We narrowed to 9,963 results for: Gnas
-
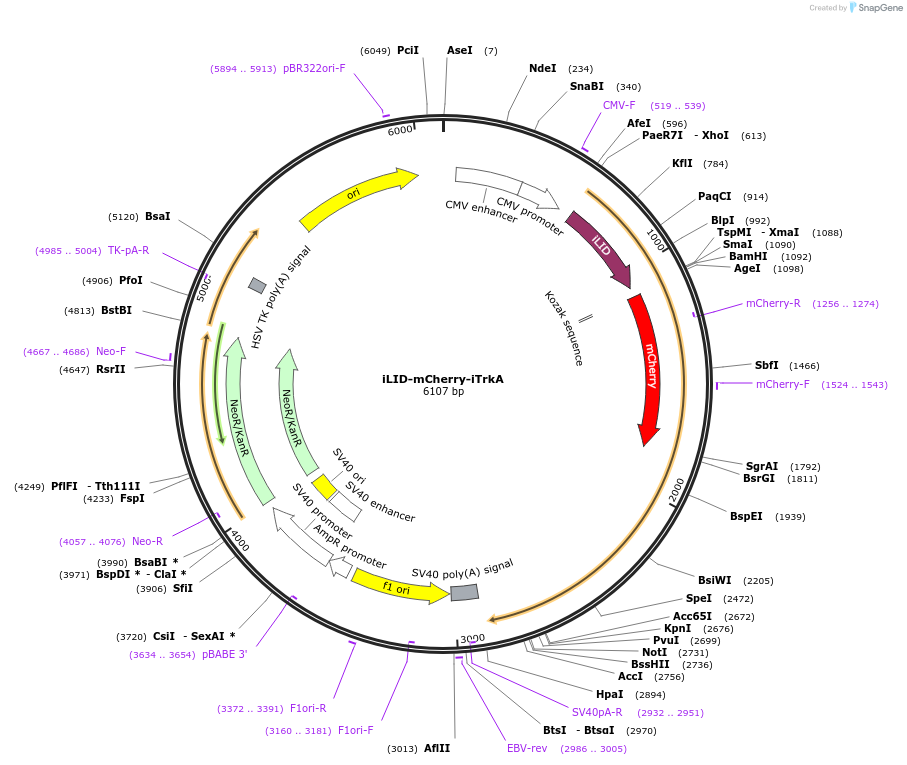
Plasmid#136509PurposeMammalian expression of iLID fused to mCherry and intracellular signaling domain of TrkA (aa 450-799)DepositorAvailable SinceMay 27, 2022AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only
-
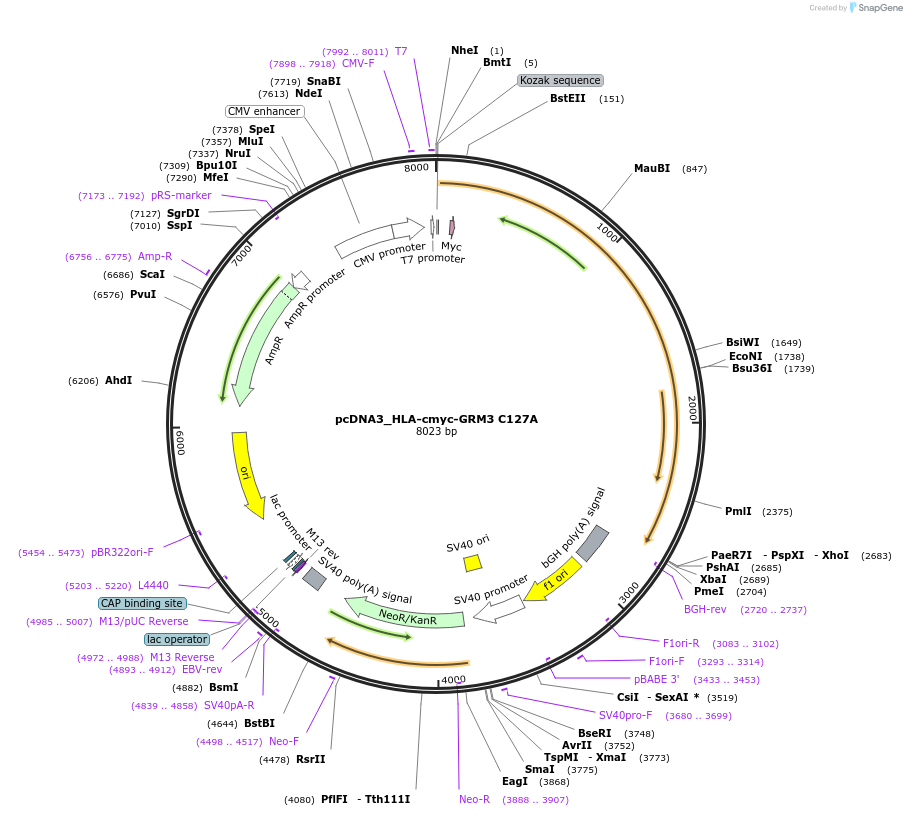
pcDNA3_HLA-cmyc-GRM3 C127A
Plasmid#140451PurposeMammalian expression plasmid for c-myc-tagged mGluR3 C127A mutantDepositorInsertGRM3 (GRM3 Human)
TagsSignal/leader sequence from HLA class I histocomp…ExpressionMammalianMutationCysteine 127 to alanineAvailable SinceJuly 11, 2022AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
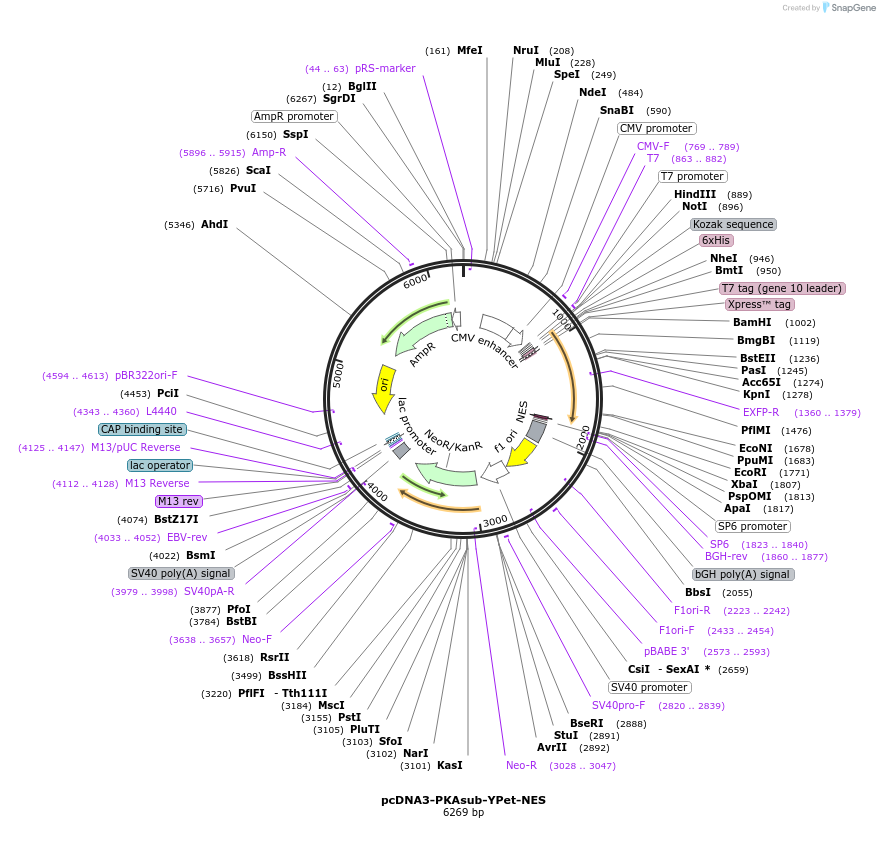
pcDNA3-PKAsub-YPet-NES
Plasmid#138203PurposeEncodes C-terminal (substrate) fragment of FRET-based bimolecular PKA activity reporter (BimAKAR); cytosol targeted. Use in conjunction with pcDNA3-Cerulean-FHA1-NES.DepositorInsertPKAsub-YPet-NES
Tags6xHIS - T7 tag (gene 10 leader) - Xpress (TM) tag…ExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceApril 20, 2023AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
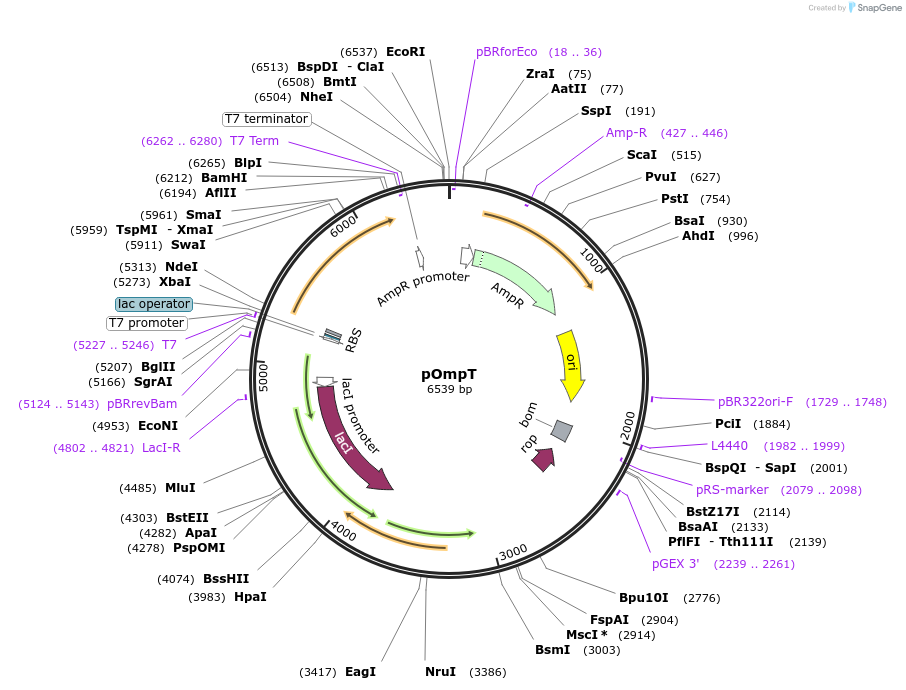
pOmpT
Plasmid#112123PurposeBacterial expression outer membrane protein T (OmpT), wild typeDepositorInsertOmpT (ompT E. coli)
ExpressionBacterialMutationN-terminal signal sequence not included and repla…PromoterT7Available SinceNov. 8, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
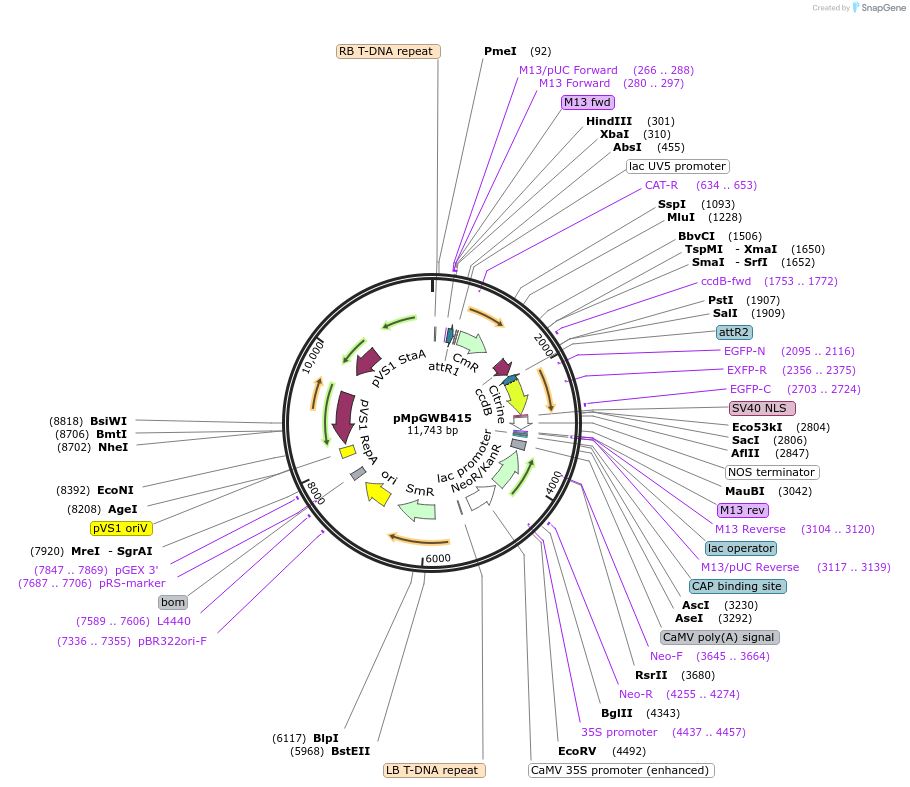
pMpGWB415
Plasmid#68680PurposeGateway binary vector designed for transgenic research with Marchantia polymorpha as well as other plantsDepositorTypeEmpty backboneTagsNuclear localization signal-tagged Citrine (Citri…ExpressionPlantAvailable SinceJune 24, 2016AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
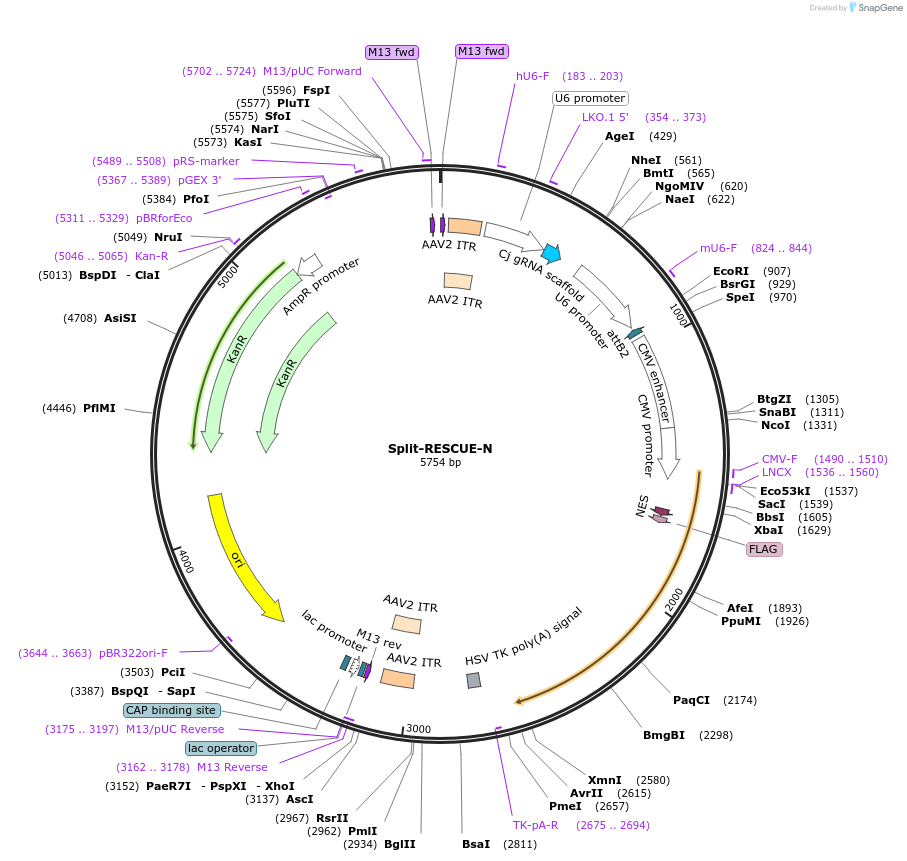
Split-RESCUE-N
Plasmid#170153PurposeAAV vector carrying the MCP-RESCUE-DDN (RESCUE is the evolved ADAR2 variant for C-U editing) with a nuclear export signalDepositorInsertNES-MCP-RESCUE-DDN
UseAAVExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceJan. 27, 2023AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
pcdna3 T7 Jip1b
Plasmid#52122Purposea mammalian scaffold protein that mediates the activation of a MAP kinase signaling pathway.DepositorAvailable SinceApril 28, 2014AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
