trypanosomeAvailable SinceMay 11, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
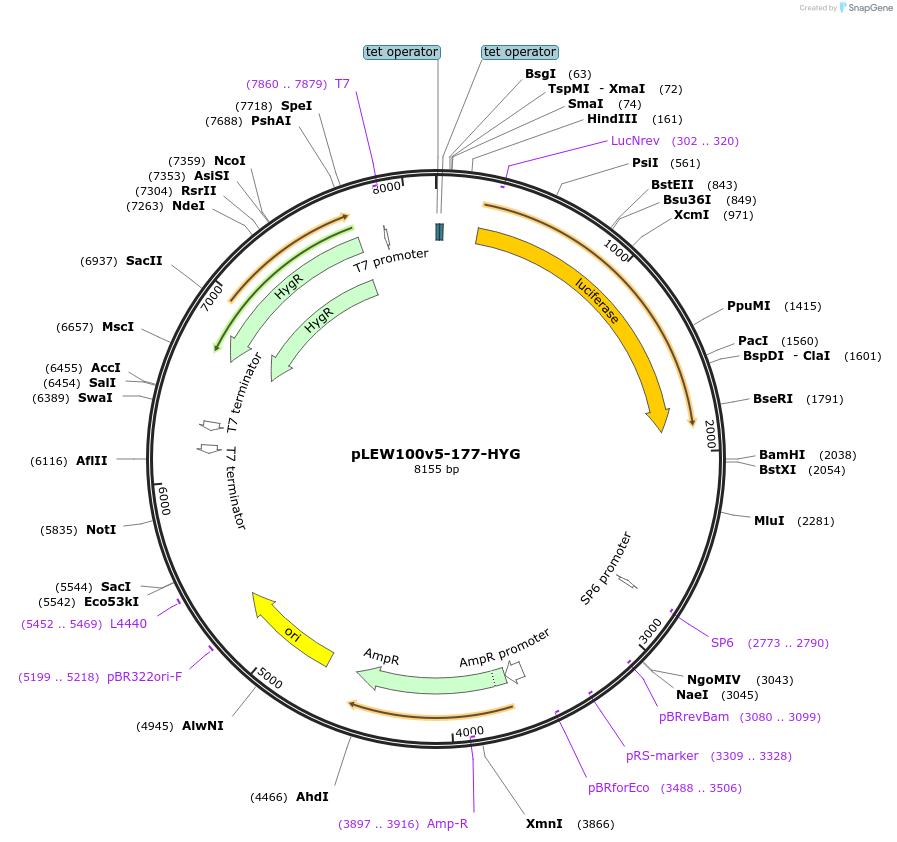
pLEW100v5-177-HYG
Plasmid#24013DepositorInsertLuciferase
UseTrypanosome expressionMutationK520RAvailable SinceFeb. 25, 2010AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
ZM (pyrFEKO-HYG TetR-T7RNAP)
Plasmid#31455DepositorInsert
UseFloxed targeting vector for trypanosomeAvailable SinceAug. 18, 2011AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
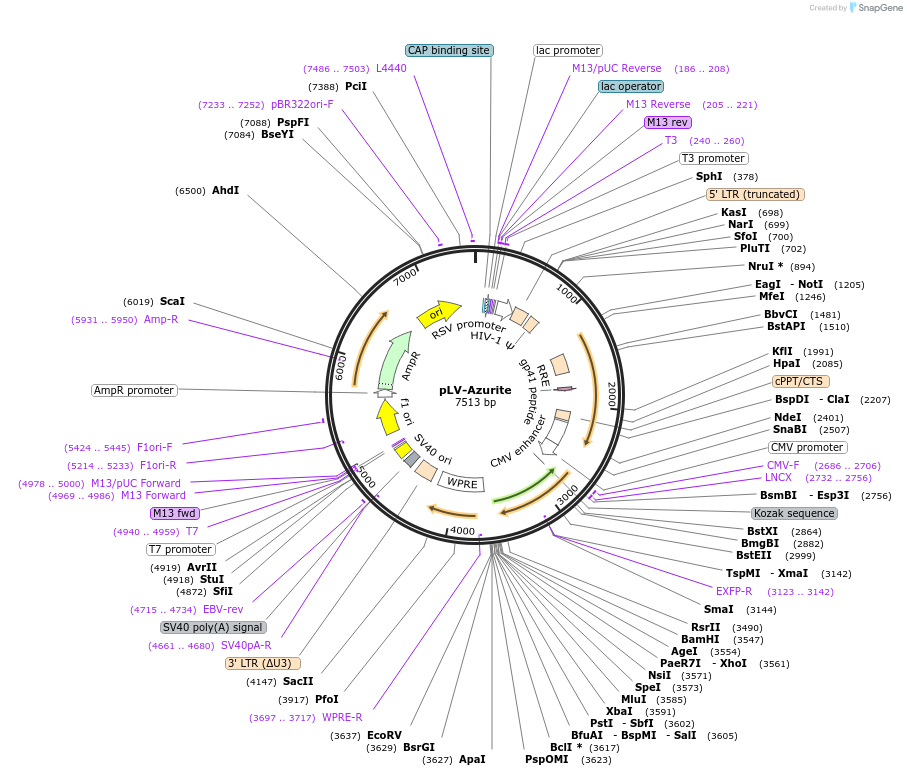
pLV-Azurite