mCherry-miniSOG-Peroxisomes-2
Plasmid#54804PurposeLocalization: Peroxisomes, Excitation: 448 / 473, Emission: 500 / 528DepositorInsertmCherry-miniSOG-Peroxisomes
TagsPeroxisomal Targeting Signal 1 (PTS1; Ser-Lys-Leu…ExpressionMammalianAvailable SinceJune 20, 2014AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
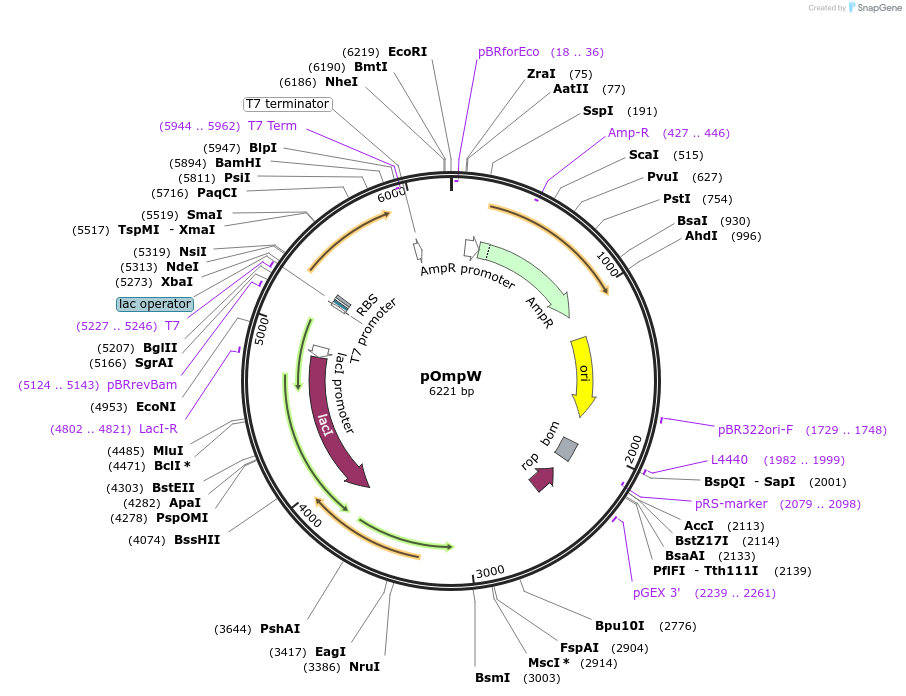
pOmpW
Plasmid#112121PurposeBacterial expression of outer membrane protein W (OmpW), wild typeDepositorInsertOmpW (ompW E. coli)
ExpressionBacterialMutationN-terminal signal sequence not included and repla…PromoterT7Available SinceNov. 8, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
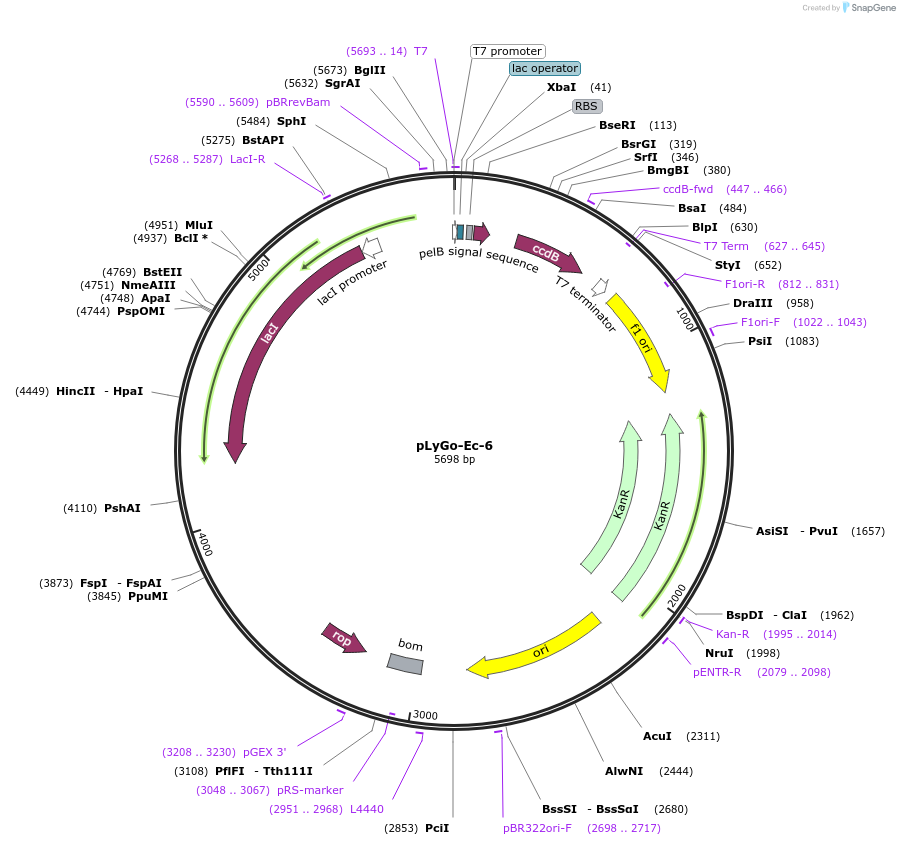
pLyGo-Ec-6
Plasmid#163132PurposepLyGo cloning vector for periplasmic expression in E. coli of a sequence of interest (LPMO). Vector encoding PelB signal peptide and the LyGo cassette (SapI-ccdB-SapI)DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseSynthetic BiologyExpressionBacterialPromoterT7Available SinceJuly 30, 2021AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
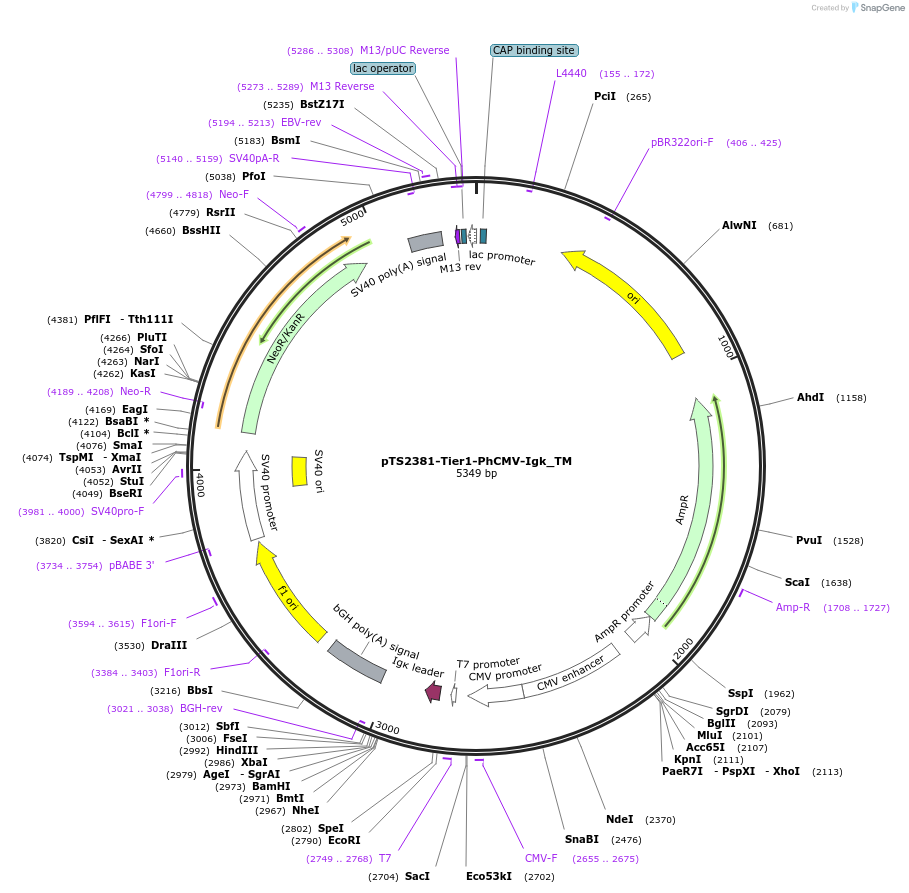
pTS2381-Tier1-PhCMV-Igk_TM
Plasmid#169487PurposeTier-1 vector encoding PhCMV-driven transmembrane domain from Junctophilin-1 (TM) for membrane localization of fusion proteins attached to a secretion signal Igk (PhCMV-IgkSS-TM-pA).DepositorInsertPCMV-driven membrane localization
ExpressionMammalianPromoterPhCMVAvailable SinceJune 14, 2022AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
-
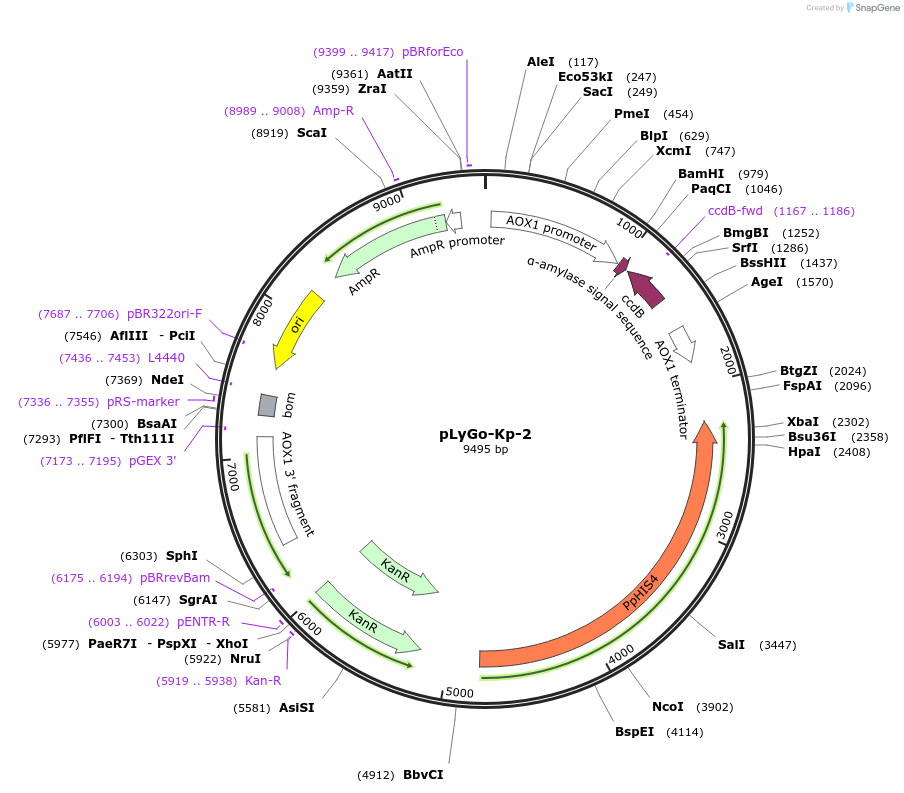
pLyGo-Kp-2
Plasmid#163144PurposepLyGo cloning vector for a sequence of interest (LPMO) in K. phaffii. Vector encoding the alfa-amylase signal peptide and the LyGo cassette (SapI-ccdB-SapI)DepositorTypeEmpty backboneUseSynthetic BiologyExpressionYeastPromoterAOX1Available SinceMay 7, 2021AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
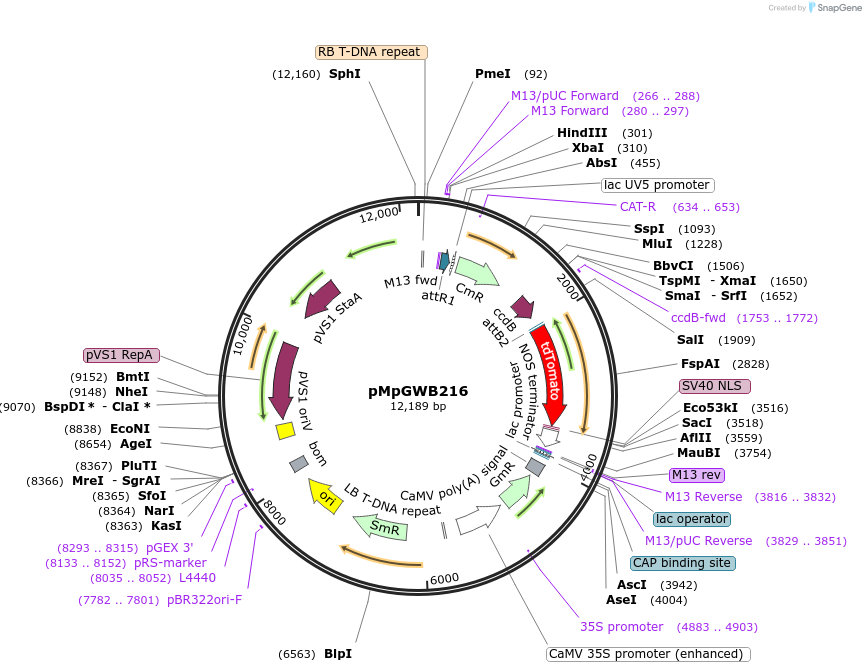
pMpGWB216
Plasmid#68607PurposeGateway binary vector designed for transgenic research with Marchantia polymorpha as well as other plantsDepositorTypeEmpty backboneTagsNuclear localization signal-tagged tdTomato (tdTo…ExpressionPlantAvailable SinceJune 24, 2016AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
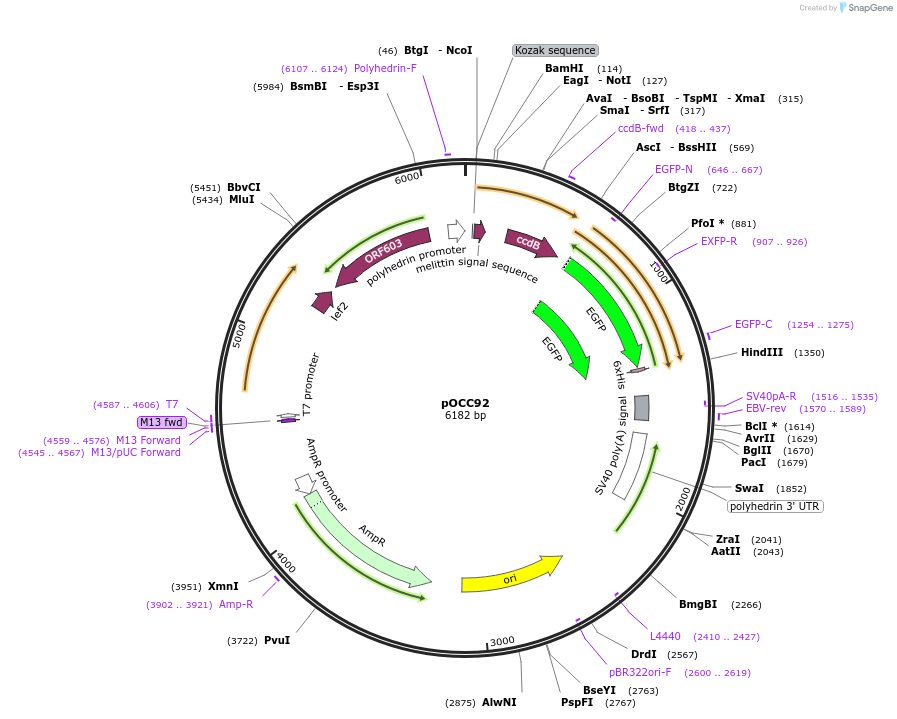
pOCC92
Plasmid#118910Purposeshuttle vector for baculovirus production, using FlashBac bacmid; for recombinant protein with honey bee melitine secretion signal and C-terminal eGFP-HIS6DepositorInsertNcoI-HBMss-NotI-ccdB-AscI-eGFP-HIS6-stop-HindIII cassette
TagseGFP-HIS6ExpressionInsectPromoterpolHAvailable SinceFeb. 5, 2019AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
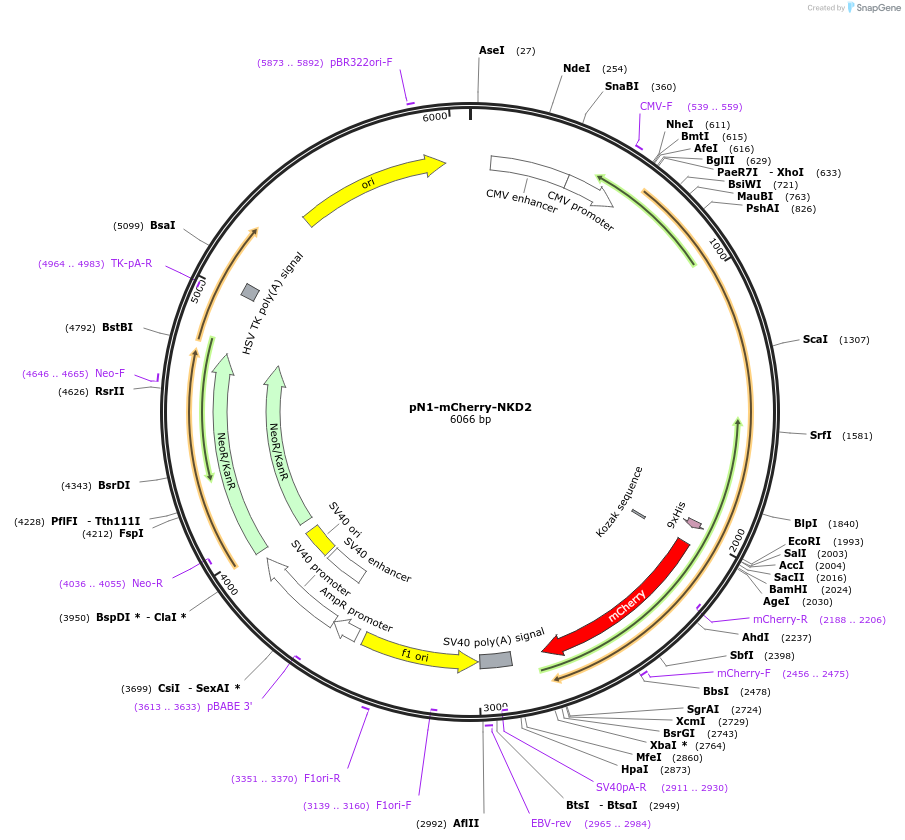
pN1-mCherry-NKD2
Plasmid#176641PurposeExpresses NKD2-mCherry fusion protein in mammalian cellsDepositorInsertHomo sapiens NKD inhibitor of WNT signaling pathway 2 (NKD2 Human)
TagsmCherry tagExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceDec. 9, 2021AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
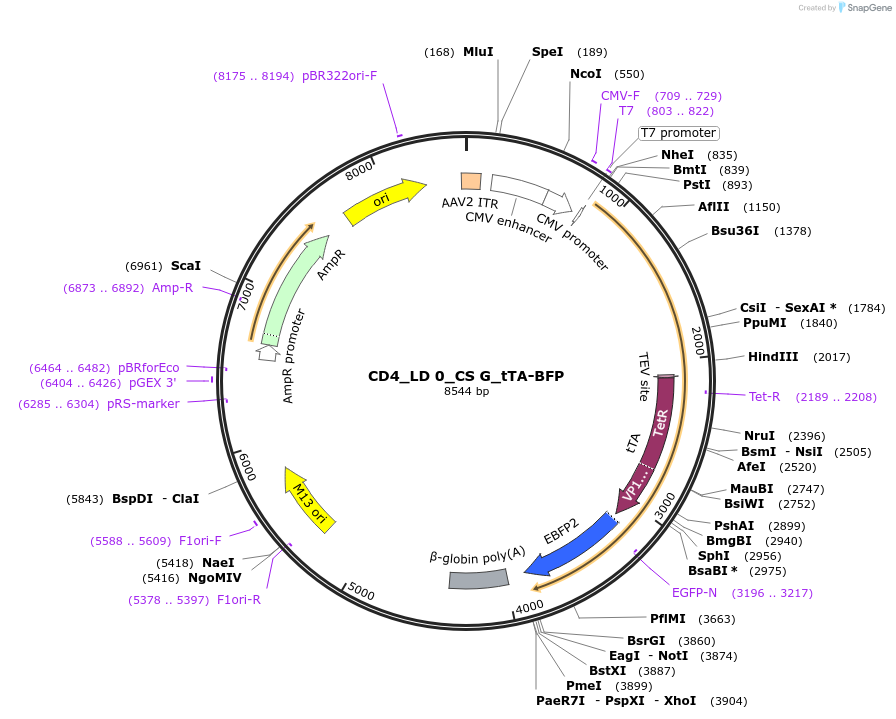
CD4_LD 0_CS G_tTA-BFP
Plasmid#58869PurposeMESA target chain with CD4 ectodomain, no linker domain, G cleavage sequence, and tTA-BFP fusionDepositorInsertMESA target chain with CD4 ectodomain, cd28 transmembrane domain, wild type TEV cleavage sequence
UseAAVTagsEBFPExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceOct. 27, 2014AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
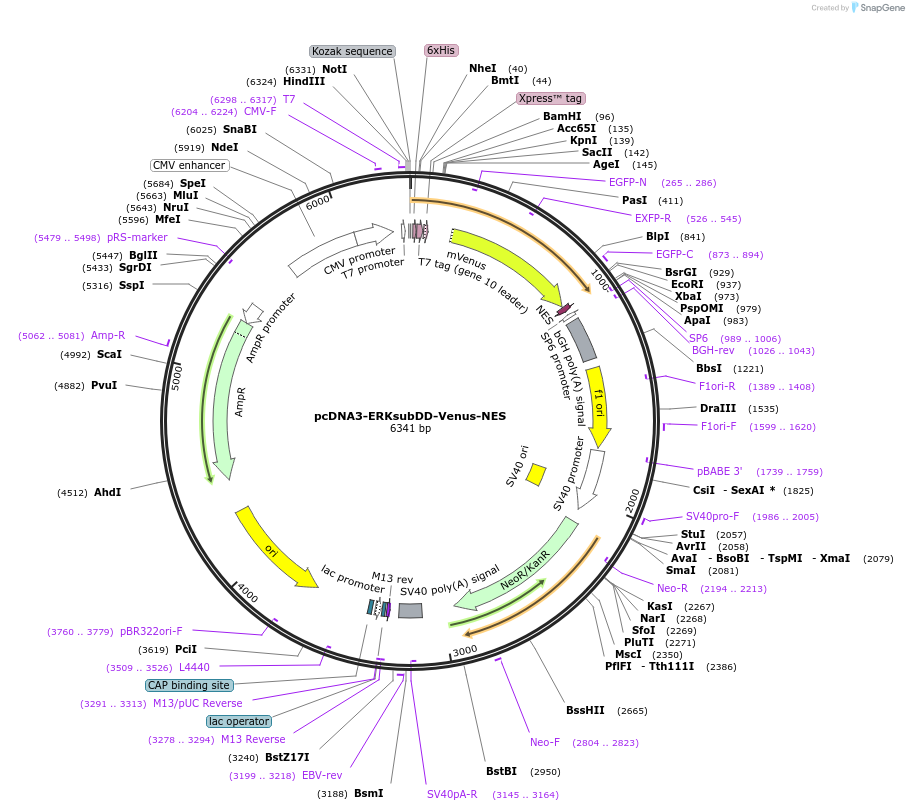
pcDNA3-ERKsubDD-Venus-NES
Plasmid#84630PurposeEncodes C-terminal (substrate) fragment of bimolecular ERK activity reporter (bimEKAR); cytosol targetedDepositorInsertERKsubDD-Venus-NES
Tags6xHis, Nuclear export signal (NES), T7 tag (gene …ExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceOct. 5, 2021AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
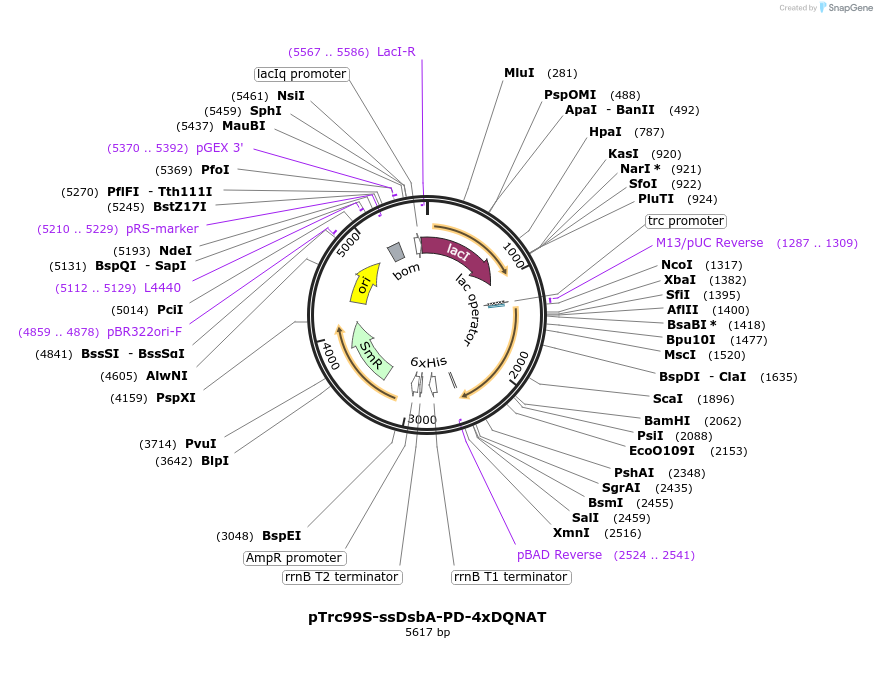
pTrc99S-ssDsbA-PD-4xDQNAT
Plasmid#128399PurposePeriplasmic expression of H. influenzae protein D with C terminal 4xDQNAT glycosylation sites in E. coliDepositorInsertH. influenzae protein D
Tags4xDQNAT glycosylation tag, 6xHis tag, and DsbA si…ExpressionBacterialPromotertrcAvailable SinceApril 13, 2021AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
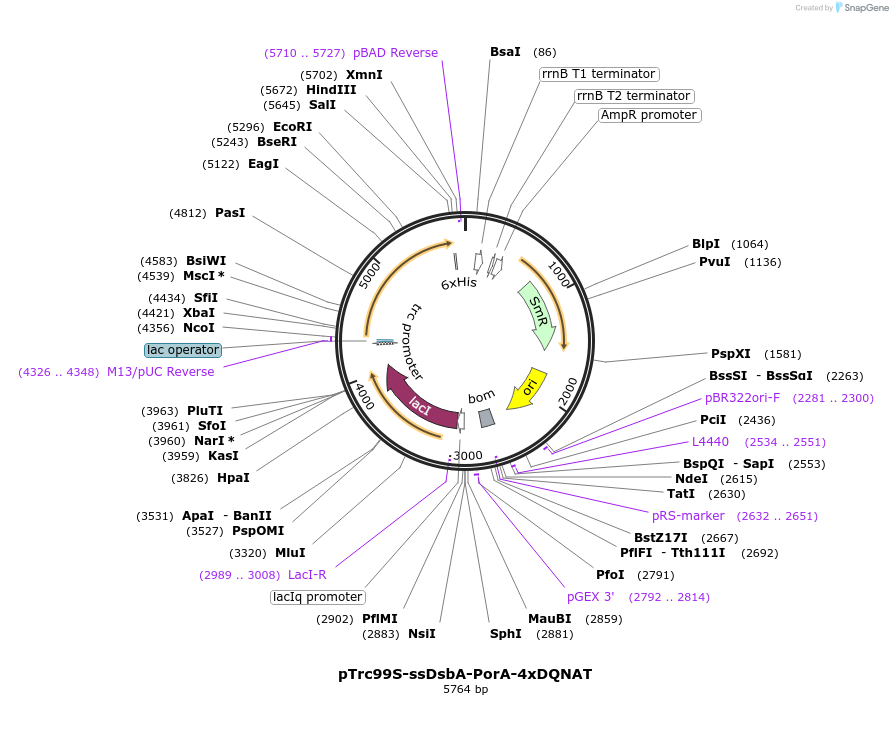
pTrc99S-ssDsbA-PorA-4xDQNAT
Plasmid#128400PurposePeriplasmic expression of N. meningitidis PorA with C terminal 4xDQNAT glycosylation sites in E. coliDepositorInsertN. meningitidis PorA
Tags4xDQNAT glycosylation tag, 6xHis tag, and DsbA si…ExpressionBacterialPromotertrcAvailable SinceApril 13, 2021AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
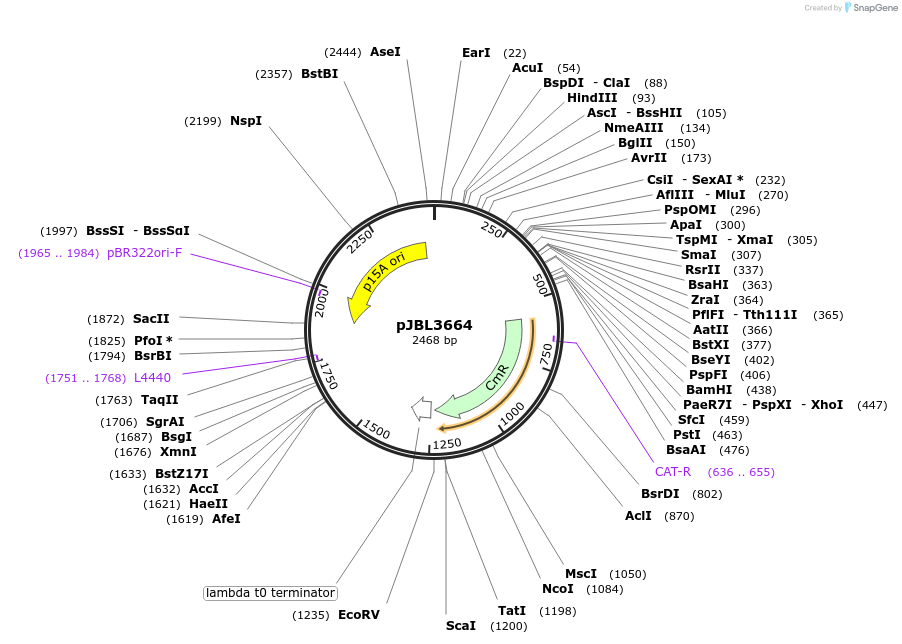