Plasmid#36086Purpose3rd generation lentiviral plasmidDepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseLentiviralExpressionMammalianAvailable SinceJune 1, 2012AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
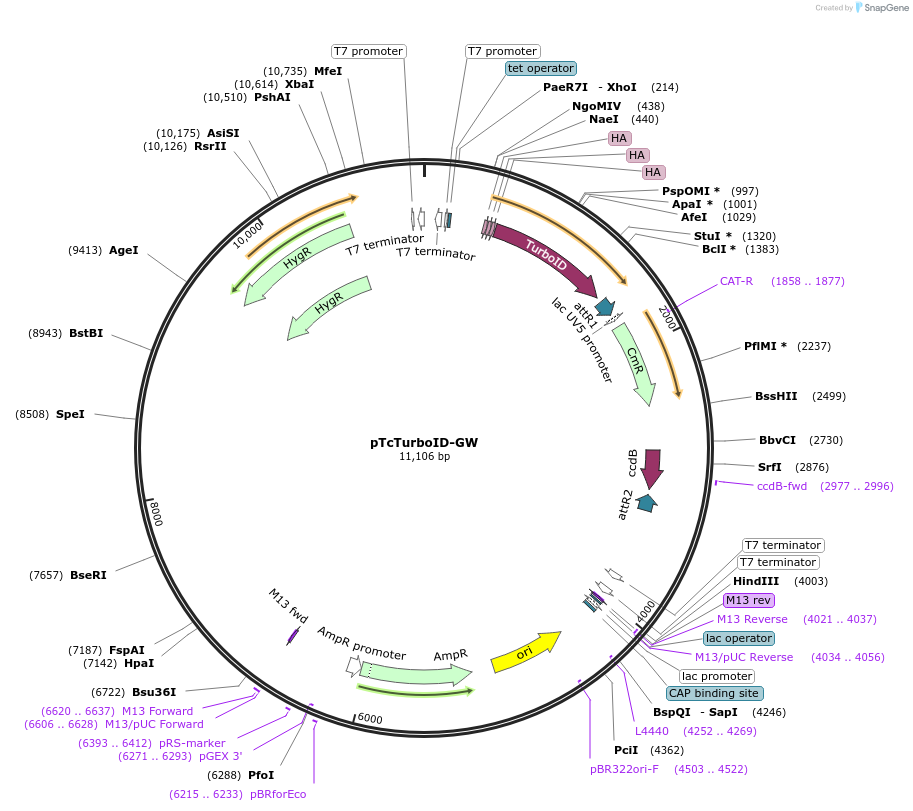
pTcTurboID-GW
Plasmid#234714PurposeUsed to express any CDS fused to 3xHA-TurboID (N-terminal) in T. cruzi. Tetracycline regulated. Modified from Alonso et al. (2014).DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseTrypanosomatid expressionTags3xHAAvailable SinceMay 30, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