pJBL3664
Plasmid#162240PurposeTranscribes E. coli SRP RNA sequence for SHAPE-SeqDepositorInsertsE. coli SRP RNA
HDV
ExpressionBacterialPromoterJ23119Available SinceDec. 21, 2020AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
pCDB368
Plasmid#110276PurposegHH_44 with a N-terminal 10-His DsbC TEV-peptide fusionDepositorInsertgHH_44
Tags10-His, Tev recognition peptide, and mature DsbC …ExpressionBacterialPromoterT7Available SinceJune 22, 2018AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
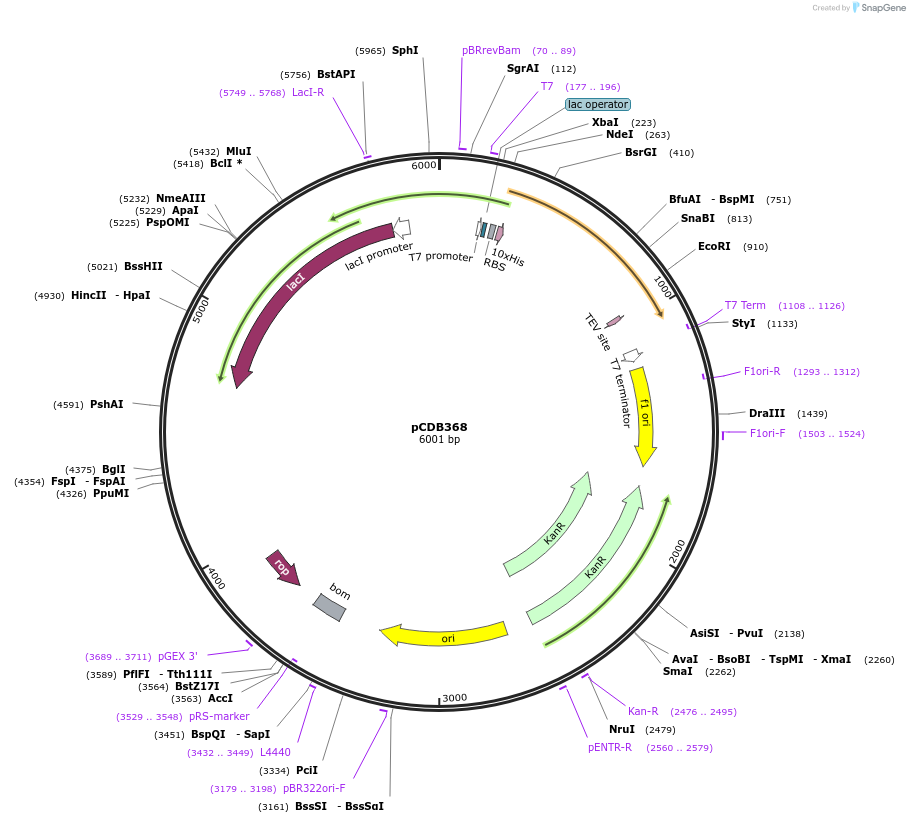
pcDNA3-RLuc8C-FHA1-NES
Plasmid#138210PurposeEncodes PAABD fragment of luminescence-based bimolecular kinase activity reporters (LumKARs); cytosol targeted.DepositorInsertRLuc8C-FHA1-NES
Tags6xHIS - T7 tag (gene 10 leader) - Xpress (TM) tag…ExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceJan. 25, 2021AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
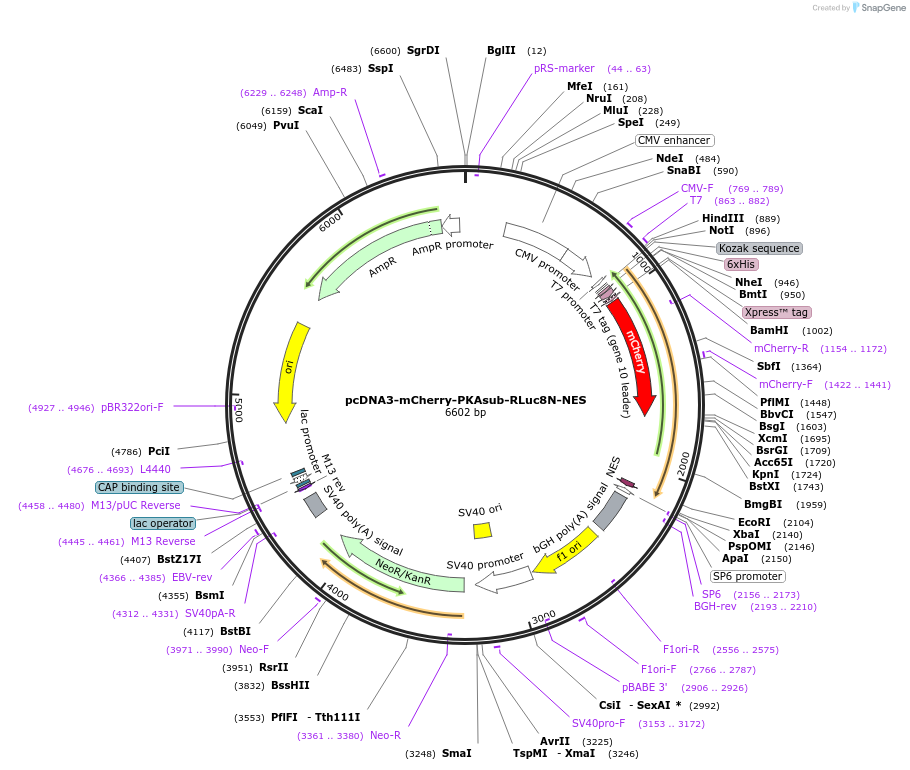
pcDNA3-mCherry-PKAsub-RLuc8N-NES
Plasmid#138211PurposeEncodes substrate fragment of luminescence-based bimolecular PKA activity reporter (LumAKAR); cytosol targeted. Use in conjunction with pcDNA3-RLuc8C-FHA1-NES.DepositorInsertmCherry-PKAsub-RLuc8N-NES
Tags6xHIS - T7 tag (gene 10 leader) - Xpress (TM) tag…ExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceJan. 25, 2021AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
L3MBTL3 (3UT1)
Plasmid#36901PurposeBacterial expression for structure determination; may not be full ORFDepositorInsertL3MBTL3 (L3MBTL3 Human)
TagsHis tag and Streptavidin-Binding Peptide (SBP)-Ta…ExpressionBacterialMutationcontains amino acid residues 228-551 onlyAvailable SinceJune 21, 2012AvailabilityIndustry, Academic Institutions, and Nonprofits -
PA-mCherry-miniSOG-Peroxisomes-2
Plasmid#54847PurposeLocalization: Peroxisomes, Excitation: 448 / 473, Emission: 500 / 528DepositorInsertPA-mCherry-miniSOG-Peroxisomes
TagsPeroxisomal Targeting Signal 1 (PTS1; Ser-Lys-Leu…ExpressionMammalianAvailable SinceJune 20, 2014AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
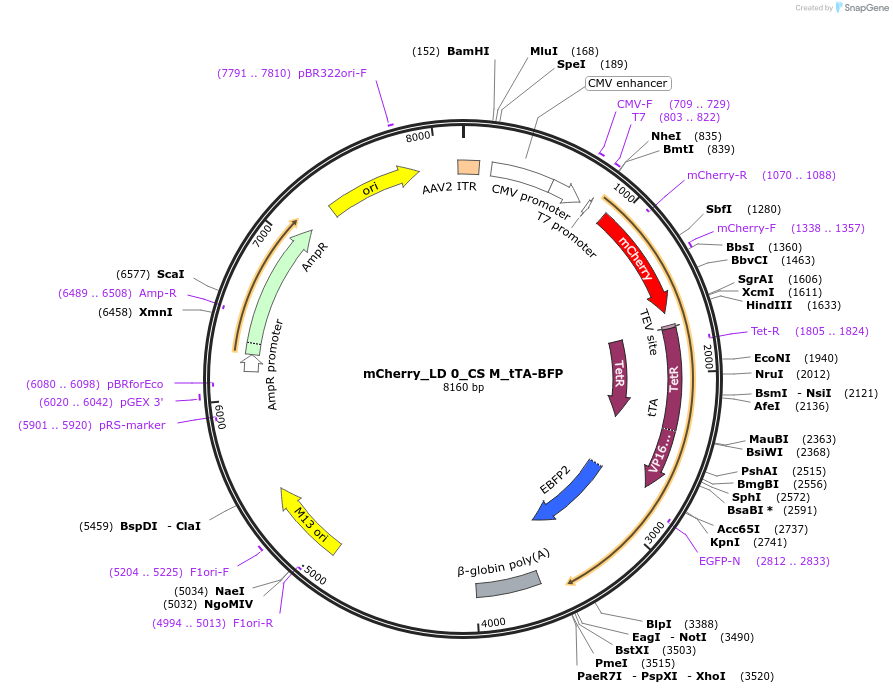
mCherry_LD 0_CS M_tTA-BFP
Plasmid#58874PurposeMESA target chain with mCherry ectodomain, no linker domain, M cleavage sequence, and tTA-BFP fusionDepositorInsertMESA target chain with mCherry ectodomain, cd28 transmembrane domain, mutated TEV cleavage sequence (M in P1')
UseAAVTagsEBFPExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceSept. 26, 2014AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
pMT1100
Plasmid#8618DepositorInsertribonuclease Sa3, barstar
TagsphoA signal sequence to RNase Sa3ExpressionBacterialMutationIn addition to the substitution of the barnase ge…Available SinceJan. 17, 2007AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
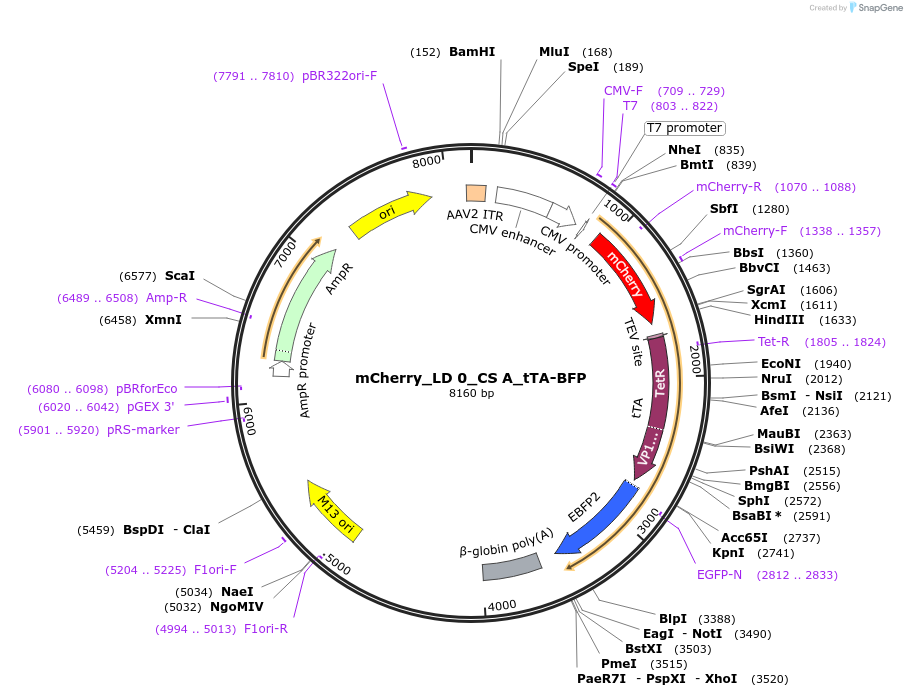
mCherry_LD 0_CS A_tTA-BFP
Plasmid#58873PurposeMESA target chain with mCherry ectodomain, no linker domain, A cleavage sequence, and tTA-BFP fusionDepositorInsertMESA target chain with mCherry ectodomain, cd28 transmembrane domain, mutated TEV cleavage sequence (A in P1')
UseAAVTagsEBFPExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceNov. 10, 2014AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
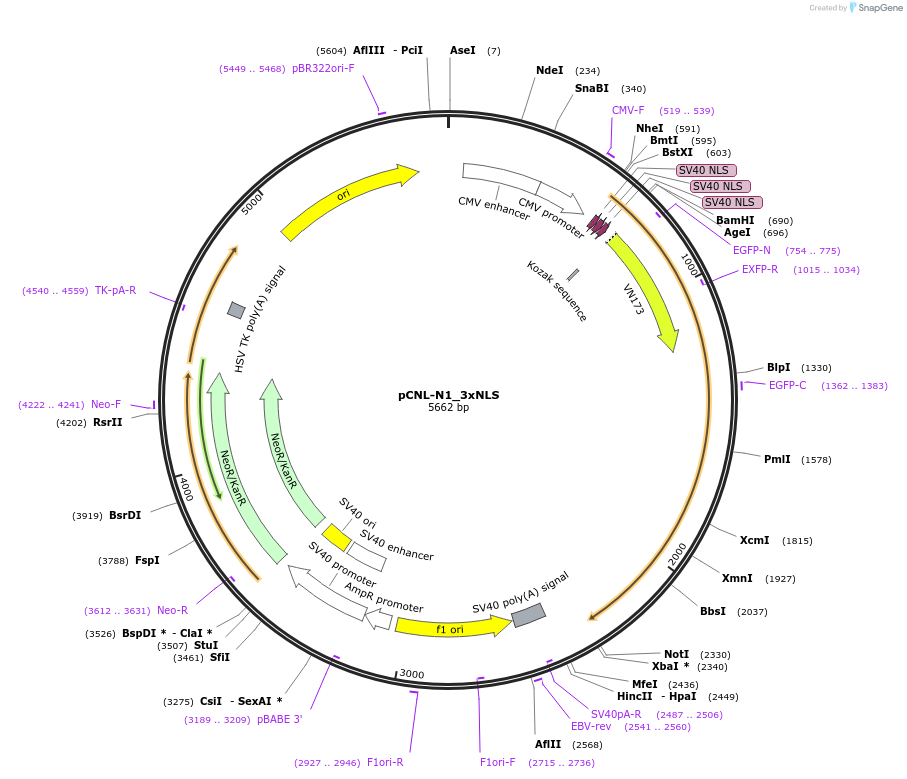
pCNL-N1_3xNLS
Plasmid#65673PurposeExpresses NLS-CNL in mammalian cellsDepositorInsertthree copies of SV40 nuclear localization signal
UseLuciferaseTagsCNLExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceJune 9, 2015AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
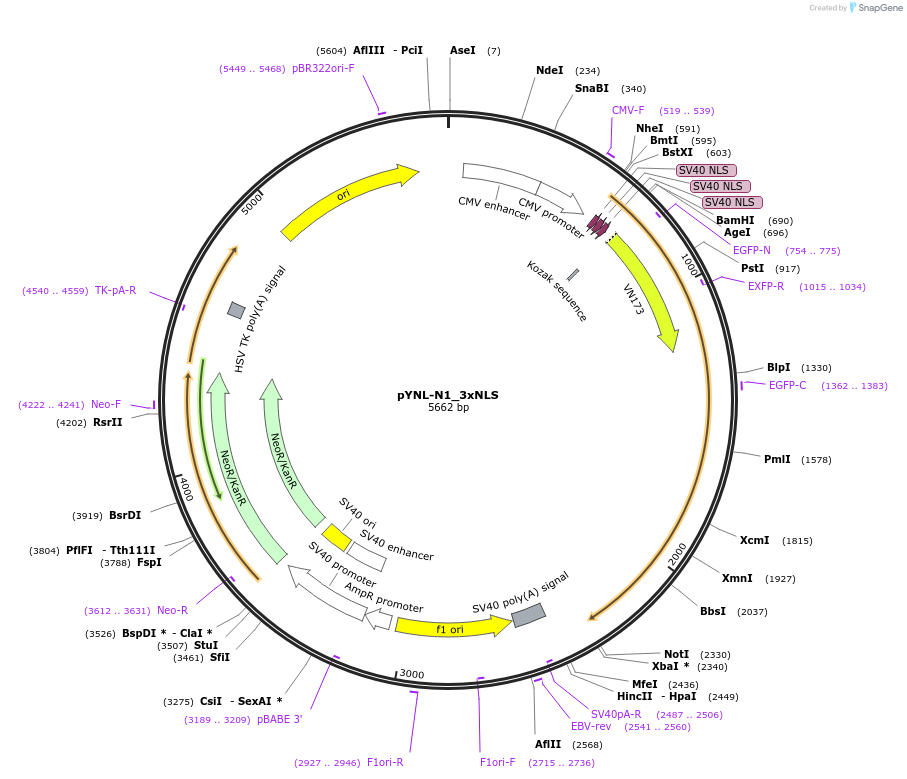
pYNL-N1_3xNLS
Plasmid#65672PurposeExpresses NLS-YNL in mammalian cellsDepositorInsertthree copies of SV40 nuclear localization signal
UseLuciferaseExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceJune 9, 2015AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
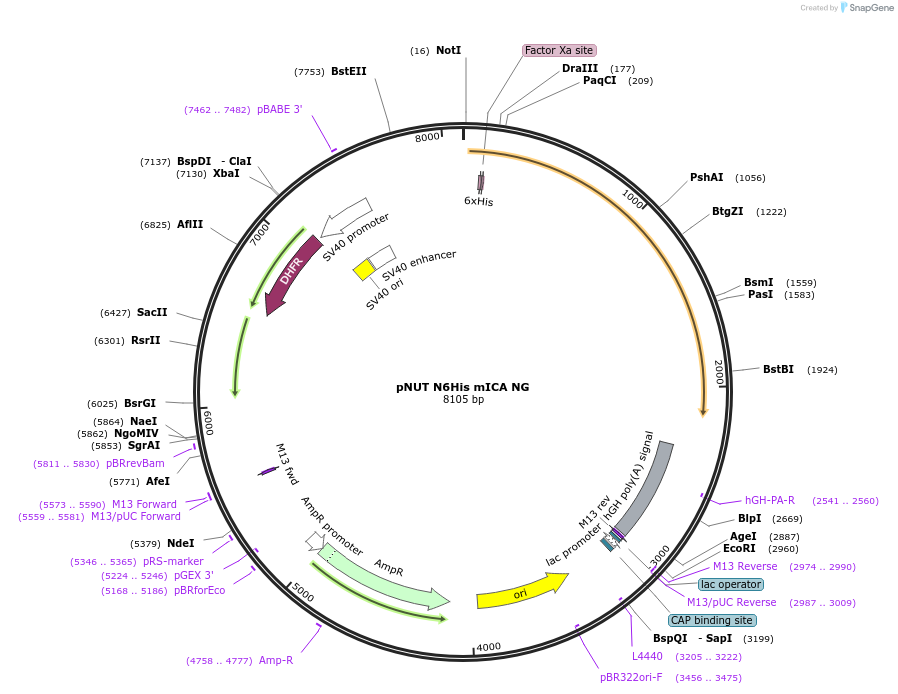
pNUT N6His mICA NG
Plasmid#70162PurposeExpresses N-His tagged nonglycosylated mouse inhibitor of carbonic anhydraseDepositorInsertmouse inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase
TagsN-terminal signal peptide, 4 aa link, 6 His, Fact…ExpressionMammalianMutationAsn470Asp and Asn645AspPromoterSV40Available SinceNov. 10, 2015AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
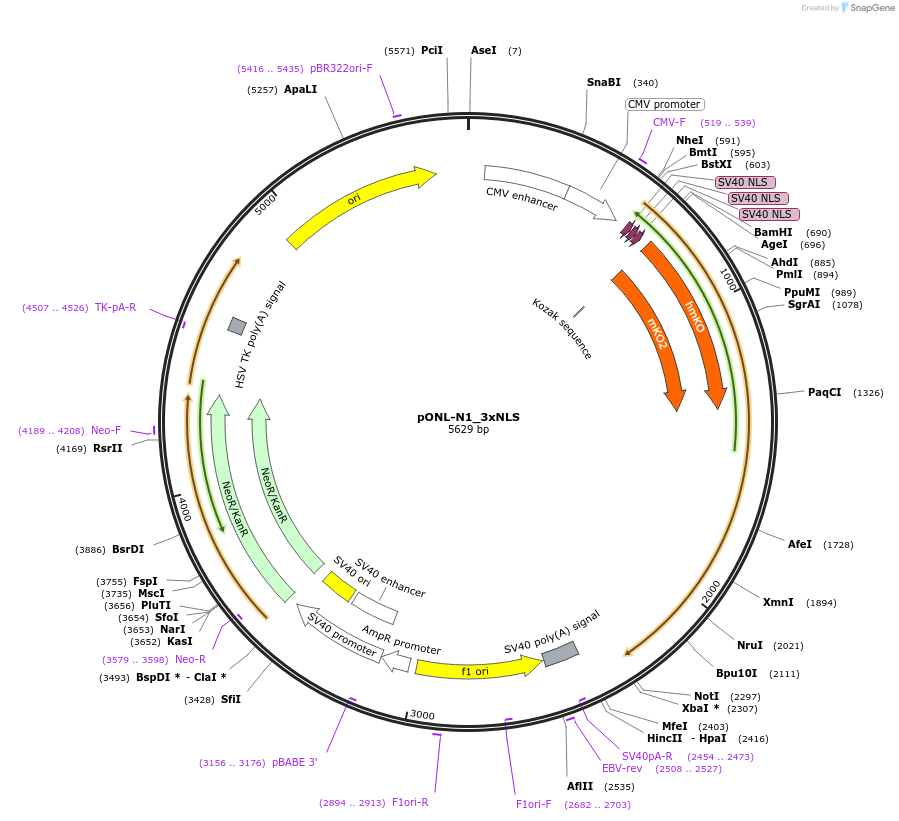
pONL-N1_3xNLS
Plasmid#65674PurposeExpresses NLS-ONL in mammalian cellsDepositorInsertthree copies of SV40 nuclear localization signal
UseLuciferaseTagsONLExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceJune 11, 2015AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
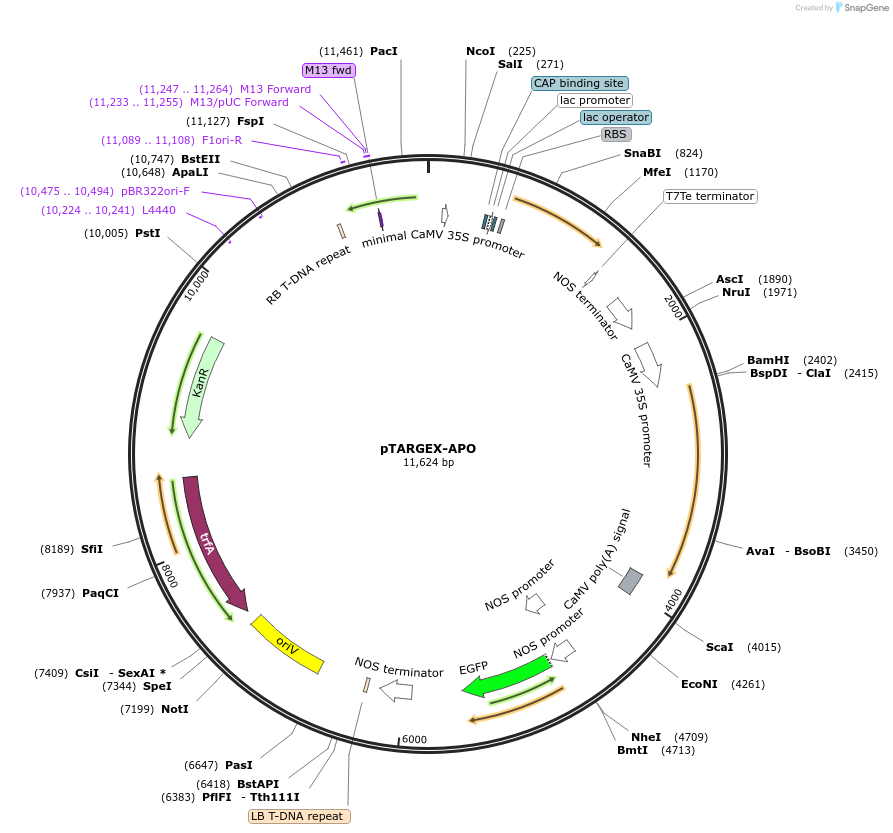
pTARGEX-APO