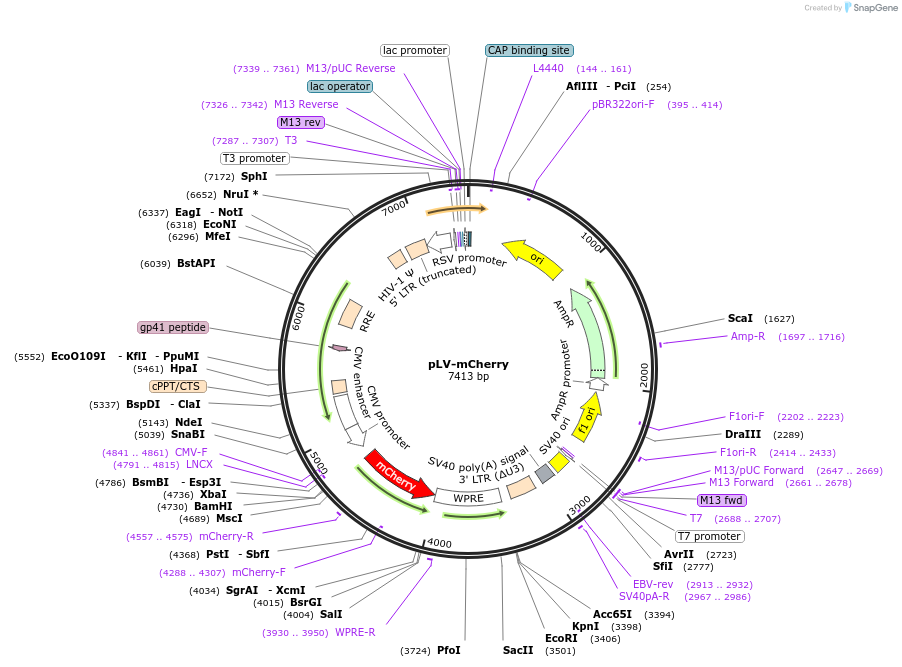
pLV-mCherry
Plasmid#36084Purpose3rd generation lentiviral plasmid expressing mCherryDepositorHas ServiceCloning Grade DNATypeEmpty backboneUseLentiviralExpressionMammalianAvailable SinceJune 1, 2012AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
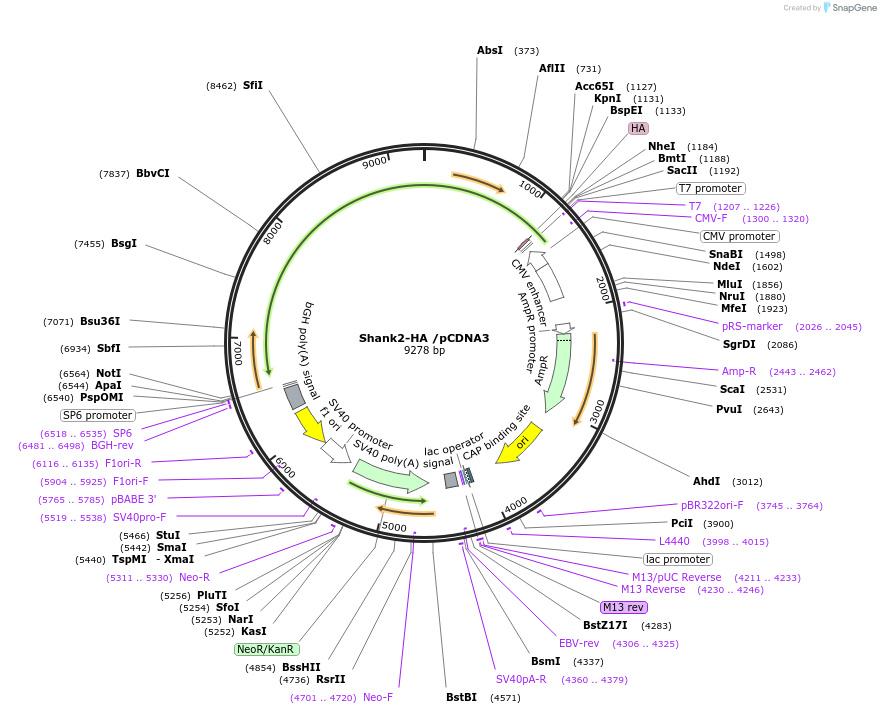
Shank2-HA /pCDNA3
Plasmid#197334PurposePlasmid expressing an antigen targeting Shank2DepositorAvailable SinceJune 16, 2023AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
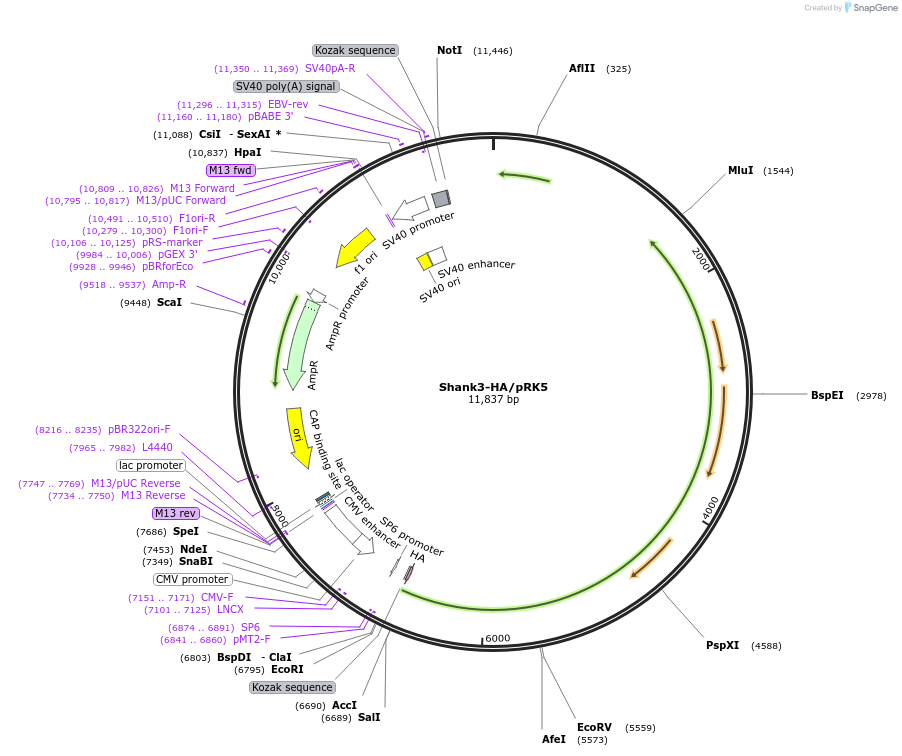
Shank3-HA/pRK5
Plasmid#197335PurposePlasmid expressing an antigen targeting Shank3DepositorAvailable SinceJune 16, 2023AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
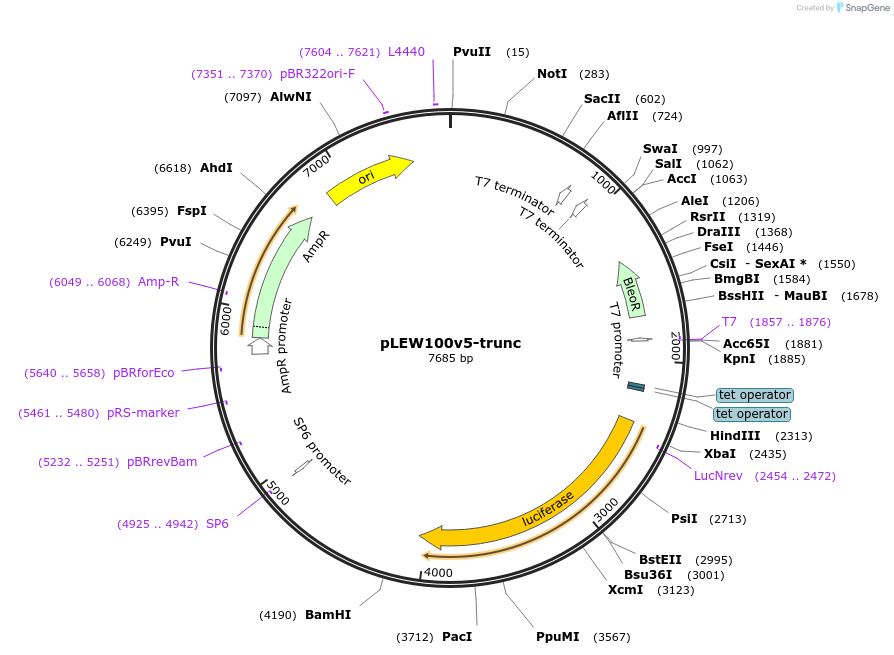
pLEW100v5-trunc
Plasmid#33346DepositorInsertLuciferase truncated to allow cytoplasmic instead of peroxisomal (glycosomal) expression
UseTrypanosoma brucei expression vectorMutation21bp of wt luciferase deletedAvailable SinceDec. 1, 2011AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