Plasmid#242446PurposeTargets high levels of recombinant protein to apoplast. Empty vector. Clone via SapI restriction site. mCherry dropout cassette will enable Red/White screening in E.coli.DepositorTypeEmpty backboneTagsN-terminal fusion with PR1b signal peptideExpressionPlantPromoterdouble 35SAvailable SinceOct. 23, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
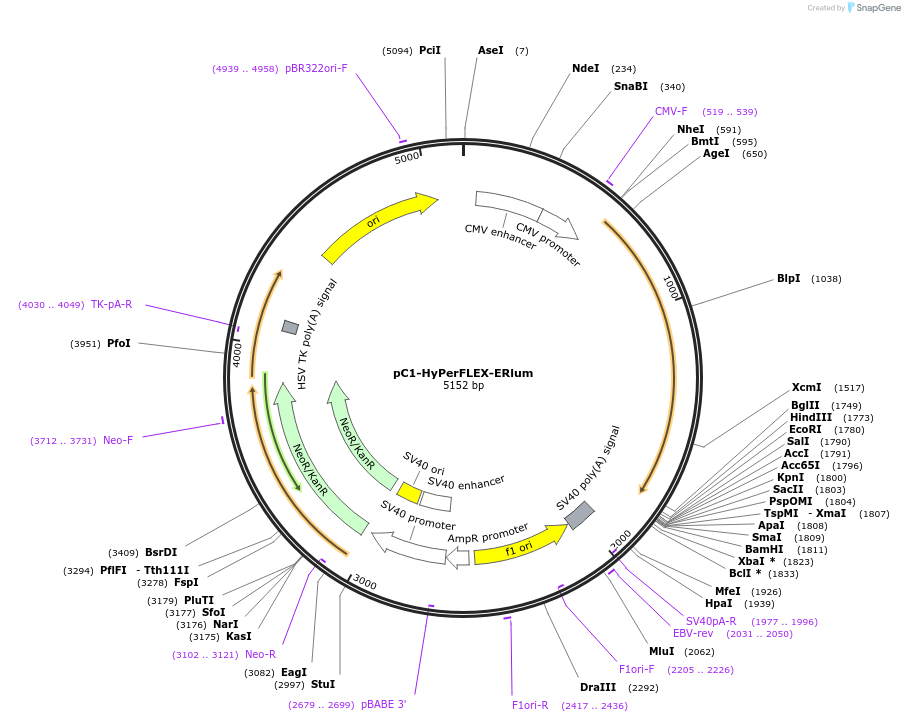
pC1-HyPerFLEX-ERlum
Plasmid#238941PurposeMammalian expression of HyPerFLEX targeted to the luminal side of the endoplasmic reticulum membranesDepositorInsertHyPerFLEX-ERlum (Calreticulin signal sequence-HyPerFLEX-KDEL)
ExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceOct. 22, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
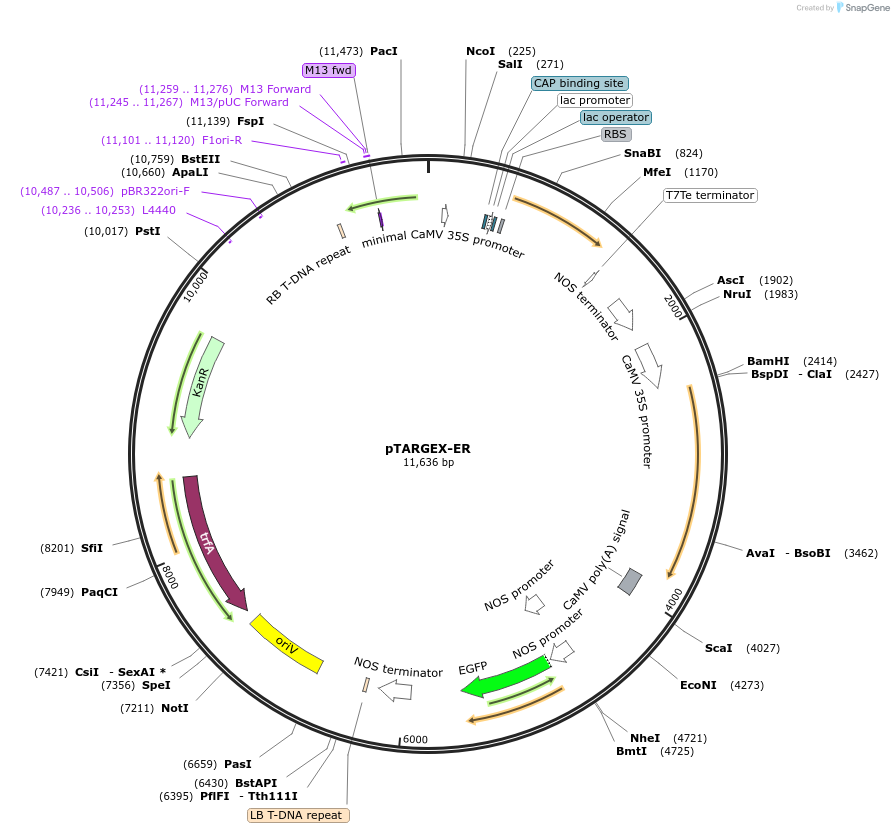
pTARGEX-ER
Plasmid#242449PurposeTargets high levels of recombinant protein for retention in ER. Empty vector. Clone via SapI restriction site. mCherry dropout cassette will enable Red/White screening in E.coli.DepositorTypeEmpty backboneTagsER-retrieval motif (KDEL) and Signal peptide deri…ExpressionPlantPromoterdouble 35SAvailable SinceOct. 16, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
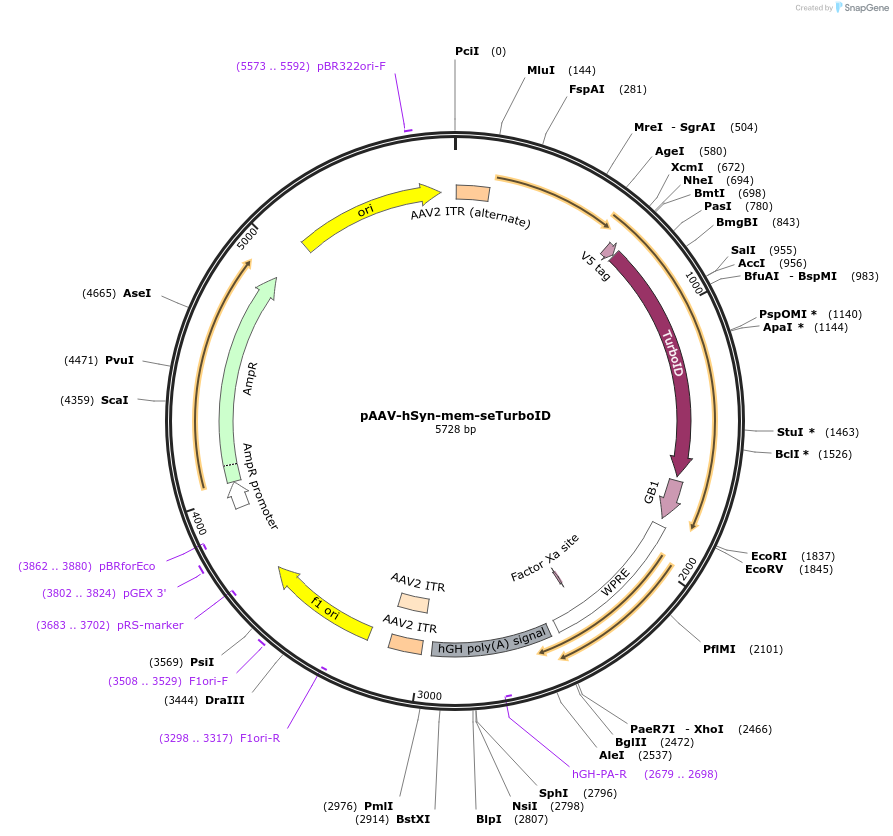
pAAV-hSyn-mem-seTurboID
Plasmid#237888PurposeAAV vector encoding membrane-tethered seTurboID under the control of human synapsin promoterDepositorInsertmem-seTurboID
UseAAVTagsGAP43 palmitoylation signal and V5 tagExpressionMammalianPromoterhuman Synapsin 1 (hSyn)Available SinceAug. 25, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
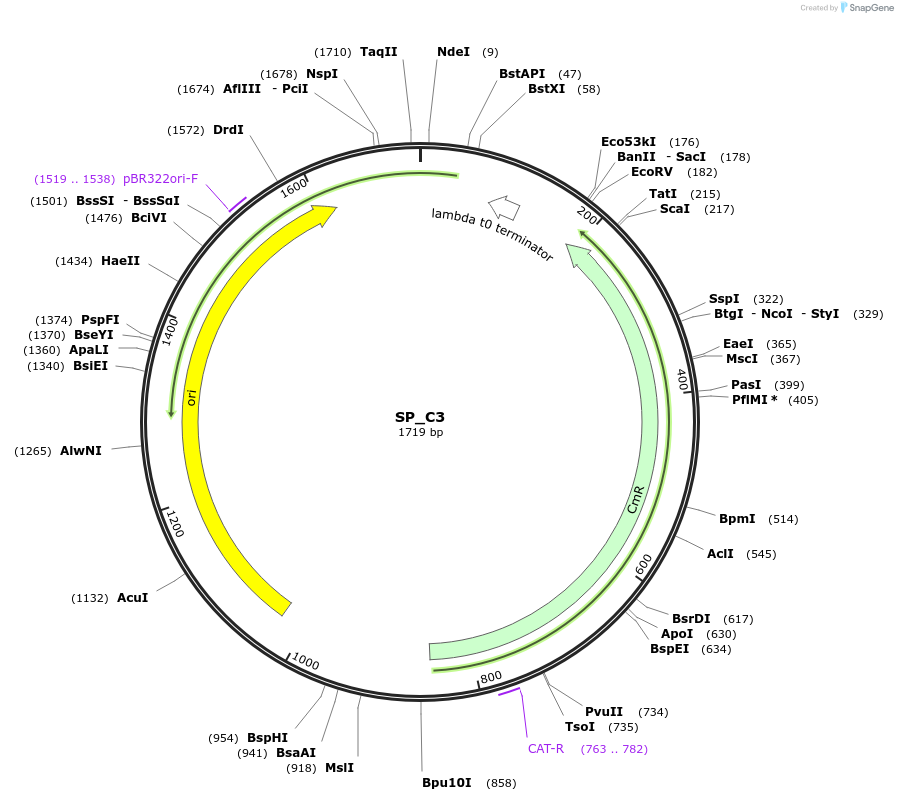
SP_C3
Plasmid#228159PurposePlasmid contains the secretion signal peptide sequence of the yeast (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) PIR1 gene for use in Combinatorial Golden Gate Assembly (BsaI restriction sites).DepositorInsertsp_Q03178_PIR1_YEAST:0-18
UseSynthetic BiologyAvailable SinceJuly 2, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
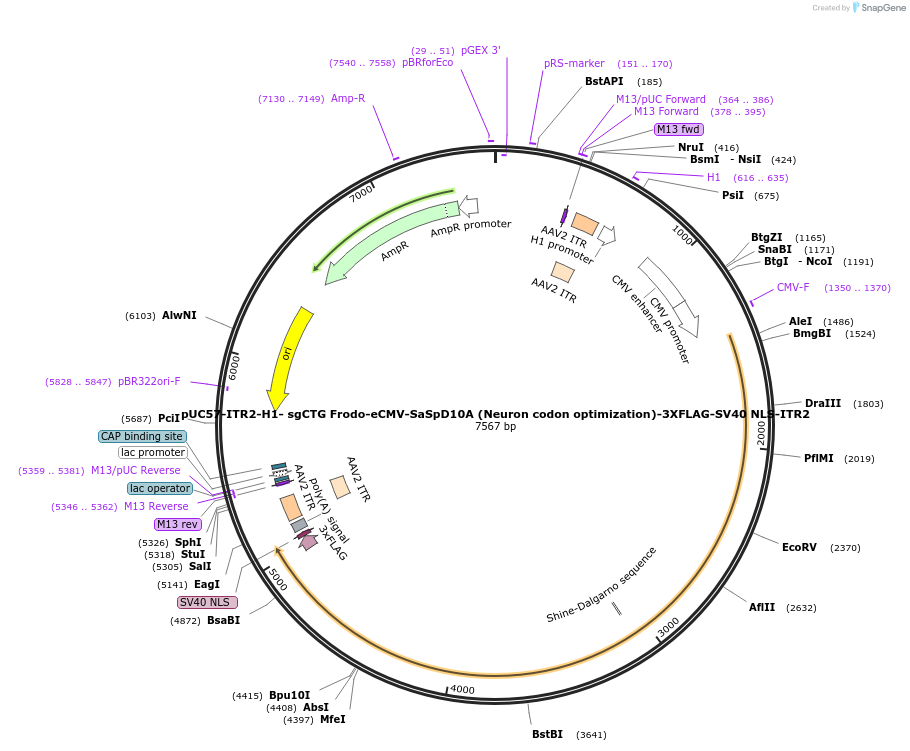
pUC57-ITR2-H1- sgCTG Frodo-eCMV-SaSpD10A (Neuron codon optimization)-3XFLAG-SV40 NLS-ITR2
Plasmid#210734PurposeCoding for SaSp D10A Cas9 alongside Frodo sgRNA targeting CAG repeatsDepositorInsertsSaSp D10A Cas9
Frodo sgCAG
UseCRISPRTags3xFLAG, SV40 NLS, PolyA signalExpressionMammalianMutationD10A, N-terminal Sa Cas9, C-terminal Sp Cas9PromoterH1 and eCMVAvailable SinceMarch 11, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