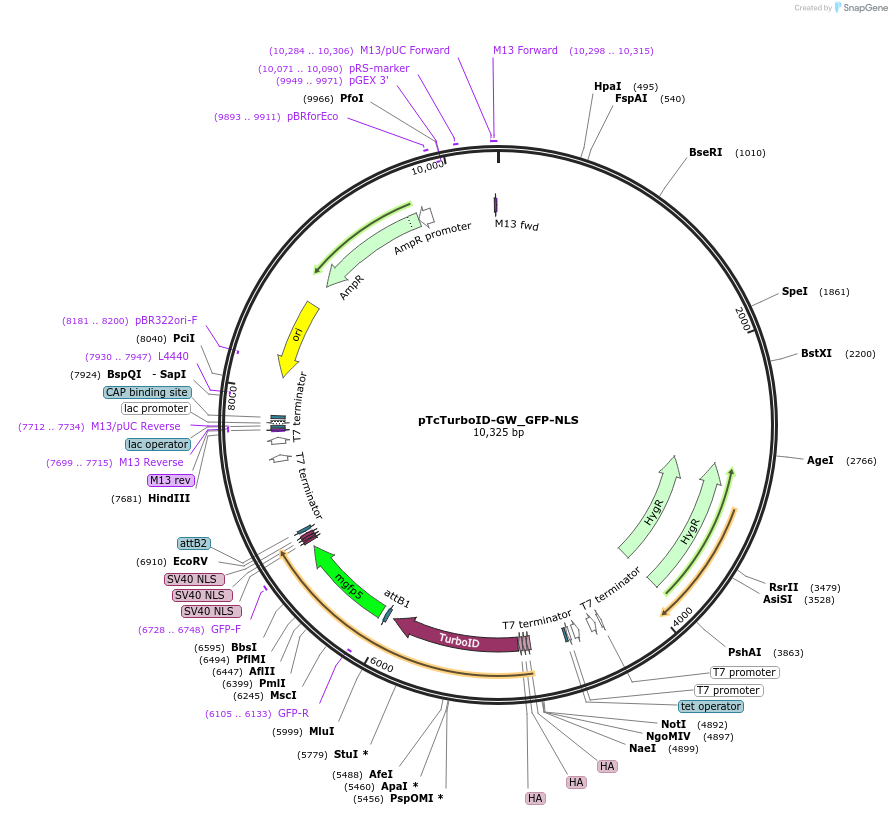
pTcTurboID-GW_GFP-NLS
Plasmid#234716PurposeUsed to express GFP-3xNLS fused to 3xHA-TurboID (N-terminal) in T. cruzi. Tetracycline regulated. Used as proximity labelling nuclear spatial control.DepositorInsertGFP-3xNLS
UseTrypanosomatid expressionTags3xHAPromoterT7Available SinceMay 30, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
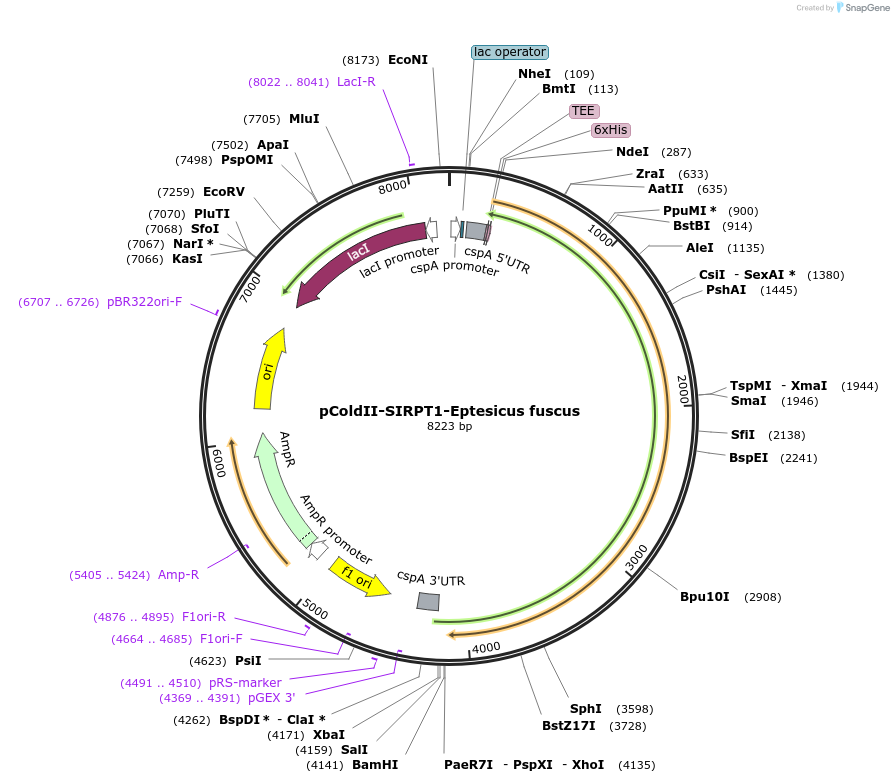
pColdII-SIRPT1-Eptesicus fuscus