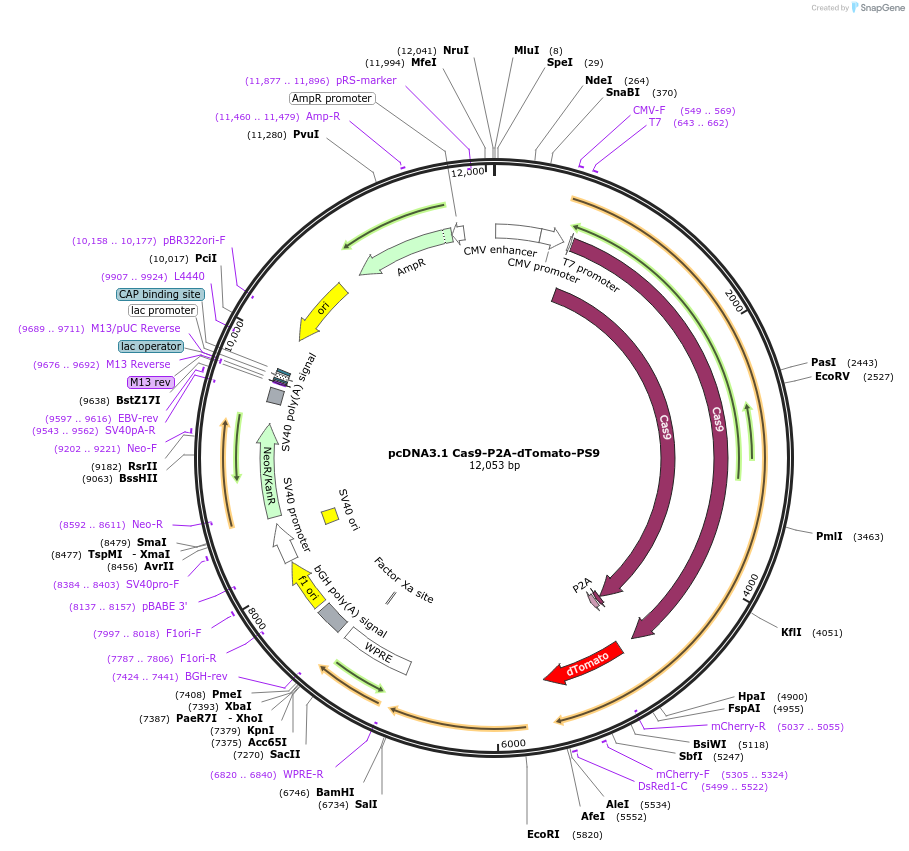
pcDNA3.1 Cas9-P2A-dTomato-PS9
Plasmid#231911PurposeFor packaging spCas9, dTomato mRNA into SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles (VLPs) with a 'PS9' packaging signalDepositorInsertCas9-P2A-dTomato
UseCRISPRExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceMarch 4, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
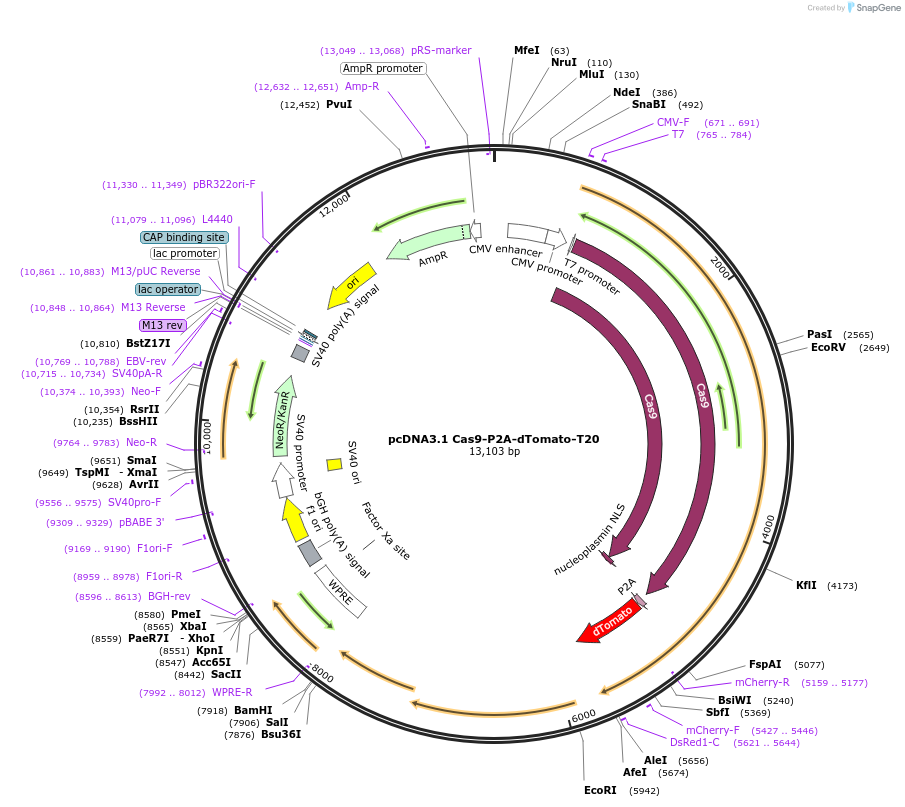
pcDNA3.1 Cas9-P2A-dTomato-T20
Plasmid#231912PurposeFor packaging spCas9, dTomato mRNA into SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles (VLPs) with a 'T20' packaging signalDepositorInsertCas9-P2A-dTomato
UseCRISPRExpressionMammalianPromoterCMVAvailable SinceMarch 4, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
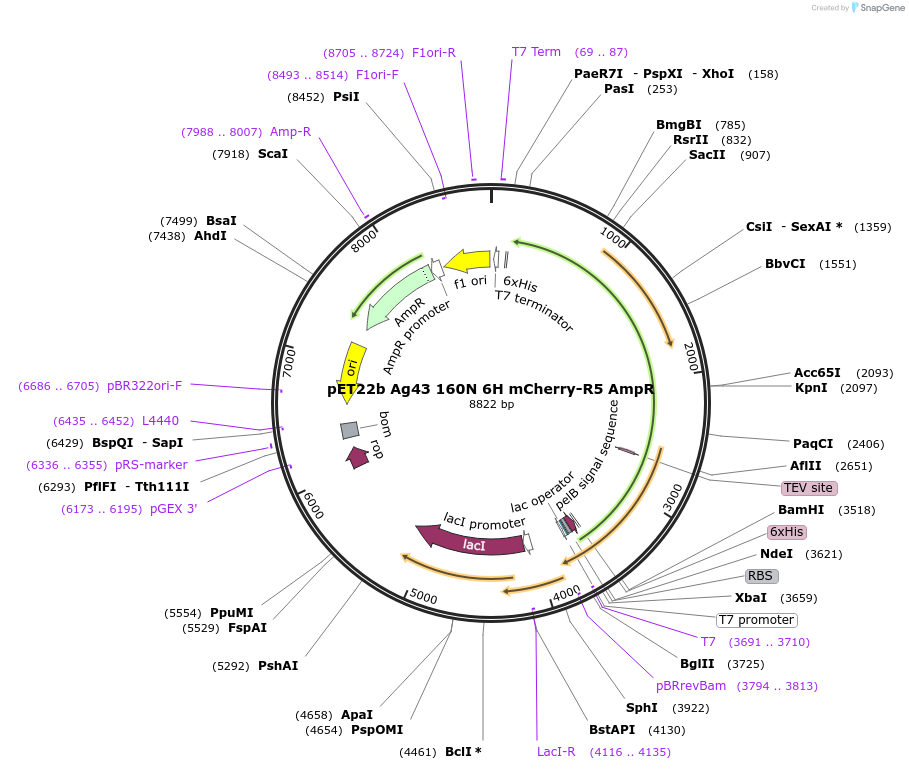
pET22b Ag43 160N 6H mCherry-R5 AmpR
Plasmid#225141PurposeRecombinant Ag43 protein fused to silaffin-R5 and mCherry. pelB as the periplasmic signal. His-tag for purification. TEV enzyme recognition site between Ag43 alpha subunit and the fluorescent protein.DepositorInsertAg43 160N, mCherry
TagsAg43 protein fused to silaffin-R5 and mCherryExpressionBacterialPromoterT7Available SinceFeb. 5, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
SARS-CoV spike all5KO mutant
Plasmid#231921PurposeFor expression of SARS-CoV spike protein with glycan deletion at N1080, N1116, N1140, N1155, N1176 by implementing Asn-to-Gln mutationDepositorInsertspike all5KO (S SARS-CoV)
TagsC9 and CD5 signal peptideExpressionMammalianMutationN1080Q, N1116Q, N1140Q, N1155Q, N1176QPromoterCMVAvailable SinceJan. 27, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
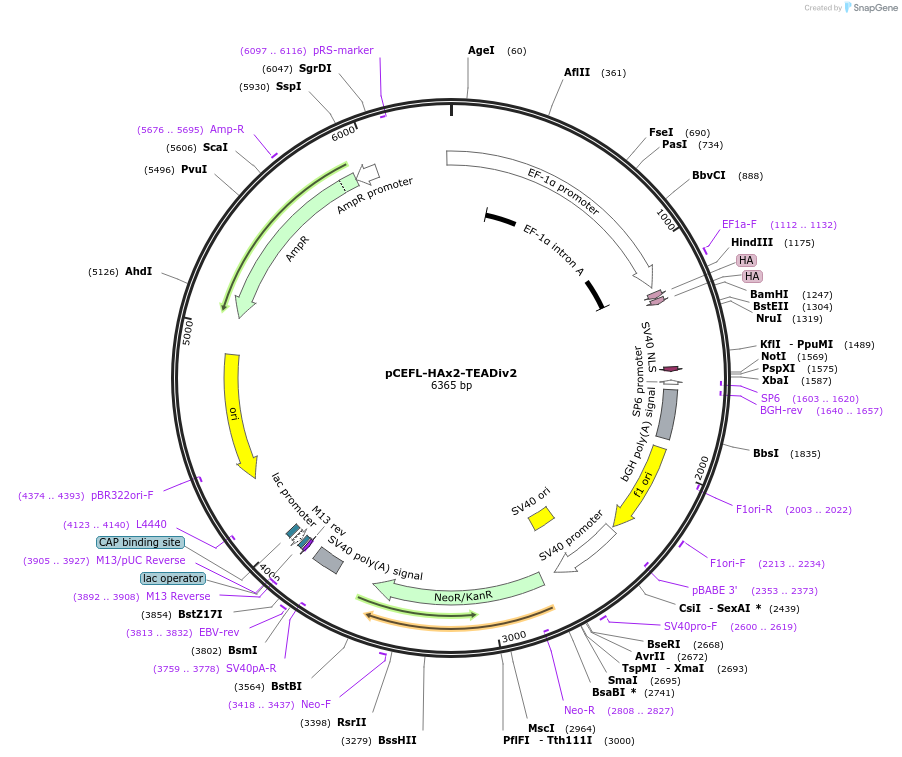
pCEFL-HAx2-TEADiv2
Plasmid#228873PurposeExpression of optimized TEAD inhibitor (TEADiv2): 2xHA-tagged inhibitor of the interaction of YAP1 and TAZ with TEAD transcription factors with nuclear localization signalDepositorInsertTEADiv2
Tags2xHAExpressionMammalianAvailable SinceJan. 13, 2025AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
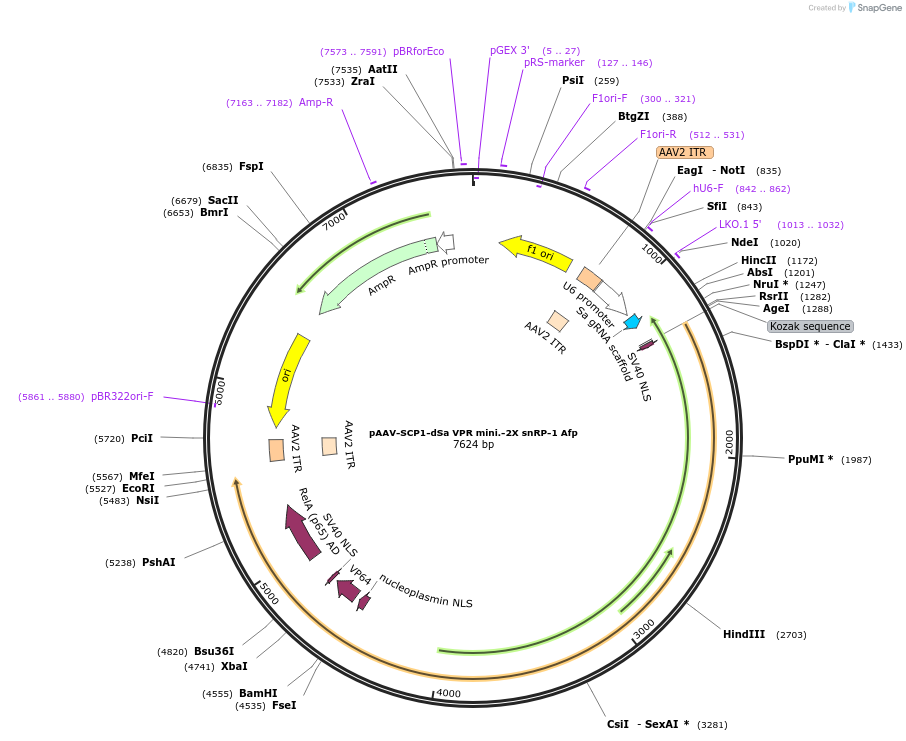
pAAV-SCP1-dSa VPR mini.-2X snRP-1 Afp
Plasmid#99696PurposeExpresses dSa Cas9 fused to optimized combination of truncated activation domains from SCP1 promoter with dual snRP1 poly adenylation signal, and Sa sgRNA for Afp, vector allows for strong activation of mouse Afp, can be packaged and delivered as AAVDepositorAvailable SinceNov. 4, 2024AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
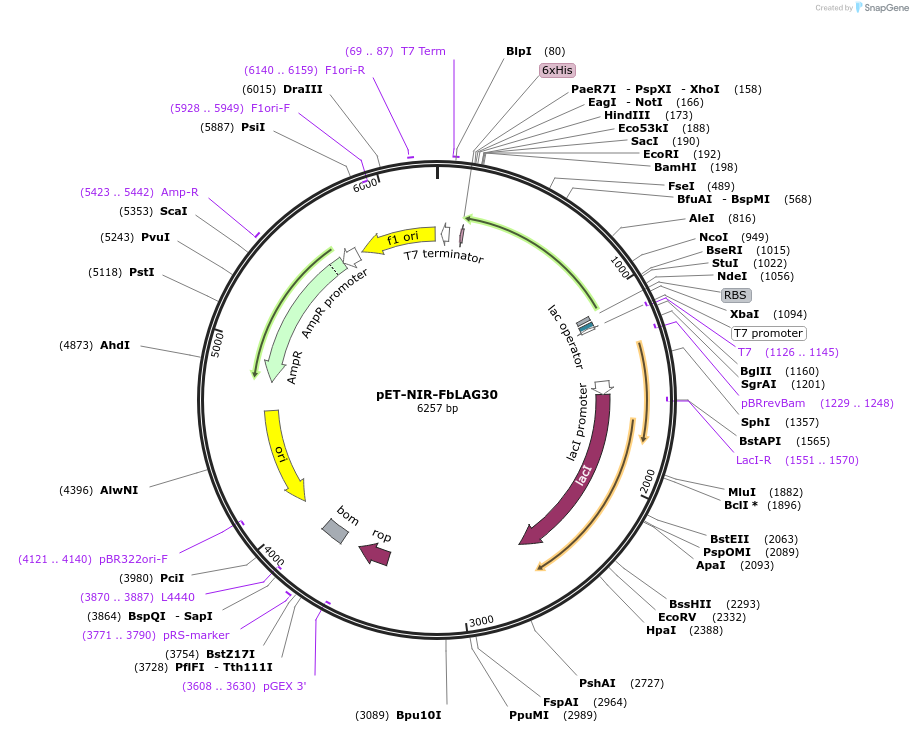
pET-NIR-FbLAG30
Plasmid#220748PurposeNIR-FbLAG30 expression in bacteria.DepositorInsertNIR-FbLAG30
UseAffinity Reagent/ AntibodyExpressionBacterialMutationFor bacterial cytoplasmic expression, the pelB si…PromoterT7Available SinceSept. 9, 2024AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
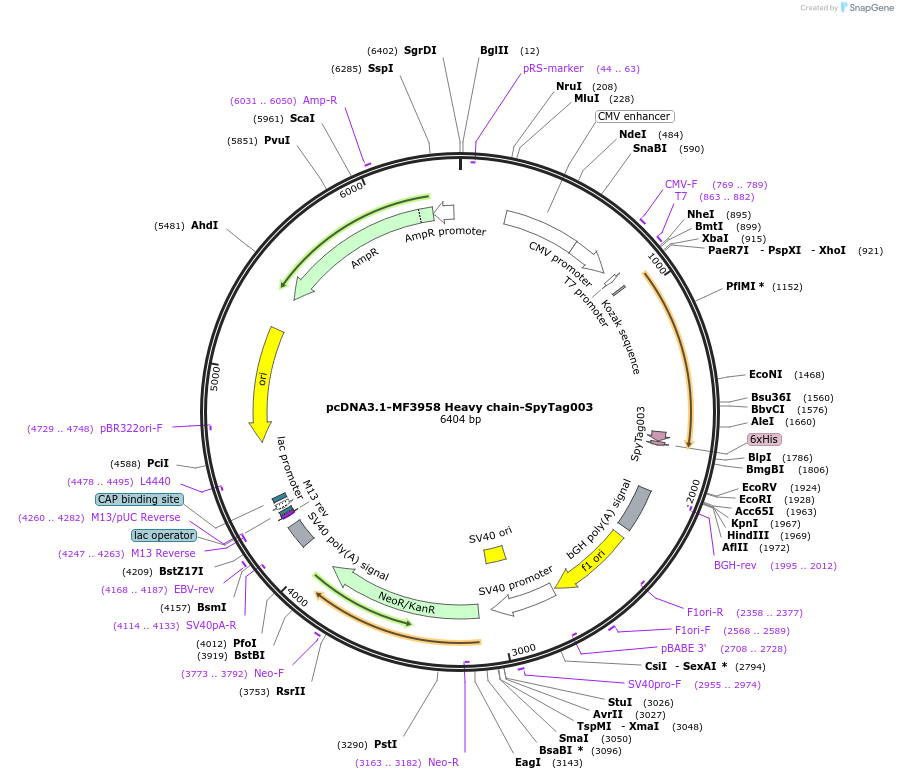
pcDNA3.1-MF3958 Heavy chain-SpyTag003
Plasmid#216303PurposeExpresses anti-HER2 MF3958 Heavy chain-SpyTag003 in mammalian cells. To be paired with MF3958 light chain to form the anti-HER2 MF3958 FabDepositorInsertMF3958 Heavy chain-SpyTag003
UseAffinity Reagent/ AntibodyTagsHis6 tag, Signal peptide, and SpyTag003ExpressionMammalianPromoterT7 promoterAvailable SinceJune 26, 2024AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
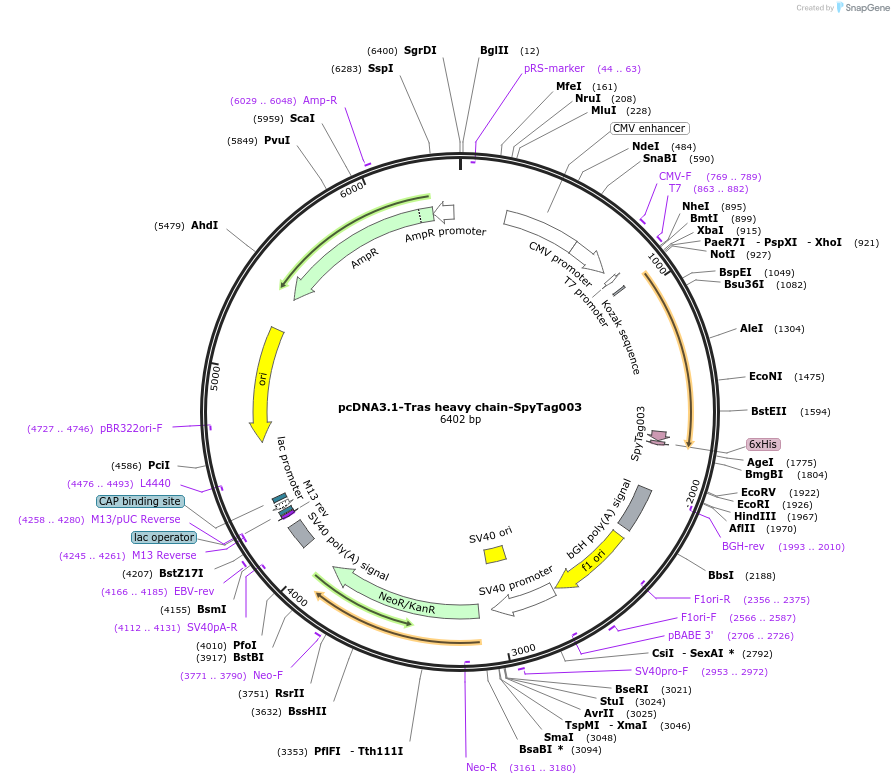
pcDNA3.1-Tras heavy chain-SpyTag003
Plasmid#216293PurposeExpresses anti-HER2 Tras Heavy chain-SpyTag003 in mammalian cells. To be paired with Tras light chain to form the anti-HER2 Tras NoLink FabDepositorInsertTras heavy chain-SpyTag003
UseAffinity Reagent/ AntibodyTagsHis6 tag, Signal peptide, and SpyTag003ExpressionMammalianPromoterT7 promoterAvailable SinceJune 26, 2024AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
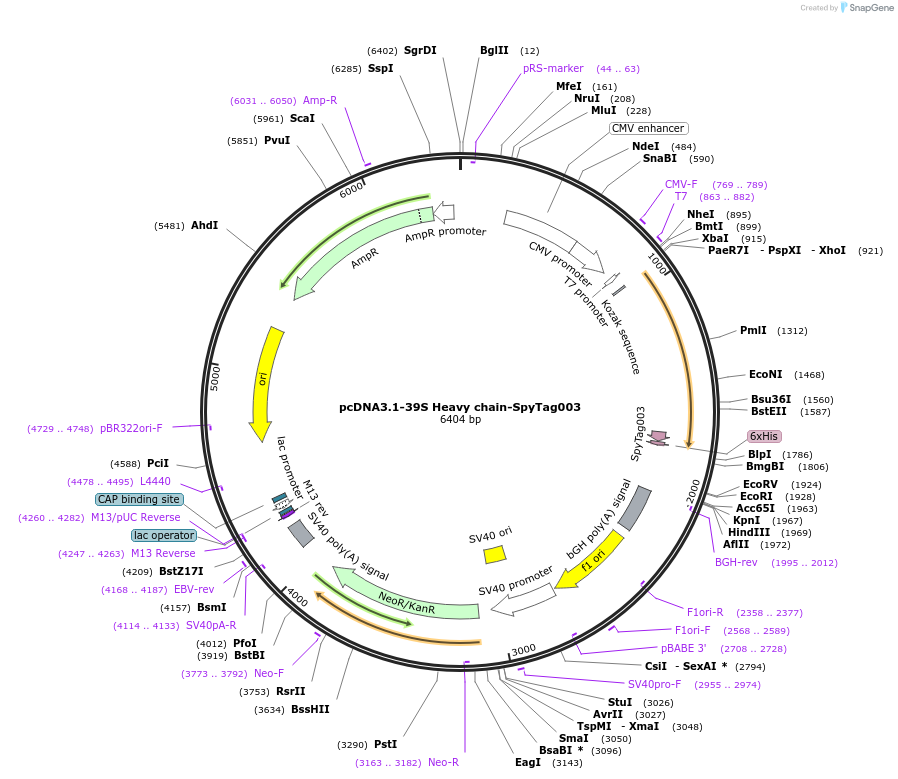
pcDNA3.1-39S Heavy chain-SpyTag003
Plasmid#216296PurposeExpresses anti-HER2 39S Heavy chain-SpyTag003 in mammalian cells. To be paired with 39S light chain to form the anti-HER2 39S FabDepositorInsert39S Heavy chain-SpyTag003
UseAffinity Reagent/ AntibodyTagsHis6 tag, Signal peptide, and SpyTag003ExpressionMammalianPromoterT7 promoterAvailable SinceJune 26, 2024AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only -
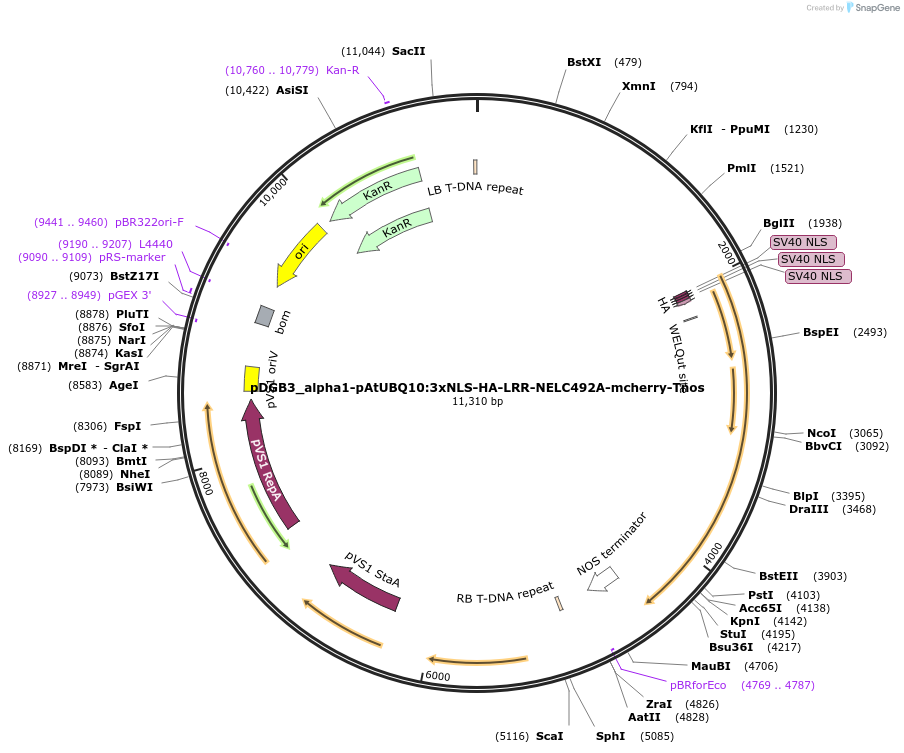
pDGB3_alpha1-pAtUBQ10:3xNLS-HA-LRR-NELC492A-mcherry-Tnos
Plasmid#211844PurposePlant transient expression cassette for the catalytically inactive E3-DART ligase containing a nuclear localization signal.DepositorInsertLRR-NEL
UseSynthetic BiologyTags3xNLS-HA and mCherryExpressionPlantMutationC492APromoterUBIQUITIN10Available SinceMarch 14, 2024AvailabilityAcademic Institutions and Nonprofits only