Plasmid#78113PurposeNt His-tag Eptesicus fuscus Sacsin 89-1368DepositorInsertSacsin Eptesicus fuscus 89-1368
TagsHis-TagExpressionBacterialAvailable SinceJuly 11, 2016AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
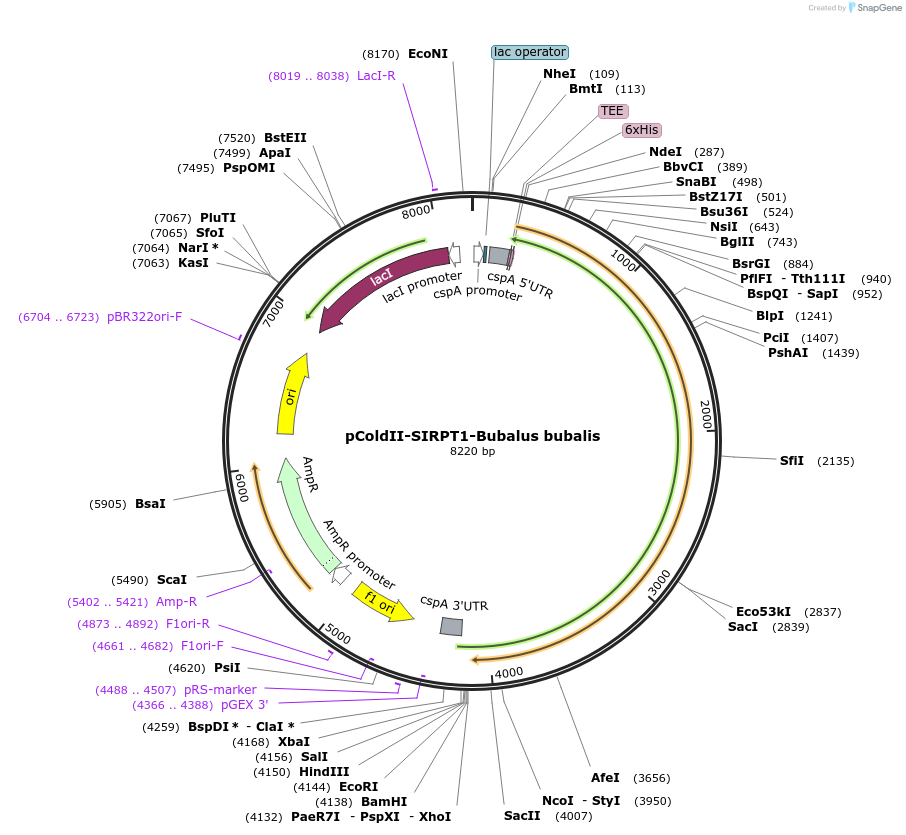
pColdII-SIRPT1-Bubalus bubalis
Plasmid#75350PurposeNt His-tag Bubalus bubalis Sacsin 86-1364DepositorInsertSacsin Bubalus bubalis 86-1364
TagsHis-TagExpressionBacterialAvailable SinceJuly 11, 2016AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
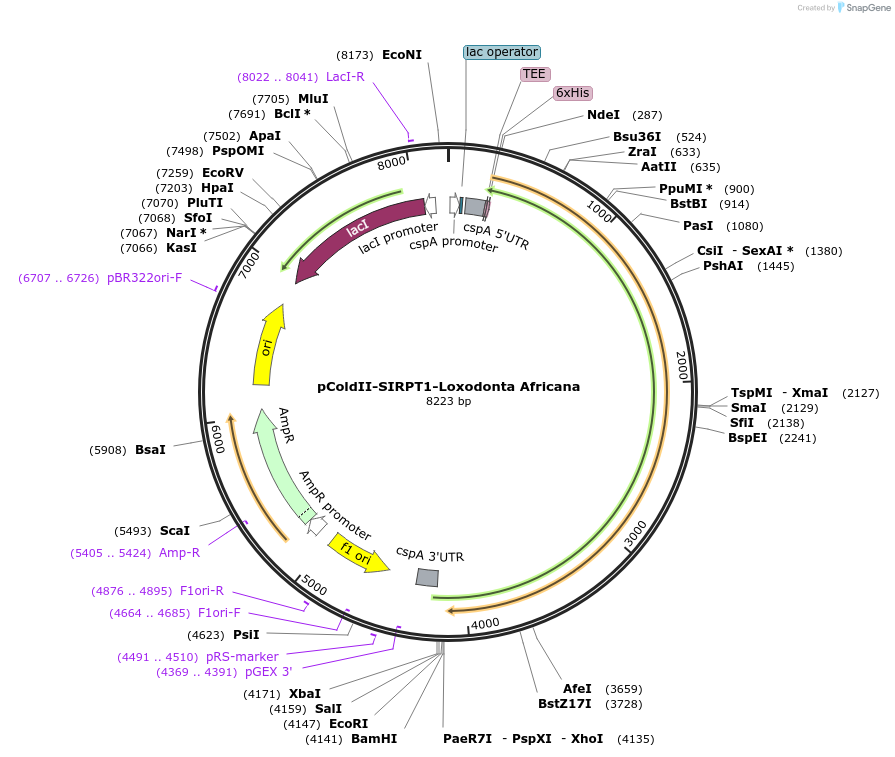
pColdII-SIRPT1-Loxodonta Africana
Plasmid#75351PurposeNt His-tag Loxodonta Africana 89-1368DepositorInsertSacsin Loxodonta Africana 89-1368
TagsHis-TagExpressionBacterialAvailable SinceJuly 11, 2016AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
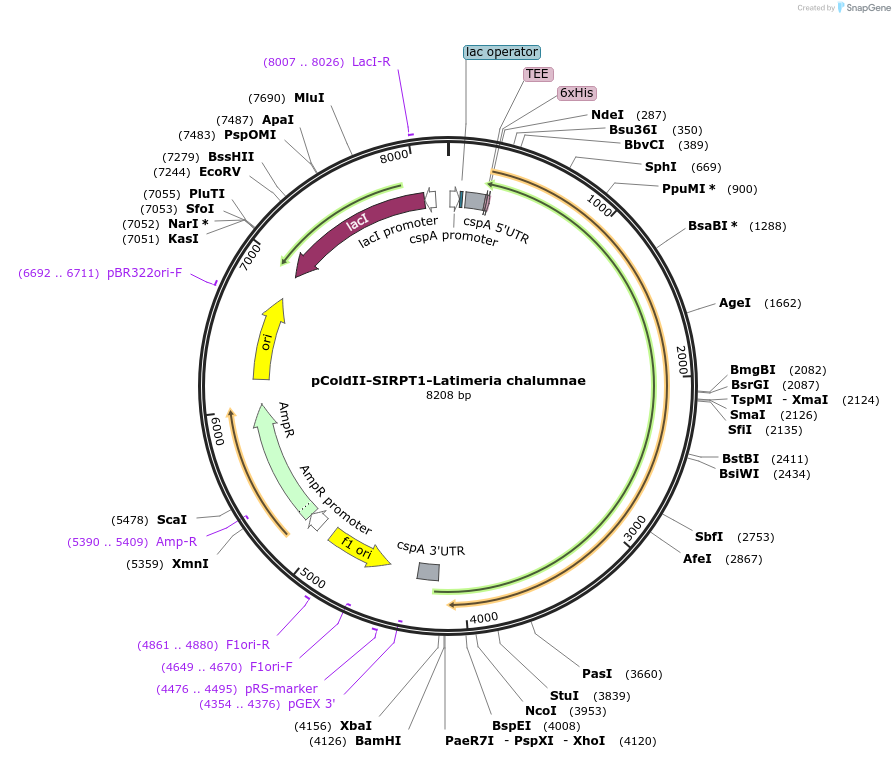
pColdII-SIRPT1-Latimeria chalumnae
Plasmid#75356PurposeNt His-tag Latimeria chalumnae Sacsin 94-1368DepositorInsertSacsin Latimeria chalumnae 94-1368
TagsHis-TagExpressionBacterialAvailable SinceJuly 11, 2016AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only